* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kingdom Protista - Animal
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
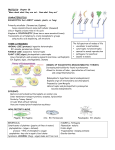
Kingdom Protista - Animal-like Protozoans Amoebae Flagellates means “change shape” Euglena unicellular – uni = one Heterotrophs - consume food for energy unicellular – uni = one uses pseudopodia (false feet) to move The Pseudopodia (false feet) surround food and eat it – process is called = phagocytosis The captured food becomes a Food Vacuole Food is digested by the lysosomes Euglena are both Heteotrophs and a Autotrophs. o Heterotrophs – Euglena consume food for energy. Euglenas can eat nutrients by absorbing them across their cell membrane when light is not available. Contractile Vacuole – pumps out excess water so amoebae does not burst AND Amoebae has a Nucleus – containing DNA - Reproductions occurs through mitosis – called binary fission o Autotrophs – self- feeding –Euglena make their own food using chloroplasts and photosynthesis. Chloroplasts in the Euglena trap sunlight that is used to make food during photosynthesis. live in ponds or puddles Parent cell Nucleus divides Cytoplasm divides Two daughter cells Eyespot at the anterior of the cell detects light FLEXIBLE cell membrane allows amoebae it to CHANGE SHAPE – it has NO cell wall Amoebae live in stagnant ponds, puddles, and inside people 2 kinds of cytoplasm o endoplasm - darker cytoplasm in the interior or center of the cell o ectoplasm – clearer cytoplasm around edges of cell membrane Cyst – in dry or cold periods, the amoeba creates a hard-walled covering to protect itself Pellicle – thick outer membrane surrounds the cell that helps the euglena scrunch up and move like an inchworm Euglena has a nucleus containing the DNA and controls the cell’s activities. The nucleolus is inside the nucleus. Contains cytoplasm Contractile Vacuole- removes excess water or the cell would explode– Contractile Vacuoles are star -shaped Amoebae can cause Amebic Dysentery – a person can get cramps and diarrhea by drinking contaminated water – water not filtered or purified. S. Miller, M. Owens, and Biologycorner.com/ Notes/J. Haugh/visual organizer/Google.com images Kingdom Protista - Animal-like Protozoans Ciliates Sporozoa Paramecium Sporozoa DO NOT move unicellular – uni = one Parasitic – any protozoan organism that lives on, in, or within another organism Heterotrophs - consume food for energy Example live in stagnant ponds part of the food chain Plasmodia Life Cycle eat algal scum chsweb.lr.k12.nj.us/.../protista/protists.htm move using cilia – tiny hair –like projections Cannot change shape - Pellicle – thick outer membrane surrounds the cell and helps the cell move Contractile Vacuoles removes excess water - star shaped Heterotrophs – Paramecium consume food for energy. The food enters the oral grove then moves to the mouth pore, then to gullet and then to food vacuoles Mosquito bites a human infected with malaria and picks us plasmodium cells Plasmodia sporozoa reproduce and migrate to the mosquito salivary gland The infected mosquito bites another human and injects saliva that contains Plasmodium sporozoites Undigested food moves to anal pore trichocysts – tiny threads to entangle a predator Sporozoites infect the lever of the human and multiply and infect the red blood cells Paramecium have the ability to avoid or move away from negative or unpleasant things 2 kinds of cytoplasm o ectoplasm – cytoplasm around edges of cell membrane o endoplasm - cytoplasm in the center of the cell The infected red blood cells burst, and release more cells that infect other red blood cells. The person becomes very sick with malaria. S. Miller, M. Owens, and Biologycorner.com/ Notes/J. Haugh/visual organizer/Google.com images Malaria cells reproduce inside the red blood cells