* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reaction Time Task
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus modality wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
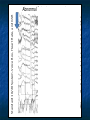
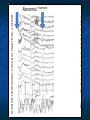
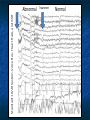
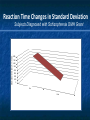
ABSTRACT This presentation discusses brain plasticity in Schizophrenia. People with Schizophrenia experience disruptions in activating and inhibiting systems in the brain. Specifically, these systems create thoughts and sensations that are generated within the brain. Brain plasticity is a set of fundamental physiological processes, which are multi-level multi-systems processes in a homeostatic brain. In Schizophrenia, brain plasticity permits the recovery of function. ABSTRACT Measurement issues include high variability associated with changes in brain states in people with Schizophrenia. The implications for measurement are that researchers need to analyze and report changes in coefficients of variation, standard deviations and variance as well as averages. Indicators of improved brain function are reduced variability and reduced magnitude of deviation from correct responses. These studies: 1. use each subject as their own control; 2. examine improved psychophysiological functioning by EEG Brain Biofeedback and 3. examine improved ecologically valid functional behavior as measured by the Orientation Remediation Module (ORM) Reaction Time and Zero Accuracy Conditioner (ZAC) subtests. ABSTRACT The results show that people with Schizophrenia can reduce the variability of their reaction time and reduce the size of error on a frontal lobe task. These results are discussed in terms of the need to develop new technologies that help people with schizophrenia keep their brain in a functional state. Caveat: The data presented are illustrative examples based on small sample sizes using each subject as their own control. The basic hypotheses and results need to be replicated with a larger sample size and a controlled study using random assignment. There is an evolving world in each person’s brain. TIMELINE Development of the Miran Therapy Basic science/ Brain function The Homeostatic Brain Model describes normal and abnormal activating and inhibiting systems. Psychiatric symptoms occur when there are disruptions in activating and inhibiting Frontal, Temporal, Parietal, and Limbic regions of the brain. The human brain is plastic, and can recover function and establish new neural-pathways. Measuring Brain Plasticity • Improved psychophysiological functioning by EEG Brain Biofeedback • Improved ecologically valid functional behavior by the Orientation Remediation Module subtest Reaction time and Zero Accuracy Condition EEG: Brain BioFeedback The EEG Record is of a subject diagnosed with Schizophrenia. Data was collected as part of a New York State Office of Mental Health Grant. The EEG Record shows a change in brain function from an abnormal state to a normal state associated with working on a computerized attention task. Standard 10/20 System-Voice Box, Heart Rate, and GSR Abnormal Treatment Normal Standard 10/20 System-Voice Box, Heart Rate, and GSR Abnormal Treatment Normal Standard 10/20 System-Voice Box, Heart Rate, and GSR Abnormal Treatment Normal Brain Activity Hallucination (left picture) and Cognitive Training (right picture) Dysfunctional Brain State Slow Delta Wave Activity -associated with Auditory and Visual -Hallucinations Functional Brain State Normal Alpha -associated with Visual Motor -Activation ZAC: Zero Accuracy Conditioner The ZAC is a computerized cognitive training task (developed by Yehuda BenYishay, Ph.D. at the NYU Rusk Institute, Working Approaches to Remediation of Cognitive Deficits in Brain Damaged Persons, 1983) Includes three subtests: Immediate stop Short coast Long coast Subtests are progressively more difficult and involve more frontal lobe activity. ZAC: Zero Accuracy Conditioner Next slide is a picture of the stimuli as seen by the subject on the computer screen Top Picture – Subject achieves the correct response. The clock hand stops at the top mark. Bottom Picture – Subject deviates from the correct response. Deviations are counted. ZAC: Zero Accuracy Conditioner ZAC Subject Diagnosed with Schizophrenia at Hopewell Number Correct Responses 3 Trials (each trial is a summary of 12 responses) Number of Correct responses 8 7 6 Immediate Stop 5 4 Short Coast 3 Long Coast 2 1 0 Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 ZAC: Correct Response by Trials The subject gradually improves ability to achieve a correct response: The summary of the immediate stop begin at a score in the range of 6-7 and increase to a score in the range close to 8 (The immediate stop is a less demanding task) The summary of the short coast begin at a score of “0” and increase sharply to a score in the range close to 3. The summary of the long coast begin at a score of “0” and increase on a straight line to the range close to 3. ZAC Subject Diagnosed with Schizophrenia at Hopewell Magnitude of Deviation from Correct Responses Magnitude of Deviation from Correct Response 3 Trials (each trial is a summary of 12 responses) 100 90 80 70 60 Immediate Stop 50 40 Short Coast 30 Long Coast 20 10 0 Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 ZAC: Magnitude of Deviation The subject gradually improves ability to achieve a smaller magnitude of deviation: The summary of the immediate stop begin at a score close to “0” and end at the same score (The immediate stop is a less demanding task). The summary of the short coast begin at a score between 20-30 and decrease to a score close to “0”. The summary of the long coast begin at a score between 80-90 and decrease to a score close to “0”. Reaction Time Task The Reaction Time Task is a computerized cognitive training task (developed by Yehuda Ben-Yishay, Ph.D. at the NYU Rusk Institute, Working Approaches to Remediation of Cognitive Deficits in Brain Damaged Persons, 1983) Variable Delay set of trials: A set of 12 Reaction Time Trials A warning tone sounds There is a variable delay A light changes color Subject presses the space bar -as soon as possible Subject’s score is recorded Reaction Time Coefficient of Variability Subjects Diagnosed with Schizophrenia OMH Grant Variable Delay: Pre vs. Post CV's (%) (Signed Rank P=0.01) 80 100 60 40 20 VD.CV.Post 140 p < 0.01 20 40 60 80 100 VD.CV.Pre 120 140 160 Reaction Time Task Subjects reduce the variability of their Reaction Times from Pretest to Post Test The raw data are Reaction Time Scores between 0000 and 9999 msec. recorded in blocks of 12. Expected value is 170 msec. The Average, Standard Deviation and Variance were computed for each block of Reaction Time responses. The Coefficient of Variation is calculated by dividing the Standard Deviation by the Mean for each block of scores. The Coefficient of Variability for the Pretest Measures were larger than the Post Test Measures. Reaction Time Changes in Standard Deviation Standard Deviation in msec. Subjects Diagnosed with Schizophrenia OMH Grant 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 Pre Post Reaction Time Task Subjects reduce the Standard Deviation of their Reaction Times Pretest vs. Post Test The Average, Standard Deviation and Variance were computed for each block of Reaction Time responses. Standard Deviations in Reaction Times on the Variable Delay Task, Pretest vs. Post Test The result suggest that individuals can: Improve psychophysiological functioning EEG Record As frontal lobe circuits are activated, hallucinations i.e. circular negative thoughts and memories are diminished by the process of reciprocal inhibition. Improve information processing and functional behavior as measured by the Orientation Remediation Module ZAC charts from 3 trials of 12 responses on a single day Reaction Time - Variable Delay The subjects are focused and are able to engage.