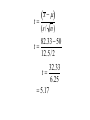* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint slides
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
One sample problems Statistics 2126 introduction • • • • Yeah z tests are great You can do statistical tests! You simply need and Ok the mean is easy, the standard deviation, not so much • What to do, what to do… A thought… • Well let’s look at the z formula z x ( / n ) • What if we could substitute something for ? Introducing…. • The t statistic! x t (s / n ) • You do just that, put s in for Powerful technique • Think about this • You now don’t really need to know anything • A theoretical value for the population mean • And a calculated sample standard deviation The critical value of t • Unlike z, t changes depending on sample size • It has a certain number of ‘degrees of freedom’ • In our case, n-1 so if we have 22 subjects we have 21 df • We look up the critical value with 21 df An example • Four black capped chickadees in a memory experiment with two alternatives. • Their average percentage correct was 82.33 • Standard deviation was 12.5 • Are they better than chance? x t (s / n ) 82.33 50 t 12.5 /2 32.33 t 6.25 5.17 Now look up the critical value • We have 3 degrees of freedom • Let’s use an alpha of .05 (as usual) • Just use the table • Critical value is 2.35 • Our obtained value is 5.17 • Reject H0 Confidence intervals? Why not… x t(s / n ) 82.33 3.18(12.5 /2) 82.33 3.18(6.25) 82.33 3.18(6.25) 82.33 19.875 62.455 102.205 Again, just think about this • That is incredible, we can estimate, we know that accuracy of the estimate and we do not need to know ANYTHING about the population beyond some theoretical population mean • (which is usually pretty easy to figure out)