Package `circular`
... the coordinate system used in the output for the objects mu and mu.all. See circular for details. ...
... the coordinate system used in the output for the objects mu and mu.all. See circular for details. ...
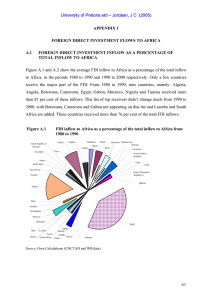
APPENDIX 1 FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT FLOWS TO AFRICA A.1
... GNP is introduced to control for the size of the investing country, except when the sample covers only one investing country. Generally, larger countries are expected to invest abroad more than smaller ones. Recorded FDIs are pure financial flows. That is, they are neither equivalent to foreign fina ...
... GNP is introduced to control for the size of the investing country, except when the sample covers only one investing country. Generally, larger countries are expected to invest abroad more than smaller ones. Recorded FDIs are pure financial flows. That is, they are neither equivalent to foreign fina ...
Chapter -11 Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion
... In many a case, like the distributions of height, weight, marks, profit, wage and so on, it has been noted that starting with rather low frequency, the class frequency gradually increases till it reaches its maximum somewhere near the central part of the distribution and after which the class freque ...
... In many a case, like the distributions of height, weight, marks, profit, wage and so on, it has been noted that starting with rather low frequency, the class frequency gradually increases till it reaches its maximum somewhere near the central part of the distribution and after which the class freque ...
chapter 8—interval estimation - College of Micronesia
... 16. From a population that is not normally distributed and whose standard deviation is not known, a sample of 6 items is selected to develop an interval estimate for the mean of the population (). a. The normal distribution can be used. b. The t distribution with 5 degrees of freedom must be used. ...
... 16. From a population that is not normally distributed and whose standard deviation is not known, a sample of 6 items is selected to develop an interval estimate for the mean of the population (). a. The normal distribution can be used. b. The t distribution with 5 degrees of freedom must be used. ...
Homework Activities
... Activity 3-1: Elvis Presley and Alf Landon a. Population: all adult Americans (record company interest) Sample: those listening to the radio who called in b. No, 56% is probably not an accurate reflection of the opinions of all adult Americans on this issue. People who chose to call in (who took the ...
... Activity 3-1: Elvis Presley and Alf Landon a. Population: all adult Americans (record company interest) Sample: those listening to the radio who called in b. No, 56% is probably not an accurate reflection of the opinions of all adult Americans on this issue. People who chose to call in (who took the ...
Bayesian analysis
... we take account of our background knowledge, , and evaluate the evidence in a manner consistent with both background knowledge and evidence. That is, the posterior likelihood (or distribution) is more aptly represented by p ( | y, ) p (y | , ) p ( | ) ...
... we take account of our background knowledge, , and evaluate the evidence in a manner consistent with both background knowledge and evidence. That is, the posterior likelihood (or distribution) is more aptly represented by p ( | y, ) p (y | , ) p ( | ) ...