* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cytoskeleton and Extracellular Matrix
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
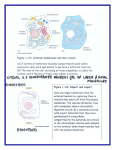
CYTOSKELETON AND EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX Block 5 Erik Kessler, Michael O’Brien, Bryan Richman CYTOSKELETON Structure: • Meshwork of fine fibers within the cell • Made up of three types of fibers – Microfilaments, Intermediate Filaments, and Microtubules Function: • Gives the cell some structural support • Plays a role in cell movement – Movement of organelles, and cell itself – Needed for muscle contraction • Regulates cellular activity More in textbook pg.64 MICROFILAMENTS Structure: Globular proteins are hydrophilic • Solid rod made mostly of the globular protein actin • Double twisted chain that is 5-9 nm in diameter Function: • Changes shape by moving subunits from the end to the front – This can change cell shape and make it move ex. Amoeba • Can interact with myosin to contract muscles • Allows a dividing cell (cytokinesis) to pinch off into two cells More in textbook pg.64 INTERMEDIATE FILAMENTS Structure: • Rope-like structure Fibrous proteins are hydrophobic • Made of fibrous protein • 8-11 nm in diameter • Made of subunits – monomer - rod connecting amino head to carboxyl tail – dimer - two monomers combine – tetramer - two dimers combined – tetramers combine into sheets which role up into its rope shape More in textbook pg.64 INTERMEDIATE FILAMENTS Function: • Keep organelles in place and holds the cell structure – ex. Hold nucleus in place • Can assemble and disassemble through phosphorylation with serine • Can bind with different proteins to improve stability or create attachment sites for protein assemblies – ex. actin filaments (microfilaments), microtubules • Help to attach chromosomes to nuclear membrane More in textbook pg.64 MICROTUBULES Structure: • Made of globular proteins • 20-25 nm in diameter Function: • Act as track for organelle movement through cytoplasm – ex. lysosomes move along microtubules to reach vacuole, also support and move cilia and flagella • Guide chromosomes when cells divide • Move by adding tubulin to one end and losing them on the other More in textbook pg.64 And watch the cilia and flagella PowerPoint for more on their function EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX Structure: • Sticky layer of glycoproteins • Made of: collagen and elastin (structural proteins), fibrillin and laminin (specialized proteins) Function: • Holds animal cells together in tissues • Protects and supports cells • Regulates cell behavior • Gives strength, protection, and support to soft parts of the body (cartilage, etc.) More in textbook pg.66 Function: CELL JUNCTIONS • Adjacent cells in animal tissues are connected by cell junctions • Regulates what comes into the cell Types: • Tight Junction: Binds cells together and forms a leak proof sheet – Prevents passage of molecules through the space between cells • Anchoring Junction: Attach cells to each other while still allowing material to pass in the area between the cells • Communicating Junction: Channels allowing water, small molecules, and ions to flow between adjacent cells- cells can communicate with electrical/ chemical signals More in textbook pg.66 SOURCES Mitchell, and Reece. "Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell." Biology: Concepts and Connections. By Campell. 3rd ed. San Francisco: Benjamin/Cummings, 2000. 64-66. Print. Digital image. Http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu. Web. 26 Nov. 2010. <http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/biology/bio4fv/page/actin1063.JPG>. Digital image. Http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu. Web. 26 Nov. 2010. <http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/biology/bio4fv/page/intermiediatefil1063.JPG>. Digital image. Http://www.bscb.org. Web. 26 Nov. 2010. <http://www.bscb.org/softcell/images/mp_tripple.gif>. Digital image. Web. 26 Nov. 2010. <http://219.221.200.61/ywwy/zbsw(E)/pic/ech4-1.jpg>. "Cytoskeleton." ISCID - International Society for Complexity Information and Design. Web. 23 Nov. 2010. <http://www.iscid.org/encyclopedia/Cytoskeleton>. "Cytoskeleton Tutorial." The Biology Project. 2004. Web. 23 Nov. 2010. <http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/tutorials/cytoskeleton/page1.html>. "Intermediate Filaments." Cell Biology and Cytochemistry. Web. 23 Nov. 2010. <http://www.cytochemistry.net/cell-biology/intermediate_filaments.htm>. "Microtubules." Cell Biology and Cytochemistry. Web. 27 Nov. 2010. <http://www.cytochemistry.net/cell-biology/microtub.htm>. "Microtubules." Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) :: Architecture, Business, Engineering, IT, Humanities, Science. Web. 23 Nov. 2010. <http://rpi.edu/dept/bcbp/molbiochem/MBWeb/mb2/part1/microtub.htm>. "Molecular Expressions Cell Biology: Intermediate Filaments." Molecular Expressions: Images from the Microscope. Web. 27 Nov. 2010. <http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/intermediatefilaments/intermediatefilaments.html> "Cytoskeleton Tutorial." The Biology Project. Web. 30 Nov. 2010. <http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/tutorials/cytoskeleton/page1.html>. <http://rpi.edu/dept/bcbp/molbiochem/MBWeb/mb2/part1/microtub.htm>. "Molecular Expressions Cell Biology: Intermediate Filaments." Molecular Expressions: Images from the Microscope. Web. 27 Nov. 2010. <http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/intermediatefilaments/intermediatefilaments.html>. "The Extracellular Matrix." 12 Apr. 2009. Web. 1 Dec. 2010. <http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/E/ECM.html>. "Microtubules." Cell Biology and Cytochemistry. Web. 27 Nov. 2010. <http://www.cytochemistry.net/cell-biology/microtub.htm>. "Microtubules." Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) :: Architecture, Business, Engineering, IT, Humanities, Science. Web. 23 Nov. 2010. "Junctions Between Cells." 10 Oct. 2010. Web. 1 Dec. 2010. <http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/J/Junctions.html>.