* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cells - (www.ramsey.k12.nj.us).
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
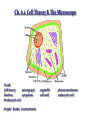
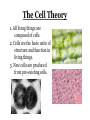
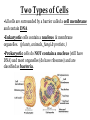
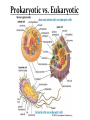
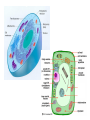
Ch. 6.1: Cell Theory & The Microscope Vocab. Cell theory micrograph Nucleus cytoplasm Prokaryotic cell People: Hooke; Leeuwenhoek organelle cell wall plasma membrane eukaryotic cell The Discovery of the Cell: Robert Hooke • In 1665 • Observes cork (plant) under microscope; – looked like thousands of tiny, empty chambers = “cells” • We now know cells are the basic units of life. The Discovery of the Cell: Von Leeuwenhoek • Developed single microscope with high quality lens, 1700 • observe pond water and other things. • Cellular/Microbiology is born! Developing the Cell Theory • Matthias Schleiden: all plants were made of cells (1838) • Theodor Schwann: all animals were made of cells (1839). • Rudolph Virchow: new cells were created only from division of preexisting cells (1855). • These discoveries led to the cell theory. Compound Light Microscope • Combination of lenses and light used to magnify small objects held on a slide •Live specimens: YES •Max magnification = 1000x Electron Microscopes • Image produced on a computer screen using a beam of electrons (not light) • More powerful (300,000x or more) than light microscopes, but specimen cannot be alive – Transmission (T.E.M) • Study of inner structure of a specimen • Samples are cut into thin slices for viewing • Images are 2-D – Scanning (S.E.M.) • Allows study of specimen surface • Images are 3-D Images from Electron Microscopes The Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from pre-existing cells. Two Types of Cells •All cells are surrounded by a barrier called a cell membrane and contain DNA •Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus & membrane organelles. (plants, animals, fungi & protists.) •Prokaryotic cells do NOT contain a nucleus (still have DNA) and most organelles (do have ribsomes) and are classified as bacteria. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cell Parts: Organelles Each has a specific job/function. You to be able to identify each organelle from a picture and explain the function of each organelle for your CELL QUIZ. Nucleus Nuclear envelope Nucleolus Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Cell Wall Ribosomes E.R. (rough & smooth) Golgi Apparatus Vacoules Lysosomes Chloroplasts Mitochondria Microtules & Microfilaments Flagella & Cilia Table of Organelles & Function http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html http://utahscience.oremjr.alpine.k12.ut.us/sciber00/7th/cells/sciber/orgtable.htm StudyStack for Organelles http://www.studystack.com/flashcard-242367 Eukaryote: Animal Cell Eukaryote: Plant Cell