* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical Reactions - thsicp-23
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic reforming wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Aromatization wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
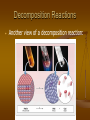
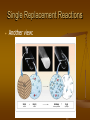
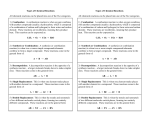
Chemical Reactions ICP – Types of Reactions • There are six types of chemical reactions we will talk about: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. • Synthesis reactions Decomposition reactions Single displacement reactions Double displacement reactions Combustion reactions Oxidation-Reduction reactions You need to be able to identify the type of reaction 1. Synthesis reactions • • Synthesis reactions occur when two substances (generally elements) combine and form a compound. (Sometimes these are called combination or addition reactions.) reactant + reactant 1 product Basically: A + B AB • • Example: 2H2 + O2 2H2O Example: C + O2 CO2 Synthesis Reactions • Here is another example of a synthesis reaction 2. Decomposition Reactions • • • • • Decomposition reactions occur when a compound breaks up into the elements or in a few to simpler compounds 1 Reactant Product + Product In general: AB A + B Example: 2 H2O 2H2 + O2 Example: 2 HgO 2Hg + O2 Decomposition Reactions • Another view of a decomposition reaction: 3. Single Replacement Reactions • • • Single Replacement Reactions occur when one element replaces another in a compound. A metal can replace a metal (+) OR a nonmetal can replace a nonmetal (-). element + compound product + product A + BC AC + B (if A is a metal) OR A + BC BA + C (if A is a nonmetal) (remember the cation always goes first!) Single Replacement Reactions • Another view: Single Replacement Reactions • Sodium chloride solid reacts with fluorine gas 2 NaCl(s) + F2(g) 2 NaF(s) + Cl2(g) Note that fluorine replaces chlorine in the compound • Aluminum metal reacts with aqueous copper (II) nitrate 2 Al(s)+ 3 Cu(NO3)2(aq)3 Cu(s) +2 Al(NO3)3(aq) 4. Double Replacement Reactions • • • Double Replacement Reactions occur when a metal replaces a metal in a compound and a nonmetal replaces a nonmetal in a compound Compound + compound product + product AB + CD AD + CB Double Replacement Reactions • • • Think about it like “foil”ing in algebra, first and last ions go together + inside ions go together Example: AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(s) AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq) Another example: K2SO4(aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) 2 KNO3(aq) + BaSO4(s) 5. Combustion Reactions • • Combustion reactions occur when a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen gas. This is also called burning!!! In order to burn something you need the 3 things in the “fire triangle”: 1) A Fuel (hydrocarbon) 2) Oxygen to burn it with 3) Something to ignite the reaction (spark) Combustion Reactions • • • In general: CxHy + O2 CO2 + H2O Products in combustion are ALWAYS carbon dioxide and water. (although incomplete burning does cause some byproducts like carbon monoxide) Combustion is used to heat homes and run automobiles (octane, as in gasoline, is C8H18) Combustion Reactions Edgar Allen Poe’s drooping eyes and mouth are potential signs of CO poisoning. Combustion • Example • • C5H12 + 8 O2 5 CO2 + 6 H2O Write the products and balance the following combustion reaction: • 11 H2O 2C10H22 +31O2 20 10 CO2 +22 Oxidation-Reduction Many of these 5 types of reactions are also oxidation-reduction reactions Oxidation: Loss of electrons Reduction: Gain of electrons You can’t have one… without the other! Reduction (gaining electrons) can’t happen without an oxidation to provide the electrons. You can’t have 2 oxidations or 2 reductions in the same equation. Reduction has to occur at the cost of oxidation LEO the lion says GER! o l x s e i e c d t a r t o i n o s n GER! a l e i e d n c u t c r t o i n o s n Another way to remember OIL RIG x s o i s d e a t i o n e s d u c t i o n a i n Catalysts 1. 2. 3. Catalysts are used in a chemical reaction to Increases or decreases rate of reaction Reduces activation energy Lowers temperature requirements Mixed Practice State the type and balance the following reactions: BaSO4 + 2HCl 1. BaCl2 + H2SO4 2. C6H12 +9 O2 6 CO2 +6 H2O 3. Zn + CuSO4 ZnSO4 + Cu 4. 2 Cs + Br2 2 CsBr 5. FeCO3 FeO + CO2 •