chapter 4 types of chemical reactions and solution stoichiometry
... a. Polarity is a term applied to covalent compounds. Polar covalent compounds have an unequal sharing of electrons in bonds that results in unequal charge distribution in the overall molecule. Polar molecules have a partial negative end and a partial positive end. These are not full charges as in io ...
... a. Polarity is a term applied to covalent compounds. Polar covalent compounds have an unequal sharing of electrons in bonds that results in unequal charge distribution in the overall molecule. Polar molecules have a partial negative end and a partial positive end. These are not full charges as in io ...
chapter 4 types of chemical reactions and solution stoichiometry
... a. Polarity is a term applied to covalent compounds. Polar covalent compounds have an unequal sharing of electrons in bonds that results in unequal charge distribution in the overall molecule. Polar molecules have a partial negative end and a partial positive end. These are not full charges as in io ...
... a. Polarity is a term applied to covalent compounds. Polar covalent compounds have an unequal sharing of electrons in bonds that results in unequal charge distribution in the overall molecule. Polar molecules have a partial negative end and a partial positive end. These are not full charges as in io ...
On the composition of ammonia–sulfuric
... system. The specific scientific questions we aim to answer here include the following: (1) what is the detailed molecular structure of the observed clusters under different atmospherically relevant conditions? (2) What are the roles of NH3 and H2 SO4 concentrations and temperature in determining the ...
... system. The specific scientific questions we aim to answer here include the following: (1) what is the detailed molecular structure of the observed clusters under different atmospherically relevant conditions? (2) What are the roles of NH3 and H2 SO4 concentrations and temperature in determining the ...
Unit 9 Stoichiometry Notes
... reaction equations to make connections between the reactants and products in reactions. Stoichiometry calculates the quantities of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. The equation must be balanced! Questions that deal with amounts in reactions are examples of reaction stoichiometry. W ...
... reaction equations to make connections between the reactants and products in reactions. Stoichiometry calculates the quantities of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. The equation must be balanced! Questions that deal with amounts in reactions are examples of reaction stoichiometry. W ...
Chapter 4
... just a proton; an electron is removed from neutral hydrogen to form H+. Acid-base reactions are commonly called proton transfer reactions. The acid is the proton donor and the base is the proton acceptor. The strong bases are (by the solubility rules) LiOH, NaOH, KOH, RbOH, CsOH, Ca(OH) 2, Sr(OH)2 a ...
... just a proton; an electron is removed from neutral hydrogen to form H+. Acid-base reactions are commonly called proton transfer reactions. The acid is the proton donor and the base is the proton acceptor. The strong bases are (by the solubility rules) LiOH, NaOH, KOH, RbOH, CsOH, Ca(OH) 2, Sr(OH)2 a ...
Introductory Chemistry
... of Introductory Chemistry, Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation, and Basic Chemistry by Steven S. Zumdahl. Several hundred new problems and questions have been prepared for the new editions of the text, which we hope will be of even greater help to your students in gaining an understanding of the fu ...
... of Introductory Chemistry, Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation, and Basic Chemistry by Steven S. Zumdahl. Several hundred new problems and questions have been prepared for the new editions of the text, which we hope will be of even greater help to your students in gaining an understanding of the fu ...
ch15
... Lead(II) chromate has been used as a bright yellow pigment in some paints. It can be produced by the reaction of potassium chromate with lead nitrate. a Write a full equation for this reaction. b What mass of potassium chromate is required to produce 6.0 g of lead chromate? c Suggest a reason why le ...
... Lead(II) chromate has been used as a bright yellow pigment in some paints. It can be produced by the reaction of potassium chromate with lead nitrate. a Write a full equation for this reaction. b What mass of potassium chromate is required to produce 6.0 g of lead chromate? c Suggest a reason why le ...
Chapter 15 Calculations in chemistry: stoichiometry
... Lead(II) chromate has been used as a bright yellow pigment in some paints. It can be produced by the reaction of potassium chromate with lead nitrate. a Write a full equation for this reaction. b What mass of potassium chromate is required to produce 6.0 g of lead chromate? c Suggest a reason why le ...
... Lead(II) chromate has been used as a bright yellow pigment in some paints. It can be produced by the reaction of potassium chromate with lead nitrate. a Write a full equation for this reaction. b What mass of potassium chromate is required to produce 6.0 g of lead chromate? c Suggest a reason why le ...
Chapter 15 Calculations in chemistry: stoichiometry
... Copper metal can be recovered from a solution of copper(II) sulfate by the addition of scrap metal iron to the solution. The equation for the reaction is: Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → Cu(s) + FeSO4(aq) What mass of copper would be obtained if 1.0 kg of scrap iron was added to enough copper sulfate to react ...
... Copper metal can be recovered from a solution of copper(II) sulfate by the addition of scrap metal iron to the solution. The equation for the reaction is: Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → Cu(s) + FeSO4(aq) What mass of copper would be obtained if 1.0 kg of scrap iron was added to enough copper sulfate to react ...
Joanna Kulesza
... Je tiens à exprimer ici la mémoire de mes anciennes amies: Anna Bresińska, Dominika Kozłowska, Anna Budzisz et Justyna Piotrowska. ...
... Je tiens à exprimer ici la mémoire de mes anciennes amies: Anna Bresińska, Dominika Kozłowska, Anna Budzisz et Justyna Piotrowska. ...
The Reactions of Osmium(VIII) in Hydroxide
... The conditional rate constants and molar extinction coefficients were calculated using custom written software. A hydride transfer mechanism, coupled with the synchronous removal of the hydroxyl proton of the alcohol, was postulated. ...
... The conditional rate constants and molar extinction coefficients were calculated using custom written software. A hydride transfer mechanism, coupled with the synchronous removal of the hydroxyl proton of the alcohol, was postulated. ...
4134gdisk doc..4134gdisk chapter .. Page501
... As in previous years, this review does not cover mechanisms of heterogeneous or solid state processes, homogenous catalysis of organic reactions, fluxional, electrochemical and photochemical processes, redox reactions involving organic substrates or organic reactions of the p-block elements. A numbe ...
... As in previous years, this review does not cover mechanisms of heterogeneous or solid state processes, homogenous catalysis of organic reactions, fluxional, electrochemical and photochemical processes, redox reactions involving organic substrates or organic reactions of the p-block elements. A numbe ...
Chapter 4 Solution Manual
... Plan: Compounds that are soluble in water tend to be ionic compounds or covalent compounds that have polar bonds. Many ionic compounds are soluble in water because the attractive force between the oppositely charged ions in an ionic compound are replaced with an attractive force between the polar wa ...
... Plan: Compounds that are soluble in water tend to be ionic compounds or covalent compounds that have polar bonds. Many ionic compounds are soluble in water because the attractive force between the oppositely charged ions in an ionic compound are replaced with an attractive force between the polar wa ...
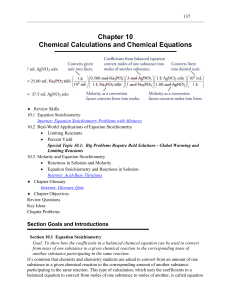
Study Guide Chapter 10: An Introduction to Chemistry
... measurable property 1 moles 1 moles 2 measurable property 2 When the reactants and products of a reaction are pure solids and pure liquids, mass is the conveniently measurable property, but many chemical changes take place in either the gas phase or in solution. The masses of gases or of solut ...
... measurable property 1 moles 1 moles 2 measurable property 2 When the reactants and products of a reaction are pure solids and pure liquids, mass is the conveniently measurable property, but many chemical changes take place in either the gas phase or in solution. The masses of gases or of solut ...