* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Single Replacement Reactions - Tri
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic reforming wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
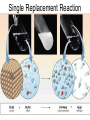
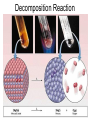
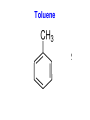
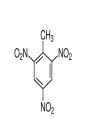
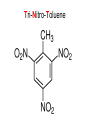
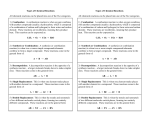
Chapter 9 Classifying Chemical Reactions Types of Reactions • We will consider five types of reactions : 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Single displacement reactions Double displacement reactions Decomposition reactions Synthesis reactions Combustion reactions 1. Single Replacement Reactions • Single Replacement Reactions occur when one element replaces another in a compound. • A metal can replace a metal (+) OR a nonmetal can replace a nonmetal (-). • element + compound compound + element A + BC AC + B (if A is a metal) OR A + BC BA + C (if A is a nonmetal) (remember the cation always goes first!) In a single replacement reaction it is better to write H2O as HOH because it will split into H+ and OH- (not H+ and O2- !!) Single Replacement • A small piece of lithium metal is added to water. Single Replacement Reaction Single Replacement Reactions • Sodium chloride solid reacts with fluorine gas NaCl(s) + F2(g) NaF(s) + Cl2(g) unbalanced Single Replacement Reactions • Zinc metal reacts with aqueous nickel (II) nitrate Zn(s)+ Ni(NO3)2(aq) Zn(NO3)2(aq) + Ni(s) 2. Double Replacement Reactions • Double Replacement Reactions occur when the cations in two compounds switch places. • compound + compound compound + compound • AB + CD AD + CB Double Replacement Reactions • KOH + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + HOH • FeS + HCl → FeCl2 + H2S • NaCl + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + HCl • NH4NO3 + NaCl → NH4Cl + NaNO3 Decomposition Reactions • Decomposition reactions occur when a compound breaks up into two or more substances. • Some examples of decomposition reactions are: – Potassium chlorate when heated breaks into oxygen gas and potassium chloride. ∆ • 2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2 – Heating sodium bicarbonate decomposes into sodium carbonate and water and carbon dioxide. ∆ 3Na CO + 3H O + 3CO • 6NaHCO3 → 2 3 2 2 3. Decomposition Reactions • The simplest decomposition reactions occur when a binary compound breaks up into its elements. Compound Element + Element • In general: AB A + B • Example: 2 H2O 2H2 + O2 • Example: 2 HgO 2Hg + O2 Decomposition Reaction This reaction is highly endothermic Energy Changes • “Many” decomposition reactions involve large changes in energy (they are highly endothermic or highly exothermic). Toluene A A A Trinitrotoluene Tri-Nitro-Toluene Nitroglycerin Nitroglycerin is a contact explosive (physical shock can cause it to explode) and it degrades over time to even more unstable forms. This makes it extremely dangerous to transport or use. Alfred Nobel • Nobel found that when nitroglycerin was added to an absorbent inert substance it became safer. • He patented this in 1867 as dynamite. Alfred Nobel “The Merchant of Death is Dead” Alfred Nobel “The Merchant of Death is Dead” • The erroneous publication in 1888 of a premature obituary of Alfred Nobel by a French newspaper, condemning him for his invention of dynamite, is said to have brought about his decision to leave a better legacy after his death. • The obituary stated "The merchant of death is dead" and went on to say, "Dr. Alfred Nobel, who became rich by finding ways to kill more people faster than ever before, died yesterday.” • In reality the newspaper had instead confused Alfred for his brother who had passed away. Nobel Prizes • Nobel signed his last will and testament and set aside the bulk of his estate to establish the Nobel Prizes. Synthesis Reactions • Synthesis reactions occur when two or more substances combine to form a compound. (Sometimes these are called combination or addition reactions.) – sulfur trioxide reacts with water to make sulfuric acid. • H2O + SO3 → H2SO4 4. Synthesis reactions • The simplest Synthesis reactions occur when two elements combine and form a binary compound. element + element compound • Basically: A + B AB • Example: 2H2 + O2 2H2O • Example: Fe + Cl2 FeCl2 Synthesis Reaction 5. Combustion Reactions • Combustion reactions occur when a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen gas. • This is also called burning!!! • The products of combustion are carbon dioxide and water. Combustion Reactions • Example: - CxHy + O2 CO2 + H2O • Combustion is used to heat homes and run automobiles (example: octane in gasoline, is C8H18). • Combustion also got you to school today. Cellular Respiration C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O Combustion Reactions • CxHy + O2 CO2 + H2O • Products in combustion are ALWAYS carbon dioxide and water. (although incomplete burning can cause by-products like carbon monoxide) Complete vs. Incomplete Combustion • Determined by the amount of oxygen. • Incomplete combustion occurs when there isn't enough oxygen to allow the fuel (usually a hydrocarbon) to react completely. • Carbon monoxide and pure carbon will be produced in addition to carbon dioxide and water in incomplete combustion. Gas Lighting and CO Poisoning • People who lived in 19th century cities were often poisoned by exposure to carbon monoxide from illuminating gas, which was a flammable mixture of gas suitable for lighting purposes that is made from coal and contained extremely high levels of CO. Poe's face has one eye drooping lower than the other while his mouth slants the other way. This same abnormality can be seen in the faces of people poisoned by CO today. It is caused by the effect of repeated CO exposure on facial nerves and can be partially if not completely reversed with months of daily oxygen therapy.(very high levels of CO exposure, in comparison, can cause complete paralysis or coma) Was Poe suffering from CO poisoning or just a troubled soul? • Poe described many symptoms of CO poisoning in his letters, poems and tales. • People poisoned by CO often have the same bizarre physical and mental symptoms he describes. Homework • Reaction Type and Balancing Worksheet (Due in two days).