Chapter 8
... In most chemical reactions several reactants combine to form products. As soon as one of the reactants runs out, the reaction will stop, even if the other reactants are still present. We define the limiting reactant as the reactant the first runs out in a chemical reaction. Note that the theoretical ...
... In most chemical reactions several reactants combine to form products. As soon as one of the reactants runs out, the reaction will stop, even if the other reactants are still present. We define the limiting reactant as the reactant the first runs out in a chemical reaction. Note that the theoretical ...
Burning a Candle in a Vessel, a Simple Experiment
... performed to discover the relationship between the change in volume of the enclosed air and the underlying chemical reaction, can be a challenging task. Wrong conclusions are typical in this experiment and in any experiment that uses a volume of gas that is not strictly closed. The origins of typica ...
... performed to discover the relationship between the change in volume of the enclosed air and the underlying chemical reaction, can be a challenging task. Wrong conclusions are typical in this experiment and in any experiment that uses a volume of gas that is not strictly closed. The origins of typica ...
Η - Knockhardy
... the strength of a bond depends on its environment so MEAN values are quoted making a bond is an exothermic process as it is the opposite of breaking a bond for diatomic gases, the bond enthalpy is twice the enthalpy of atomisation the smaller the bond enthalpy, the weaker the bond and the easier it ...
... the strength of a bond depends on its environment so MEAN values are quoted making a bond is an exothermic process as it is the opposite of breaking a bond for diatomic gases, the bond enthalpy is twice the enthalpy of atomisation the smaller the bond enthalpy, the weaker the bond and the easier it ...
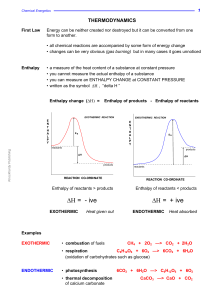
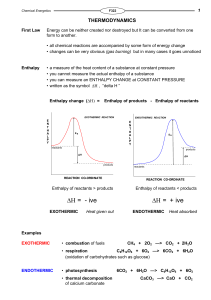
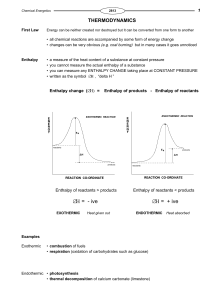
Enthalpy change
... Imagine that, during a reaction, all the bonds of reacting species are broken and the individual atoms join up again but in the form of products. The overall energy change will depend on the difference between the energy required to break the bonds and that released as bonds are made. energy release ...
... Imagine that, during a reaction, all the bonds of reacting species are broken and the individual atoms join up again but in the form of products. The overall energy change will depend on the difference between the energy required to break the bonds and that released as bonds are made. energy release ...
Effect of Potassium on Sol-Gel Cerium and Lanthanum Oxide
... to burn this particulate material [7] [9]. The catalyst deposited in the ceramic filters could oxidize the soot, reducing its emission into the atmosphere. However, the temperatures at which the gases emitted into the atmosphere are cooled between 300˚C and 400˚C, coal is burned at temperatures that ...
... to burn this particulate material [7] [9]. The catalyst deposited in the ceramic filters could oxidize the soot, reducing its emission into the atmosphere. However, the temperatures at which the gases emitted into the atmosphere are cooled between 300˚C and 400˚C, coal is burned at temperatures that ...
Candle Lab (Word)
... When the students place the beaker containing the ice water above the candle, they should see condensation on the bottom of the beaker. If they hold it too close, they will not see the condensation and will see soot form. Students will usually recognize that the condensation is made of water, but th ...
... When the students place the beaker containing the ice water above the candle, they should see condensation on the bottom of the beaker. If they hold it too close, they will not see the condensation and will see soot form. Students will usually recognize that the condensation is made of water, but th ...
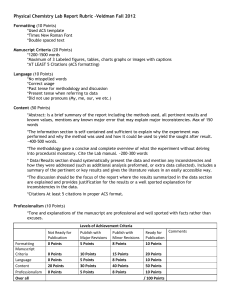
Physical Chemistry Lab Report Rubric –Veldman Fall 2012
... of oxygen gas. Once the bomb has been placed into a known volume of water, and the initial temperature has been determined and measured for a certain amount of time, the bomb is ignited and an electrical current passes through to ignite the substance. Firing of the bomb, and consequently combustion ...
... of oxygen gas. Once the bomb has been placed into a known volume of water, and the initial temperature has been determined and measured for a certain amount of time, the bomb is ignited and an electrical current passes through to ignite the substance. Firing of the bomb, and consequently combustion ...
Thermodynamics
... In order to get maximum calorific output, a burner should have an optimum fuel to oxygen ratio which corresponds to 3 times as much oxygen as is required theoretically for complete combustion of the fuel. A burner which has been adjusted for methane as fuel (with x litre/hour of CH4 and 6x litre/hou ...
... In order to get maximum calorific output, a burner should have an optimum fuel to oxygen ratio which corresponds to 3 times as much oxygen as is required theoretically for complete combustion of the fuel. A burner which has been adjusted for methane as fuel (with x litre/hour of CH4 and 6x litre/hou ...
SCH 3U - mquagliaoths
... magnesium hydroxide to generate magnesium oxide. b) MgCO3(s) MgO(s) + CO2(g) or Mg(OH)2(aq) H2O(l) + MgO(aq) Pg. 145 15a) both – because the metal is burning in oxygen (combustion) and two smaller compounds are forming a larger one (synthesis) b) complete combustion of a hydrocarbon c) synthesis ...
... magnesium hydroxide to generate magnesium oxide. b) MgCO3(s) MgO(s) + CO2(g) or Mg(OH)2(aq) H2O(l) + MgO(aq) Pg. 145 15a) both – because the metal is burning in oxygen (combustion) and two smaller compounds are forming a larger one (synthesis) b) complete combustion of a hydrocarbon c) synthesis ...
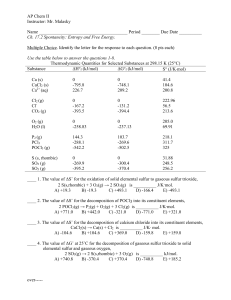
AP Chem II Instructor: Mr. Malasky Name Period ______ Due Date
... ____ 5. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the decomposition of gaseous sulfur dioxide to solid elemental sulfur and gaseous oxygen, SO2(g) → 2 S (s,rhombic) + O2(g) is __________ kJ/mol. A) +395.2 B) +269.9 C) -269.9 D) +300.4 E) -300.4 ____ 6. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the formation of POCl3 from it ...
... ____ 5. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the decomposition of gaseous sulfur dioxide to solid elemental sulfur and gaseous oxygen, SO2(g) → 2 S (s,rhombic) + O2(g) is __________ kJ/mol. A) +395.2 B) +269.9 C) -269.9 D) +300.4 E) -300.4 ____ 6. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the formation of POCl3 from it ...
Answers to Homework Problem Sheet 8
... ΔH = {2 × [Δ atomH (C2H6)] + 7 × [Δ atomH (O2)] } - {4 × [Δ atomH (CO2)] + 6 × Δ atomH (H2O)] } = {2 × [346 (C-C) + 6 × 414 (C-H)] + 7 × [498 (O=O)] } - {4 × [2 × 804 (C=O)] + 6 × [2 × 463)] } kJ mol-1 = -2842 kJ mol-1 This is for the combustion of two moles of C2H6 so the heat of combustion for one ...
... ΔH = {2 × [Δ atomH (C2H6)] + 7 × [Δ atomH (O2)] } - {4 × [Δ atomH (CO2)] + 6 × Δ atomH (H2O)] } = {2 × [346 (C-C) + 6 × 414 (C-H)] + 7 × [498 (O=O)] } - {4 × [2 × 804 (C=O)] + 6 × [2 × 463)] } kJ mol-1 = -2842 kJ mol-1 This is for the combustion of two moles of C2H6 so the heat of combustion for one ...
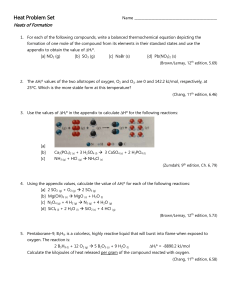
Heats of Formation WS
... 7. The Ostwald process for the commercial production of nitric acid from ammonia and oxygen involves the following steps: 4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) 4 NO (g) + 6 H2O (g) 2 NO (g) + O2 (g) 2 NO2 (g) 3 NO2 (g) + H2O (l) 2 HNO3 (aq) + NO (g) [a] Use the values of ∆Hfº to calculate the value of ∆Hº for ...
... 7. The Ostwald process for the commercial production of nitric acid from ammonia and oxygen involves the following steps: 4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) 4 NO (g) + 6 H2O (g) 2 NO (g) + O2 (g) 2 NO2 (g) 3 NO2 (g) + H2O (l) 2 HNO3 (aq) + NO (g) [a] Use the values of ∆Hfº to calculate the value of ∆Hº for ...
Single Replacement Reactions - Tri
... water. (although incomplete burning can cause by-products like carbon monoxide) ...
... water. (although incomplete burning can cause by-products like carbon monoxide) ...
Power point types of chemical rxn
... 1. Ionic compounds may decompose to produce elements, like the following: • Table salt, sodium chloride, can be broken down into sodium metal and chlorine gas by melting salt at 800ºC and running electricity through it. ...
... 1. Ionic compounds may decompose to produce elements, like the following: • Table salt, sodium chloride, can be broken down into sodium metal and chlorine gas by melting salt at 800ºC and running electricity through it. ...
de Caux - Combustion of Methane Demonstration
... Combustion is the reaction of a substance with oxygen to produce oxides, light and heat. Most combustion reactions involve organic compounds. The combustion of methane is an example of an exothermic reaction. More energy is released when the bonds in the products are formed than is used to break the ...
... Combustion is the reaction of a substance with oxygen to produce oxides, light and heat. Most combustion reactions involve organic compounds. The combustion of methane is an example of an exothermic reaction. More energy is released when the bonds in the products are formed than is used to break the ...
File
... Calculate the mass of each element in a given compound given data such as the masses of CO2 and H2O formed in a combustion reaction. Use mass, mole, stoichiometry, and/or combustion information to calculate the empirical formula and molecular formula of an unknown substance. ...
... Calculate the mass of each element in a given compound given data such as the masses of CO2 and H2O formed in a combustion reaction. Use mass, mole, stoichiometry, and/or combustion information to calculate the empirical formula and molecular formula of an unknown substance. ...
Combustion Seminar - The Masonry Heater Association (MHA
... •Requires absence of flame (smoldering) to form •90% of particles are smaller than 1 micron (= 0.001 mm) •Blue smoke -- The wavelength of blue light is 0.5 microns •Contains PAH’s – polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons – a major health concern, can be carcinogenic •Measurable with a filter, but requires ...
... •Requires absence of flame (smoldering) to form •90% of particles are smaller than 1 micron (= 0.001 mm) •Blue smoke -- The wavelength of blue light is 0.5 microns •Contains PAH’s – polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons – a major health concern, can be carcinogenic •Measurable with a filter, but requires ...
lecture 13
... marked the moment we learned to transform brittle iron ores to iron metal. This affected everything from how we grew food to how we waged wars. ...
... marked the moment we learned to transform brittle iron ores to iron metal. This affected everything from how we grew food to how we waged wars. ...
Combustion

Combustion /kəmˈbʌs.tʃən/ or burning is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion in a fire produces a flame, and the heat produced can make combustion self-sustaining. Combustion is often a complicated sequence of elementary radical reactions. Solid fuels, such as wood, first undergo endothermic pyrolysis to produce gaseous fuels whose combustion then supplies the heat required to produce more of them. Combustion is often hot enough that light in the form of either glowing or a flame is produced. A simple example can be seen in the combustion of hydrogen and oxygen into water vapor, a reaction commonly used to fuel rocket engines. This reaction releases 242 kJ/mol of enthalpy (heat):2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g)Uncatalyzed combustion in air requires fairly high temperatures. Complete combustion is stoichiometric with respect to the fuel, where there is no remaining fuel, and ideally, no remaining oxidant. Thermodynamically, the chemical equilibrium of combustion in air is overwhelmingly on the side of the products. However, complete combustion is almost impossible to achieve, since the chemical equilibrium is not necessarily reached, or may contain unburnt products such as carbon monoxide, hydrogen and even carbon (soot or ash). Thus, the produced smoke is usually toxic and contains unburned or partially oxidized products. Any combustion at high temperatures in atmospheric air, which is 78 percent nitrogen, will also create small amounts of several nitrogen oxides, commonly referred to as NOx, since the combustion of nitrogen is thermodynamically favored at high, but not low temperatures. Since combustion is rarely clean, flue gas cleaning or catalytic converters may be required by law.Fires occur naturally, ignited by lightning strikes or by volcanic products. Combustion (fire) was the first controlled chemical reaction discovered by humans, in the form of campfires and bonfires, and continues to be the main method to produce energy for humanity. Usually, the fuel is carbon, hydrocarbons or more complicated mixtures such as wood that contains partially oxidized hydrocarbons. The thermal energy produced from combustion of either fossil fuels such as coal or oil, or from renewable fuels such as firewood, is harvested for diverse uses such as cooking, production of electricity or industrial or domestic heating. Combustion is also currently the only reaction used to power rockets. Combustion is also used to destroy (incinerate) waste, both nonhazardous and hazardous.Oxidants for combustion have high oxidation potential and include atmospheric or pure oxygen, chlorine, fluorine, chlorine trifluoride, nitrous oxide and nitric acid. For instance, hydrogen burns in chlorine to form hydrogen chloride with the liberation of heat and light characteristic of combustion. Although usually not catalyzed, combustion can be catalyzed by platinum or vanadium, as in the contact process.