* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - wentworth science
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
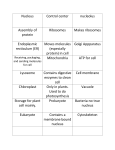
Features of Life and the Cell Features of Living Things The word living can be difficult to define Biologists recognize that ALL living things share certain features Our textbook describes 8 features of ALL living things Features of ALL Living Things 1. Living things reproduce This simply means that all living things produce offspring There are two types of reproduction: sexual and asexual Sexual reproduction is when two cells combine there DNA to produce a new, unique cell Asexual reproduction is when one cell simply splits into two new cells Paramecium dividing Cell fertilization Features of ALL Living Things 2. Living things grow Living things grow by using materials and energy from their environment to increase their size Features of ALL Living Things 3. Living things develop Development is all the changes that occur in a living thing as it grows Features of ALL Living Things 4. Living things need food Food, in this context, means an energy source Organisms are either consumers or producers Consumers consume, or eat, other living things Producers (like plants, algae and some bacteria) produce, or make, their own food source Features of ALL Living Things 5. Living things use energy. Energy can be defined as “the ability to do work” It is what causes the movement and/or change in matter All biological functions require energy to carry out their chemical reactions Consumers eat other organisms to get energy Producers make their own food during photosynthesis or chemosynthesis Features of ALL Living Things How do organisms get energy from the food they eat? This happens by way of a process called cellular respiration In this process, food molecules (usually a sugar called glucose) are chemically broken down in the cell and new molecules are formed that release energy when the organism needs it Features of ALL Living Things 6. Living things are made of cells The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in ALL living things Organisms can be multicellular (made of many cells) or unicellular (made of one cell) Features of ALL Living Things 7. Living things respond to input from their environment When input is received from the environment, living things react Sometimes this reaction is a chemical change in the body Sometimes it is a physical change such as movement Examples: sweating, plants growing toward light, your dog comes when you call it, flinching when Mrs. Motroni throws something at you Features of ALL Living Things 8. Living things are adapted to their environments A trait that makes an organism better able to survive in its environment is called an adaptation Better adapted organisms are able to live longer and reproduce more frequently than less adapted individuals All of the, roughly, 10 million species on earth are here because they are the best adapted to their respective environments The Chemistry of Life Living things are made of matter What’s matter? Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space Matter is made of atoms Atoms make up the elements Elements are substances that are made of only one type of atom The Chemistry of Life Two or more elements that are bonded together form a compound When chemistry is done and two elements bond together, the properties of the new compound are usually different than the properties of the elements by themselves Examples: hydrogen and oxygen are elements. They are flammable gases. They are gases at room temperature. When they bond together they make water, which is a liquid at room temperature. Sodium metal + chlorine gas The Chemistry of Life Each element has a specific symbol used to represent it. H for hydrogen, O for oxygen, Na for sodium, W for tungsten When these combine to make a compound, the symbols are joined to make a molecular formula Water is H2O, table salt (sodium chloride) is NaCl, sugar is C6H12O6 The Chemistry of Life Most living things are made of the following elements Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus, calcium, and sulfur These elements combine to make 99% of all the molecules in all living things on Earth Cell Theory 1655, English scientist, Robert Hooke, looks at this slices of cork under a microscope He observed that the cork was made of many small parts that he called cells Nineteenth Century, Robert Brown discovers the nucleus, Schleiden and Schwann determine that all plants and animals are made of cells These experiments lead to the to development of the cell theory “ ” Cork cells Plant cells animal cells Cell Theory The cell theory has three major parts 1. ALL living things are made of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in ALL living things 3. ALL cells come from other, pre-existing cells Watch this Cell Parts and Their Jobs As you know, cells are the basic unit of structure and function of ALL living things This means that all living things are made of cells and that the cells carry out all functions necessary for life There are single-celled organisms and there are multi-celled organisms Multi-celled organisms, like us, are made of lots of different types of cells. Each type does a specific job in our bodies Cells, however, contain even smaller things called organelles Organelles do specific jobs in each cell Cytoplasm The cytoplasm is the gel-like fluid inside the cell All the other cell parts are suspended in the cytoplasm Cell Membrane The cell membrane surrounds the cell It holds in the cytoplasm The cell membrane’s two major jobs are to 1. maintain the shape of the cell 2. control what goes into and out of the cell Nucleus The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle This membrane is called the nuclear envelope. It has openings in it known as nuclear pores. It is usually the largest organelle in the cell The nucleus is considered the “control center” of the cell This is so because the nucleus contains the DNA The DNA is the molecule that contains the genetic code and determines what proteins are to be made by the cell and therefore, all the physical traits of an organism Chromosomes are actually DNA molecules that are all folded up on themselves Nucleolus The nucleolus is found inside the nucleus Its job is to make very important structures called ribosomes Ribosomes Ribosomes are very small organelles Their major function is to produce protein molecules Ribosomes are found floating around in the cytoplasm AND stuck to the side of another organelle called the endoplasmic reticulum Endoplasmic reticulum This organelle is like a series of highways that connect different parts of the cell together Its job is to transport materials throughout the cell Golgi Body The Golgi body is an organelle that looks like a bunch of folded up sacs Its job is to process protein molecules and get them ready to be used by the cell or by other cells in the body Vacuoles Vacuoles are liquid filled sacs that are used to store food, water, and minerals Some vacuoles store waste products until the cell is ready to get rid of them Most plant cells have a very large vacuole inside of them, this vacuole helps to provide structural support for the cell Centrioles Centrioles are present in animal cells but NOT in plant cells They are located near the nucleus and help with cell reproduction Chloroplasts Chloroplasts are found in plant cells NOT in animal cells They contain the pigment chlorophyll, so they are green This is why plant leaves are green Chlorophyll absorbs sunlight and uses it to make sugar molecules during photosynthesis Cell Wall The cell wall is different than the cell membrane Cell walls are found in plant cells, fungus cells, algae cells, and some bacteria cells but, NOT in animal cells Their job is to provide protection and support to the cells Cell walls often remain after the rest of the cell has died A piece of wood is made of the cell walls of the dead tree cells mitochondria Sometimes called the power house of the cell This is where sugar molecules are broken down to make useable enrgy for the cell Special Cell Processes: Diffusion and Osmosis Diffusion is a naturally occurring event where particles move from an area of high concentration (large amount) towards an area of low concentration (small amount) This happens because ALL particles of matter are in constant motion Particles bounce of each other and off the inside walls of whatever they are contained in Diffusion Through the Cell Membrane There are small openings in the cell membrane called pores These pores allow particles, like oxygen or carbon dioxide, to diffuse into and out of the cell Osmosis When water diffuses across a cell membrane it is called osmosis When there is more water molecules inside the cell than out, water will move out of the cell What happens when there is more water molecules outside the cell than there are inside? Osmosis is Important Osmosis is important because if too much water leaves the cell it can wilt and die If too much water enters a cell it can rupture and die This is why salt is a natural preservative When food is packed in salt, it dries the food out, this prevents bacteria and fungi from growing on the food This is also one of the steps in making a mummy Organization Living things are organized in special ways Single celled organisms perform all life functions in that one cell Multi-celled organisms have many types of cells, each doing a specific job Groups of cells that do the same job are called tissues Bone, muscle, skin, blood, and nerve are examples of different types of tissues organs Tissues can be organized into groups too Organs are made when groups of similar tissues work together doing a job What are some organs? Organ system Organ systems are made when several different organs work together to perform a particular job Example: the brain, spinal cord, and all the nerves in your body make up the nervous system organism All the organ systems together make the organism some organisms are only one cell but multi-celled organisms have several organ systems What are some organ systems?