* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fermentation - cloudfront.net
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
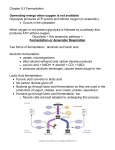
Step 1: Glycolysis Mitochondria Glucose C C C Enzyme C C C C6H12O6 • Where? In cytoplasm • What happens? A) Glucose (from our food) is broken down into 2 pyruvates B) 2 ATP molecules released for cellular processes What’s after Glycolysis? glycolysis ATP ATP Step 2: Fermentation Yeast perform alcoholic fermentation to make bread. Why isn’t bread alcoholic? Alcohol evaporates in the baking process During prolonged exercise, the oxygen you inhale mainly goes to your brain. Howmuscles to relieve Your aresore nowmuscles: lacking oxygen. 1) Massage 2) Bananas 3) Stretch after 4) Hydrate Muscle cells perform fermentation to keep you going! • Two Types of Fermentation (both anaerobic): A) Lactic Acid fermentation – Performed by animals when muscles are not receiving oxygen – Lactic acid waste created B) Alcoholic fermentation – Performed by yeast, some plants, bacteria – Alcohol & CO waste created Lactic Acid vs. Alcoholic Fermentation glycolysis Lactic acid glycolysis Alcohol + CO2 Lactic acid fermentation Lactic Acid • Location: Cytoplasm • Amount of ATP created: Zero • The Point? Make molecules to restart glycolysis • Waste: Lactic acid Alcoholic fermentation Alcoholic • Location: Cytoplasm • Amount of ATP created: Zero • The Point? Make molecules to restart glycolysis • Waste: Alcohol and CO2 Aerobic Respiration Where? In the mitochondria Steps? Kreb’s cycle and electron transport chain Glycolysis: -- In the cytoplasm -- Glucose is split into 2 pyruvate -- 2 ATP created What happens? Pyruvate converted into 34 ATPs Fermentation (anaerobic respiration) Where? In the cytoplasm Glycolysis restarts What happens? Pyruvate is broken into either lactic acid or alcohol Molecules to restart glycolysis created (No ATP) Recap 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Name the two types of fermentation. How much ATP does glycolysis create? How much ATP does fermentation create? Which molecule is broken down during glycolysis? A buildup of which molecule causes sore muscles? Which waste molecules are created by alcoholic fermentation? 7) Is fermentation aerobic or anaerobic? What does this mean? 8) Why is aerobic respiration preferred vs. fermentation?