* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Med Term Chapter 10
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
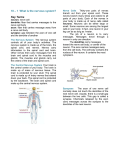
Chapter 10: Nervous System Horse’s tail Define the following Afferent (sensory) Nerves Efferent (motor) Nerves Carry messages related to Message is carried AWAY changes in the environment TOWARD the spinal cord and brain from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles, telling them what to do. Cranial and Spinal Nerves Mainly Voluntary Involved with sensations of : Smell Taste Sight Hearing Muscle Movement Autonomic Nervous System Peripheral Nerves Function Involuntarily Generally Carries Impulses AWAY from the Central Nervous System to: Heart Glands Blood Vessels Muscles of the Intestines, Stomach, Urinary Bladder More about Autonomic Nerves Some are SYMPATHETIC Stimulate the body in times of stress: Stimulates Adrenal Glands Increase Heart Rate Dilate Airways Increase B/P Slows Digestion Some are PARASYMATHETIC Balance the Sympathetic Response: Slows Heart Rate Contracts Pupils Lowers B/P Increases saliva Stimulates peristalsis/digestion Define Plexus A large network of nerves in the PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM!!! Cervical Plexus Brachial Plexus Lumbosacral Plexuses Solar Plexus (sympathetic nerves and ganglia located in the peritoneal cavity behind the stomach and having branching tracts that supply nerves to the abdominal viscera. ) Dendrites Cell Body Cell Nucleus Axon: carries pulses away from cell Myelin Sheath; covers axon/white matter Terminal End Fibers: nerve impulse leaves cell Synapse: jumps neuron to neuron. Pronunciation and definition: Definition of Parenchyma Parenchyma:The key elements of an organ essential to its functioning, as distinct from the capsule that encompasses it and other supporting structures. The parenchyma is thus opposed to the connective tissue framework, or stroma, of an organ. The parenchyma of the testis consists of what are called the seminiferous tubules. The word is pronounced "pa-ren-ki-ma" with the "y" in "parenchyma" pronounced as a short "i" rather than as "eye." Quick Question What is the nervous system parenchyma? A. B. C. D. Neuronal tissue Glial tissue Ventricles Connective tissue What is a Neuron? Individual Nerve Cells Define Glial Cells Glial cells, commonly called neuroglia or simply glia (Greek for "glue"), are nonneuronal cells that provide support and nutrition, maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and participate in signal transmission in the nervous system. In the human brain, glia are estimated to outnumber neurons by about 10 to 1. Remember that STROMAL TISSUE… Is the SUPPORTIVE/CONNECTIVE TISSUE of the Organ Nervous System Stromal Tissue : Glia Astrocytes (Astroglial Cells): transports water and salts between capillaries and neurons. Microglial Cells: as phagocytes protect neurons from inflammation. Oligodendroglial Cells (Oligodendrocytes): form myelin sheath Ependymal Cells: line membranes within the brain and spinal cord where CSF circulates. Glial Cells (framework) Astrocytes (astroglial cells) transports water and salts between capillaries and neurons. 2009 Howard Hughes Medical Institute Microglial Cell Protect neurons in response to inflammation. Courtesy of Fred Maxfield Oligodendroglial Cells These cells form the myelin sheath. Lee PR and Fields R (2009) Define….. Oligodenroglial Olig/o dendr/o glial Scanty/Few Dendrites = branching fibers of neurons Stromal tissue of the nervous system Oligodendrocytes form a protective sheath, known as myelin, that insulates the fibrous cables, or axons, radiating from nerve cells. In multiple sclerosis, the immune system's T cells and B cells attack oligodendrocytes, ultimately damaging the myelin sheath to the point that the electrical signals transmitted by the axons beneath it are disrupted. (David Rowitch, et al. University of California - San Francisco.) Multiple sclerosis destroys myelin sheaths surrounding nerves and is thought to be an autoimmune disease. Symptoms: numbness tingling of the hand and toes, loss of coordination, weakness, loss of bladder and bowel control, eyesight problems, mood swings, slurred speech. stanford.wellsphere.com/.../591402 Ependymal Cells line membranes within the brain and spinal cord where CSF circulates. Spinal cord central canal (H&E stain). The central canal of the spinal cord is lined by ependymal cells which have cilia (arrows) that project into the lumen of the central canal. Quick Question The “balance” of the nervous system is the: oA. autonomic nervous system oB. the central nervous system oC. sympathetic nerve oD. parasympathetic nerves Quick Question The transfer of a nervous impulse across the synapse depends on: o A. neurotransmitters o B. synaptic chains o C. the sympathetic nervous system o D. the parasympathetic nervous system Lobotomies were used to treat many different types of mental illnesses, including anxiety, depression and schizophrenia. The procedure was also performed on people who were considered extremely emotional, difficult to handle or simply "moody.“ (Shanna Freeman) Medieval doctor “letting the devil out” Walter Freeman performing a lobotomy in 1949 at the Western State Hospital (Image Credit: Shedding Light on Shadowland) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_0aNILW6ILk There have been a few famous cases over the years. For example, Rosemary Kennedy, sister to John, Robert, and Edward Kennedy, was given a lobotomy when her father complained to doctors about the mildly retarded girl’s embarrassing new interest in boys. Her father never informed the rest of the family about what he had done. She lived out her life in a Wisconsin institution and died January 7, 2005, at the age of 86. Her sister, Eunice Kennedy Shriver, founded the Special Olympics in her honor in 1968. http://dda604.wordpress.com/2009/08/18/ Myelo – spinal cord Radicul/o – spinal nerve root Hematoma – Collection of blood (what?) Subdural Hematoma: collection of blood within the meningeal layers Quick Question Bradykinesia means from the terminology section means: A. Partial paralysis B. Slow movement C. Slow thinking D. Slow speech Dura Mater: Outer most membrane Subdural Space: below dural membrane Arachnoid Membrane: web like fibers attached to other meninges Subarachnoid Space Pia Mater: blood supply Pia and Arachnoid may be referred to as pia-arachnoid. Quick Question The thinnest of the meninges: oA. arachnoids oB. dura mater oC. pia mater Quick Question Motor aphasia (aka broca) means: o A. the patient cannot speak o B. the patient knows what they want to say but cannot say it o C. the patient has difficulty understanding and cannot repeat written and verbal ___language disturbance caused by a lesion of the brain, making an individual partially or totally impaired in his ability to speak, write, or comprehend the commands. Anesthesia – condition of no nervous sensation Paresthesia – abnormal sensation of tingling or prickling Myelo – spinal cord Ultrasound Showing Spina Bifida Tourette Syndrome http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HPmpIY7XJVE Parkinson Disease Deficiency of dopamine made by the basal ganglia Palliative Tx only (relieving, but not curing) Characterize by person with a “shuffling gait” webpages.scu.edu sportsillustrated.cnn.com fitsugar.com http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ECkPVTZlfP8 This is the most malignant form of astrocytoma’s or brain tumors of the glial cells Brain Tumor – Arise from Glial Cells (Astrocytoma’s Glioma’s) or Meninges (Meningioma’s) Glio/blast/oma Glial cells Blast/o Supportive tissue of nervous system Immature cells Oma Tumor Blastoma Immature tumor cells A highly malignant brain tumor Stroke or CVA (Cerebrovascular accident) Disruption in normal blood supply to the brain Quick Question A stroke caused by a dislodged thrombus is called a: oA. hemorrhagic oB. thrombotic oC. embolic Shingles: Itching painful rash/blisters that follow the course of the sensory nerve. shinglesonface.com/ Googleimages.com True or False: Sympathetic nerves stimulate the body in times of stress and crisis and the parasympathetic nerves normally act as a balance for the sympathetic nerves. True Quick Question Part of the nerve cell that first receives the nervous impulse is the: A. Axon B. Cell body C. Convolution D. Dendrite E. Neurilemma Quick Question Space between nerve cells is called the: A. Stimulus B. Subdural space C. Synapse D. Subarachnoid space Quick Question Paralysis of four extremities: A. Hemi paresis B. Hemiplegia C. Paraplegia D. Quadriplegia E. Apraxia Quick Question Fainting A.Shingles B. Hyperesthesia C.Ataxia D.Syncope E. Palsy Quick Question Condition of no nervous sensation: A. B. C. D. Analgesia Anencephaly Anesthesia Alzheimer disease Quick Question Inability to Speak A. B. C. D. E. Apraxia Dysplasia Aphasia Aphagia Ataxia Epilepsy Chronic brain disorder characterized by recurrent seizure activity Aura – peculiar sensation experienced by the affected person before onset of a seizure (dizziness, numbness and visual or olfactory disturbances) Tonic-clonic seizure (grand mal or ictal events) Major form of seizure Sudden loss of consciousness, falling down, tonic and clonic contractions Absence seizure (petit mal seizure) Minor form of seizure Momentary clouding of consciousness and loss of awareness of a person’s surroundings