* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Control of Cell Function and Inheritance
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
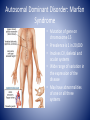
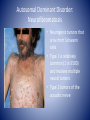
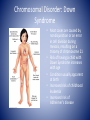
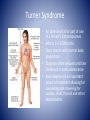
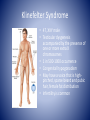
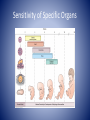
Genetic Control of Cell Function and Inheritance NUR 304 Dr. Dory Roedel Ferraro It’s All in the DNA • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – extremely stable macromolecule • Contains within its structure the basic information needed to: – Direct the function of our cells – Influence our appearance – Influence how we respond to our environment – Serve as a unit of inheritance that is passed on from generation to generation DNA • Long, double-stranded helical structure composed of nucleotides, which consist of phosphoric acid, deoxyribose, and one of four nitrogenous bases (T,C,A or G) • Spiral staircase with paired bases representing the steps • Nitrogenous bases carry the genetic information – – – – Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Adenine (A) Guanine (G) • Precise complimentary pairing of purine and pyrimidine – A is paired with T – G is paired with C Replicating DNA Helix DNA • Each nucleotide in a pair is on one strand of the DNA molecule • Bases on opposite DNA strands are bound together by hydrogen bonds • Double-stranded structure of DNA molecules allows them to replicate precisely by separation of the two strands, followed by synthesis of two new complimentary strands • Only one strand is used in transcribing • Both strands are involved in DNA duplication Chromosomes • Discrete bundles of DNA containing genetic information • Arranged in pairs; one from the mother and one from the father • Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes • 22 are autosomes (have same appearance in males and females) • 23rd pair are the sex chromosomes (determine the sex of an individual) – Males have an x and y – Females have two x chromosomes Patterns of Inheritance • Genotype- total sum of the genetic information that is stored in the genetic code of a person • Phenotype- represents the recognizable traits, physical and biochemical, associated with the genotype • Expressivity- refers to the expression of a gene in the phenotype • Penetrance- the ability of a gene to express its function • Gene locus- the point on the DNA molecule that controls the inheritance of a particular trait Patterns of Inheritance • Alleles- alternate forms of a gene (one from each parent) • Locus- the position they occupy on the chromosome • Alleles at a gene locus may carry recessive or dominant traits • Mendelian (single-gene) patterns of inheritance include autosomal dominant and recessive traits that are transmitted from parents to their offspring in a predictable manner Patterns of Inheritance • Recessive trait is one expressed only when two copies (homozygous) of the recessive alleles are present • Dominant trait are expressed with either homozygous or heterozygous pairing of alleles • Dominant traits are labeled with caps (D) • Recessive with lower case (d) Punnett Square Autosomal Dominant Disorders • Single mutant gene from an affected parent is transmitted to an offspring regardless of sex • The affected parent has a 50% chance of transmitting the disorder to each offspring • Unaffected siblings of the offspring do not transmit the disorder • In some cases, the person with an autosomal dominant trait does not have an affected parent, but rather it is owed to a mutation involving either the sperm or the ovum Autosomal Dominant Disorder: Marfan Syndrome • Mutation of gene on chromosome 15 • Prevalence is 1 in 20,000 • Involves CV, skeletal and ocular systems • Wide range of variation in the expression of the disease • May have abnormalities of one or all three systems Autosomal Dominant Disorder: Neurofibromatosis • Neurogenic tumors that arise form Schwann cells • Type 1 is relatively common (1 in 3500) and involves multiple neural tumors • Type 2 tumors of the acoustic nerve Autosomal Recessive Disorder • Manifested only when both members of the gene pair are affected • Both parents may be unaffected but are carriers of the defective gene • Affect both sexes • Tay-Sachs, Phenylketonuria are autosomal recessive disorders • Occurrences – One in four for affected child – Two in four for a carrier child – One in four for a normal child (unaffected, non-carrier) Chromosomal Disorder: Down Syndrome • Most cases are caused by nondisjunction or an error in cell division during meiosis, resulting on a trisomy of chromosome 21 • Risk of having a child with Down Syndrome increases with age • Condition usually apparent at birth • Increased risk of childhood leukemia • Increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease Maternal Age and Risk of Down Syndrome http://www.ndss.org/Down-Syndrome/What-Is-Down-Syndrome/ Turner Syndrome • An absence of all or part of one of a female’s X chromosomes • Affects 1 in 5000 births • Short stature with normal body proportions • Diagnosis often delayed until late childhood or early adolescence • Early diagnosis is an important aspect of treatment allowing for counseling and screening for cardiac, renal, thyroid and other abnormalities Klinefelter Syndrome • 47, XXY male • Testicular dysgenesis accompanied by the presence of one or more extra X chromosomes • 1 in 500-1000 occurrence • Congenital hypogonadism • May have a voice that is highpitched, sparse beard and pubic hair, female fat distribution • Infertility is common Disorders Due to Environmental Influence • Physiologic status of the mother – General state of health (DM associated with congenital defects) – Hormone balance – Nutritional status – Medications she takes • Smoking • Alcohol • Infectious agents Teratogenic Agents • Radiation (microcephaly, skeletal malformations, intellectual disability) • Environmental chemicals (mercury) • Medications and illicit drugs • Alcohol • Infectious agents • Nutrient deficiencies Medications and Illicit Drugs • Many drugs can cross the placenta • Lipid soluble drugs cross more readily and enter the fetal circulation • Determining factors – Rate at which a drug crosses the placenta – Duration of exposure – Stage of placental and fetal development at the time of exposure – Molecular weight of the drug (< 500 can cross easily) Sensitivity of Specific Organs Teratogenic Drugs • Thalidomide • Antimetabolites used in the treatment of cancer • Anticonvulsants • Warfarin • Alcohol • Cocaine Alcohol • Variable effects on fetal development ranging from minor abnormalities to fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) • Prenatal or postnatal growth retardation • CNS involvement: neurologic abnormalities, developmental delays, skull and brain malformation, characteristic facial features Clinical Features of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Infectious Agents • • • • Many microorganisms cross the placenta TORCH T=toxoplasmosis (animal excrement) O=other (varicella zoster, Epstein-Barre, syphilis) • R=rubella • C=cytomegalovirus • H=herpes simplex type 2 Prenatal Screening and Diagnosis • • • • • • Ultrasonography Maternal serum markers Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) Amniocentesis Chorionic villous sampling Percutaneous umbilical cord sampling