* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide for Chapter 4 - Cells: Basic Unit of Life
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
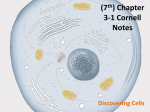
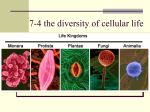
Study Guide for Chapter 4 - Cells: Basic Unit of Life Below you will find general questions covering the material we discussed from Chapter 4. You are not required to answer these questions. But can you answer them? If not, make sure you find the answer before the day of the test. NOTE: Please understand that these are only general questions. Any information you read, took notes on, saw in a movie, practiced in an activity, answered on a worksheet, etc. could be found on the test, including questions, topics, and vocabulary we used in class that is not listed here. 1) What is a cell? Who was the first person to describe cells? 2) What are the three basic parts of the cell theory? Do you understand what they mean? 3) Why are cells generally small? - Your answer should talk about surface area to volume comparisons and why that is important. 4) What are the main structures that ALL cells (plant, animal, bacteria, etc) have in common? 5) What are the two different types of cells? What makes them the same? Different? 6) What is unicellular? What are the benefits of being Unicellular? Disadvantages? 7) What is multicellular? What are the benefits of being Multicellular? Disadvantages? 8) What does function mean? What does structure mean? 9) What are the different Levels of Organization in a living organism? 10) Why is specialization of cells in a multicellular organism important? 11) What is a tissue? What are the names and functions of the four basic types of tissues? 12) What are some examples of tissues, and their functions? 13) What is an organ? What makes it different from a tissue? 14) What are some examples of organs, and their functions? 15) What is an organ system? What makes it different from an organ? 16) What are some examples of organ systems, and their functions? 17) What are the main differences between a plant and animal cell? 18) What is a cell wall? What is cellulose? What is its purpose? 19) What is the cell membrane? What is it made of? What is its main purpose? 20) What does “selectively permeable” mean? 21) What is a cytoskeleton? What is its purpose? 22) What is the nucleus? What is its purpose? Why does it have a double membrane? 23) What are amino acids? What are proteins? What does the ribosome do? 24) What is the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)? What purposes does it serve the cell? What are the differences between smooth and rough ER? 25) What are mitochondria? What purpose does it serve the cell? 26) What is ATP? What is its purpose? 27) What are chloroplasts? What is their purpose? What is chlorophyll purpose? 28) What is photosynthesis? What are the reactants: what the cell uses in the process? What are the products: what it makes after the process? 29) What is a Golgi Complex? What is its function? How is it similar to ER? Different? 30) What is a vesicle? What is the function of lysosome? Vacuoles? 31) What is a large, central vacuole? Why do you think only plants have one? Make sure you ask questions before the test date. You can ask during class, before or after school, or make arrangements during break or lunch, if you would like further clarification on the topics.