* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download tissues and membranes
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
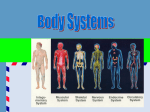
TISSUES AND MEMBRANES Tissues cells that are grouped because they are similar in shape, size, structure, and function EPITHELIAL TISSUE protects the body by covering internal and external surfaces, and produces secretions CONNECTIVE TISSUE supports and connects organs and tissue Types of Connective Tissue • Adipose tissue (fat) • Areolar (loose) tisue—surrounds various organs • Dense fibrous—Ligaments & tendons • Bone tissue • Cartilage • Blood • Lymph More about Connective Tissue • ADIPOSE TISSUE – type of connective tissue that stores fat cells • LIGAMENTS – strong, flexible bands of connective tissue that hold bones firmly together at the joints • TENDONS – white bands of connective tissue attaching skeletal muscle to bone • CARTILAGE – firm, flexible support of the embryonic skeleton and part of the adult skeleton MUSCLE TISSUE Has the ability to contract and move the body NERVOUS TISSUE Cells that react to stimuli and conduct an impulse MEMBRANES Formed by putting two thin layers of tissue together, cells may secrete a fluid MUCOUS MEMBRANES Lines digestive, respiratory, reproductive and urinary systems – produces mucous to lubricate and protect the lining SEROUS MEMBRANES Double-walled membrane – produces a watery fluid, lines closed body cavities • the outer part of the membrane that lines the cavity is the PARIETAL membrane • the part that covers the organs is the VISCERAL membrane. Parts of Serous Membrane Types of Serous Membranes • PLEURAL MEMBRANE --lines thoracic or chest cavity and protects the lungs • PERICARDIAL MEMBRANE – lines the heart cavity and protects the heart • PERITONEAL MEMBRANE – lines the abdominal cavity and protects abdominal organs ORGAN SYSTEM a group of organs which act together to perform a specific, related function Integumentary Skin and its appendages Skeletal Bones Muscular Different types of muscles in the body Digestive stomach, intestines & other organs Respiratory lungs and other structures for breathing Circulatory Heart and blood vessels Nervous Brain, spinal cord, nerves Urinary System Rids body of waste in form of urine Endocrine Glands that produce hormones Reproductive organs that allow for production of offspring