* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CMS Curriculum Guides 2011-2012 7th Grade Math Unit Title
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Numbers (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Bernoulli number wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
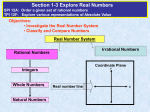
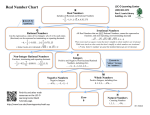
Real number wikipedia , lookup
P-adic number wikipedia , lookup
CMS Curriculum Guides 2011-2012 7th Grade Math Unit Title: Accentuate the Negative Suggested Time: 20 days Enduring understanding (Big Idea): Use appropriate notation to indicate positive & negative numbers; Compare & order positive and negative rational numbers (fractions, decimals, and zero) and locate them on a number line; Understand the relationship between a positive or negative and its opposite (additive inverse); Develop algorithm for adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing positive and negative numbers; Write mathematical sentences to show relationships; Write and use related fact families for addition/subtraction and multiplications/division to solve simple equations; Use parentheses and rules for the order of operations in computations; Understand and use Commutative Property for addition and multiplication; Apply the Distributive Property to simplify expressions and solve problems; Graph points in four quadrants; Use positive and negative numbers to model and answer questions about situations Essential Questions: How do negative and positive numbers help in describing the situation? What will addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division of positive and negative numbers tell about the problem? What model(s) for positive and negative numbers would help in showing the relationships in the problem situation? Unit Plans Common Core Standards Alignment Connection to 2003 Standards Investigation 1-Extending the Number System 7.NS.1.b Objective: 1.02 Problems 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, & Math Reflections Assign specific ACE problems Understand p + q as the number located a distance |q| from p, in the positive or negative direction depending on whether q is positive or negative. Show that a number and its opposite have a sum of 0 (are additive inverses). Interpret sums of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. 7.EE.3 Solve multi-step real-life and mathematical problems posed with positive and negative rational numbers in any form (whole numbers, fractions, and decimals), using tools strategically. Apply properties of operations to calculate with numbers in any form; convert between forms as appropriate; and assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies. Investigation 2 -Adding and Subtracting Integers Problems 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4. 2.5 & Math Reflections Assign specific ACE problems 7.NS.1 Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram. 7.NS.1.a Describe situations in which opposite quantities combine to make 0 Objective: 1.02 CMS Curriculum Guides 2011-2012 7th Grade Math 7.NS.1.b Understand p + q as the number located a distance |q| from p, in the positive or negative direction depending on whether q is positive or negative. Show that a number and its opposite have a sum of 0 (are additive inverses). Interpret sums of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. 7.NS.1.c Understand subtraction of rational numbers as adding the additive inverse, p – q = p + (–q). Show that the distance between two rational numbers on the number line is the absolute value of their difference, and apply this principle in real-world contexts. 7.NS.1.d Apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract rational numbers. 7.NS.3 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. 7.EE.3 Solve multi-step real-life and mathematical problems posed with positive and negative rational numbers in any form (whole numbers, fractions, and decimals), using tools strategically. Apply properties of operations to calculate with numbers in any form; convert between forms as appropriate; and assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies. Investigation 3 - Multiplying and Dividing Integers 7.NS.2 Problems 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, & Math Reflections Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. Assign specific ACE problems 7.NS.2.a Understand that multiplication is extended from fractions to rational numbers by requiring that operations continue to satisfy the properties of Objective: 1.02, 1.03 CMS Curriculum Guides 2011-2012 7th Grade Math operations, particularly the distributive property, leading to products such as (–1)(–1) = 1 and the rules for multiplying signed numbers. Interpret products of rational numbers by describing realworld contexts. 7.NS.2.b Understand that integers can be divided, provided that the divisor is not zero, and every quotient of integers (with non-zero divisor) is a rational number. If p and q are integers, then –(p/q) = (–p)/q = p/(–q). Interpret quotients of rational numbers by describing real world contexts. 7.NS.2.c Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide rational numbers 7.NS.2.d Convert a rational number to a decimal using long division; know that the decimal form of a rational number terminates in 0s or eventually repeats. 7.NS.3 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. Investigation 4- Properties of Operations Problems 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 Math Reflections 7.EE.3 Solve multi-step real-life and mathematical problems posed with positive and negative rational numbers in any form (whole numbers, fractions, and decimals), using tools strategically. Apply properties of operations to calculate with numbers in any form; convert between forms as appropriate; and assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies. 7.NS.1 Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram. Objective: 1.02, 1.03 CMS Curriculum Guides 2011-2012 7th Grade Math Looking Back & Looking Ahead 7.NS.1.d Assign specific ACE problems Apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract rational numbers. 7.NS.2 Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. 7.NS.2.c Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide rational numbers 7.NS.3 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. 7.EE.3 Solve multi-step real-life and mathematical problems posed with positive and negative rational numbers in any form (whole numbers, fractions, and decimals), using tools strategically. Apply properties of operations to calculate with numbers in any form; convert between forms as appropriate; and assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies. Mathematical Practices Standards for Common Core 1-Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them 2-Reason abstractly and quantitatively 3-Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others 4-Model with mathematics 5-Use appropriate tools strategically 6-Attend to precision 7-Look for and make use of structure 8-Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning Prior Knowledge: Developing understanding of whole numbers and rational numbers; Using models to develop understanding of mathematical concepts; Understanding and applying arithmetic operations with rational numbers; Using a coordinate grid with positive coordinates; Using a number line to develop equivalence and operations of fractions and decimals; Developing understanding of the Commutative Property using whole numbers and rational numbers; Using the order of operations to solve problems in a context CMS Curriculum Guides 2011-2012 7th Grade Math Essential Terms Developed in This Unit Useful Terms Referenced in This Unit Terms Developed in Previous Unit Commutative Property Distributive Property Integers Negative Numbers Opposites Order of Operations Positive Numbers Rational Numbers Absolute Value Additive Inverse Associative Property Expanding Factoring Quadrant I, II, III, IV Algorithm Area* Coordinate Grid Decimals* Expressions Fact Family* Fractions* Income/Profit Mathematical Sentence* Number Line* Operations* Ordered Pair Variable * Denotes in previous year Resources Lab-Sheet Additional Practice/Skills Worksheets CMP2 Website –online & technology resources Formal Assessment Check-Ups Partner Quiz Unit Test Assessment Options Notebook check Multiple-Choice Question Bank ExamView CD-ROM Parent Guide-Unit Letters Spanish Assessment Resources PHSchool.com TeacherExpress CD-ROM LessonLab Online Courses Unit Technology Tips