* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit G Rev #2 - Mr. Lesiuk
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
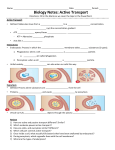
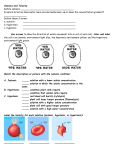
Name : ________________ Date: ________ The Cell Membrane : Review #2 Cell Membrane Structure and Function (Learning Outcomes G3-G8) L.O. G – 3 Facilitated Transport vs. Active Transport ___ 1. Both Facilitated Transport and Simple Diffusion are methods of passive transport, How do they differ? ___ 2. Explain the similarities and differences between Facilitated Transport and Active Carrier Transport. ___ 3. How many different types of molecules can be typically transported by a particular carrier molecule? ___ 4. Substances in facilitated transport can only move from an area of ______________ concentration to an area of ________________concentration. ___ 5. In Active Carrier Transport, how do the molecules move with respect to the concentration gradient? ___ 6. What is the required energy molecule for any method of Active Transport? ___ 7. What cell organelle do you think would be present in large numbers in cells that frequently perform lots of Active Transport? ___8. Which types of bodily cells contain high numbers of Na+/K+ Pumps? ___ 9. How is the same carrier able to carry two different ions/atoms? L.O. G – 4 Factors Affecting Diffusion ___ 1. How does the size of the molecules, affect the rate at which the molecule can move from one location to another? ___ 2. Explain how temperature affects the rate of diffusion? ___ 3. Explain why cells lining the intestine would fold their cell membrane up an down as seen in the picture below. Think ! L.O. G – 5 Endocytosis and Exocytosis ____1. Both endocytosis and exocytosis require ATP to re-arrange the cell membrane into vesicles. So are they considered methods of Active Transport or Passive Transport. OVER ___ 2. There are two different types of endocytosis; name them and explainwhat makes them different from one another. ___ 3. When an amoeba ingests a paramecium what type of endocytosis would that be? ___ 4. After a white blood cell uses Endocytosis (phagocytosis) to engulf a bacterial cell, what type of cell organelle would fuse with the incoming vesicle to release hydrolytic enzymes into the vesicle to destroy the Bacterium? ___ 5. Define exocytosis. L.O. G – 6 Hypertonic, Hypotonic, and Isotonic ____1. If a core of potato is placed into distilled water, the potato is considered (Isotonic/Hypertonic/Hypotonic) to the water? - Choose the correct term ___ 2. What term is used to describe what happens to a Plant (potato) cell when placed into Test Tube #11 (pure distilled water) ___ 3. What term is use to describe what happens to an animal cell when it is placed in a hypertonic solution? ___ 4. What term is used to describe what happens to an animal cell when it is placed in a hypotonic solution? G – 7 Data And Graphs - Refer to Potato Osmosis Lab to learn Learning Outcomes L.O. G – 8 Surface Area vs. Volume (read p. 48 from Ch.3) ___ 1. Each time the length of the sides of a cube is doubled, how much is the surface area of the cube increased? – See notes ___ 2. Each time the length of the sides of a cube is doubled, how much is the volume of the cube increased? – See notes ___ 3. What is happening to the "surface area : volume ratio" as a cell increase in size? ___ 4. Why is a high Surface Area : Volume - Ratio a good thing for a cell? Practice Quiz :