* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CST Review Sheet 2 DNA and RNA 1. The unit to the right which
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
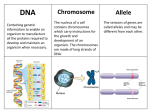
CST Review Sheet 2 DNA and RNA 1. The unit to the right which connects together to other similar units to make DNA is called a __________________ 2. Label its three parts to the right. 3. What types of bonds hold together DNA? a. hydrogen b. molecular c. covalent d. hydrogen and covalent 4. DNA replication results in two DNA molecules a. each with two new strands c. one with two new strands and the other with two original strands b. each with two original strands d. each with one new strand and one original strand 5. Write the complimentary DNA strand ACCATAGATACT 6. Which information was most important to the development of genetic engineering techniques? A the observation of nondominant alleles B the discovery of lethal genes C the formulation of Punnett squares D the structure of a DNA molecule Protein Synthesis 1. Fill in the blanks with the correct organelles: Protein synthesis starts in the ________________, then moves into the ____________________ and ends on a ______________________. 2. Label the picture ______________________ _ ______________________ _ 3. a. Transcribe this DNA: GGACTAGAATCCATC b. How many codons are there? ______ 4. Translate this mRNA: AUGCAGAUCACCGGAUAGUAA 5. Make the protein this DNA codes for: TACCCATGATAGGACCAGATT 6. 5' ATCAGCGCTGGC 3' The above sequence of DNA is part of a gene. How many amino acids are coded for by this segment? a. 4 b. 8 c. 12 d. 20 Meiosis 1. A chromosome is made of _________________ wrapped tightly around __________________________. 2. How many chromosomes does a human gamete contain? ______ How many chromosomes does a human body cell contain? ______ 3. What two chromosomes do you need to be female? ________ What two chromosomes do you need to be male? ________ 4. What are homologous chromosomes? 5. The diagram to the right shows a cellular process that occurs in organisms. This process is known as A meiosis. B mitosis. C endocytosis. D phagocytosis. 6. Which of the following statements correctly describes meiosis? A Cells divide only once during meiosis. B Meiosis does not occur in reproductive cells. C The cells produced at the end of meiosis are genetically identical to the parent cell. D The cells produced at the end of meiosis contain half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. 7. Which of the following best describes meiosis? A It is carried out in all tissues that require cell replacement. B It occurs only in cells in the reproductive structures of the organism. C It happens in all tissues except the brain and spinal cord. D It is the first stage of mitosis. 8. Based only on the sex chromosomes in typical human egg and sperm cells at fertilization, the probability of producing a female is A 25%. B 50% C 75% D 90%. Genetics 1. What does heterozygous mean? What does homozygous mean? 2. What is the law of segregation? 3. What is the law of independent assortment? 4. In flowers, blue flower petals are dominant to red flower petals. What are the possible phenotypes for the following flowers with these genotypes? BB _______________________Bb _______________________bb _______________________ 5. What is the phenotype of a heterozygous person if T is tall and t is short? 6. In humans, big ears are dominant to small ears. B=________________ What are the genotypes for a person with big ears? _____,_____ What is the genotype for a person with small ears? ______ b=________________ 7. In dogs, short hair (H) is dominant to long hair (h). If a heterozygous short hair dog is crossed with a long hair dog, what percentage of the offspring will have long hair. 8. In certain breeds of dogs, deafness is due to a recessive allele (d) of a particular gene, and normal hearing is due to its dominant allele (D). What percentage of the offspring of a normal heterozygous (Dd) dog and a deaf dog (dd) would be expected to have normal hearing? A 0% B 25% C 50% D 100% 9. In fruit flies, the gene for red eyes (R) is dominant and the gene for sepia eyes (r) is recessive. What are the possible combinations of genes in the offspring of two red-eyed heterozygous flies (Rr)? A RR only B rr only C Rr and rr only D RR, Rr, and rr only 10. If a human baby boy inherits a recessive allele from his mother, in which circumstance would he most likely show the trait coded for by the recessive allele? A The baby inherits the dominant allele from his father. B The allele is on an autosomal chromosome and the baby is a twin. C The allele is on the X chromosome. D The allele is on the Y chromosome. 11. A healthy individual is a carrier of a lethal allele but is unaffected by it. What is the probable genotype of this individual? A two dominant normal alleles C one recessive lethal allele and one dominant normal allele B one recessive lethal allele and one dominant lethal allele D one dominant lethal allele and one recessive normal allele