* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Transport Matching w Pictures
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
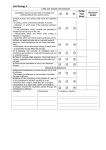
Cell Transport Matching Name ______________ Provide an example from the book. concentration gradient Provide an example from the book. equilibrium Provide an example from the book. passive transport Provide an example from the book. Types of Passive Transport- substances move down the concentration gradient Diffusion How is this different from diffusion? osmosis Why can’t ions slide through the membrane like water? ion channel carrier proteins Why can’t sugars and amino acids slide through the membrane like water? (hint: think about their size) What are some examples of molecules that travel this way? facilitated diffusion Types of Active Transport- substances move against the concentration gradient active transport Are substances still randomly spreading out or are they being purposely sorted? a) Would diffusion move these ions in the same directions the pump does? sodiumpotassium pump b) Why does this pump require so much energy? (hint: think of fish swimming upstream) What types of substances are transported this way? endocytosis Why? What types of substances are transported this way? exocytosis Why? Cell Transport Matching Cut out the definitions and pictures and use pages 73-83 in your Biology book to match the correct definition and picture with each term on the next page. The pictures, definitions or summaries are not identical to the wording the book provides, you will need to think about each description to determine which word it fits with. Answer the questions on the right of the page about each of the terms and transportation methods. A the cell membrane wraps around a substance and forms a bubble or vesicle that carries it into the cell E vesicles filled with materials bump into and fuse with the cell membrane releasing their contents outside of the cell I movement that requires energy from the cell because substances are moved against their concentration gradient B transporters that carry F J substances across the exists when a a tunnel that allows cell membrane that substance is equally ions to diffuse through cannot cross on their spread throughout an the cell membrane own thru normal area. diffusion C pumps sodium out of G random bumping of K the cell and potassium particles causes a net exists when a into the cell, both are movement from a substance is not pushed against their highly concentrated equally spread concentration area to a lowly throughout an area gradients concentrated area D H movement that L water moves through a uses carrier proteins to requires no energy selectively permeable carry larger from the cell because membrane to an area substances through substances move with lower the cell membrane down their concentration of water concentration gradient 1 6 2 7 3 8 high concentration low concentration 4 9 5 10 Name ______________ Cell Transport Matching Cut out the definitions on the next page and use pages 73-83 in your Biology book to match the correct definition with each term. The definitions or summaries are not identical to the wording the book provides, you will need to think about each description to determine which word it fits with. Answer the questions on the right of the page about each of the terms and transportation methods. Provide an example from the book. concentration gradient K= exists when a substance is not equally spread throughout an area. Provide an example from the book. equilibrium passive transport F= exists when a substance is equally spread throughout an area. Provide an example from the book. H= movement that requires no energy from the cell because substances move down their concentration gradient G= Diffusion osmosis ion channel random bumping of particles causes a net movement from a highly concentrated area to a lowly concentrated area Provide an example from the book. How is this different from diffusion? L= water moves through a selectively permeable membrane to an area with lower concentration of water J= a tunnel that allows ions to diffuse through the cell membrane Why can’t ions slide through the membrane like water? carrier proteins facilitated diffusion active transport sodiumpotassium pump endocytosis exocytosis B = transporters that carry substances Why can’t sugars and amino acids slide through the membrane like water? (hint: think about their size) across the cell membrane that cannot cross on their own thru normal diffusion D= uses carrier proteins to carry larger substances through the cell membrane I= movement that requires energy from the cell because substances are moved against their concentration gradient C = pumps sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell, both are pushed against their concentration gradients A = the cell membrane wraps around a Are substances still randomly spreading out or are they being purposely sorted? c) Would diffusion move the sodium and potassium ions in the same directions the pump does? d) Why do you think this pump requires so much energy? (hint: think of fish swimming upstream) What types of substances are transported this way? Why? substance and forms a bubble or vesicle that carries it into the cell E = vesicles filled with materials bump into and fuse with the cell membrane releasing their contents outside of the cell What types of substances are transported this way? Why?