* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Avoiding Dangerous Anthropogenic Climate Change
Climate change in the Arctic wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Saskatchewan wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
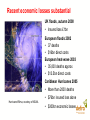
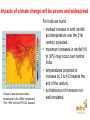
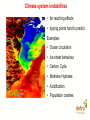
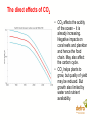
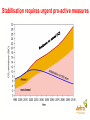
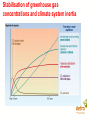
Overview of Climate Change Impacts David A Warrilow Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs Climate change and sustainable development New Delhi, 7-8 April 2006 Widespread impacts on the natural world already evident • Widespread melting of glaciers globally • Increased river flow into the Arctic • 8% loss of Arctic sea-ice in last decade • Melting permafrost • Rising sea levels 1-2 cm per decade • Earlier spring activity in plants and animals Recent economic losses substantial UK floods, autumn 2000 • Insured loss £1bn European floods 2002 • 37 deaths • $16bn direct costs European heat-wave 2003 • 35,000 deaths approx • $13.5bn direct costs Caribbean Hurricanes 2005 • More than 2000 deaths • $76bn insured loss alone Hurricane Wilma, courtesy of NOAA • $300bn economic losses Extreme events are increasing in size/frequency • European hot summer of 2003 • over 35,000 deaths • risk of such a summer 2-4 times greater with greenhouse gases. Hadley Centre Temperatures are predicted to continue to rise (1.4 to 5.8C by 2100, IPCC AR3) Observed and predicted European summer temperatures. 2003 type heatwaves will be common by 2040 Impacts of climate change will be severe and widespread Change in annual mean surface temperature by the 2080s compared to 1961-1990, from the IPCC A2 scenario. For India we found: • marked increase in both rainfall and temperature over the 21st century projected. • maximum increases in rainfall (10 to 30%) may occur over central India. • temperatures projected to increase by 3 to 4C towards the end of the century. • but behaviour of monsoon not well simulated. Climate Change a will affect all sectors and countries Agriculture vulnerable to temperature increases and rainfall changes • A 2 C rise in temperature decreases Indian wheat yield - Up to 6% in sub tropical areas - 17-18% in tropical areas • For rice a 2 C rise projected to reduce yields by 10-16% and a 4°C rise led to a 21-30% reduction. • Sensitivity to monsoon - 19% rainfall deficit in 2002 reduced Indian GDP by 3% Human Health also vulnerable • More incidences of malaria in areas that are already malaria-prone, and introduced into new areas. • Sensitive to the arrival of the monsoon. Transmission Window of Malaria in different states of India a) base case, b) with climate change Sea-Level rise and storm surges Indian study showed: • Mean sea level rise for Mumbai slightly less than 1mm/year and a possible decrease at Chennai, but no info on land movements. • Storm surges show increase in number of high surges under climate change. • Cyclone frequency and strength increases in the Bay of Bengal, particularly in the post-monsoon period. Frequency Distribution of Maximum surges associated with each cyclone (2050) Climate system instabilities • far reaching effects • tipping points hard to predict Examples: • Ocean circulation • Ice sheet behaviour • Carbon Cycle • Methane Hydrates • Acidification • Population crashes The direct effects of CO2 • CO2 affects the acidity of the ocean – it is already increasing. Negative impacts on coral reefs and plankton and hence the food chain. May also affect the carbon cycle. • CO2 helps plants to grow, but quality of yield may be reduced. But growth also limited by water and nutrient availability. Impacts depend strongly on socioeconomic development pathway. • Project developed four socio-economic scenarios in line with national plans for development, and associated projections for population and economic growth Framework for visions of socio-economic change for India s to prepare for ply nity nal Adaptation an essential but limited response • Adaptation recognised as an essential response but not a substitute for mitigation • No one solution • Not an easy option • Easier for new build • It has its limits Avoiding Dangerous Anthropogenic Climate Change - Exeter conference 2005 • For different levels of climate change what are the key impacts? • What would such levels of climate change imply in terms of greenhouse gas stabilisation concentrations and emission pathways required to achieve such levels? • What options are there for achieving stabilisation of greenhouse gases at different stabilisation concentrations in the atmosphere? See www.stabilisation2005.com How much climate change is too much? 1-2 C Above preindustrial Major impacts on ecosystems and species; wide ranging impacts on society, including developing county agriculture. 1.5 – 3 C Greenland ice-cap starts to melt irreversibly (7 m) 2-3C Major loss of coral reef ecosystem; considerable species loss; large impacts on agriculture; water resources; health; economies. General increase in droughts and extreme rainfalls as temperature increases. Up to 88cm sea level rise in next 100 years. 2-3C Terrestrial carbon sink becomes a source. 1-4 C North Atlantic circulation collapses 2 - 4.5 C West Antarctic ice sheet collapses (5 m) Stabilisation requires urgent pro-active measures Stabilisation of greenhouse gas concentrations and climate system inertia Conclusions • • • • • • • • • Climate change impacts are already being seen Climate change will affect all sectors and all countries Above 1-3 C rise many impacts could become critical. System changes could generate major impacts but hard to predict. Sea level rise a significant long term issue Ocean acidification a serious direct impact of CO2 Adaptation essential – but has its limits Need to limit climate change – 2 C? Without stabilisation of greenhouse gases at a level which avoids dangerous anthropogenic climate change sustainable development will not be possible