* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 教案编写基本格式与要求
Survey
Document related concepts
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
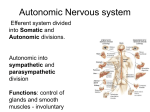
Teaching Plan of International Education School of KMU Teaching Department: Department of Pharmacology Class time:September , 2016 subject Pharmacology grade 2014 major Clinical Name of Yunyu profession Associated Lecture or Lecture Class 80minute teacher al title professor experiment hour topic( chapter) Choline receptor agonists teaching material TEXTBOOK OF PHARMACOLOGY (book title,chief Original editors editor, publishing Bertram G. Katzung house , publishing Joel G. Hardman Lee E. Limbird time,edition) Alfred Goodman Gilman Science Press Teaching aims & requirements: 1. Correctly identify the different classes of drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system(autonomic drugs) 2. Inactivation of neurotransmitters effects 3. The nomination, type and effect of perepheral neuvous system receptor 4. Physiological functions of pereferal nervous system Key teaching points & difficult points: Key teaching points: Physiological functions of pereferal nervous system Difficult points: None Teaching methods: Multimedia, traditional , question Design of PPT and blackboard-writing: 1. Organization of Nervous system (5min) 2. Anatomy of the ANS efferent neurons(5min) 3. the differences between sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of ANS(10min) 4. the ANS function(10min) 5. the difference between the autonomic nerve system and somatic nerve system(5min) 6. Chemical signaling between cells(2min) 7. Types of neurotransmitters(3min) 8. Signal transduction in the effector cell(10min) 9. Neurotransmitters of ENS(10min) 10. Autanomic drugs (10min) There are several drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system which, for a better understanding of specific drugs, are classified into groups. A. Drugs acting on the sympathetic nervous system a) Sympathomimetics or adrenergic drugs: are drugs that mimic the effects of sympathetic nerve stimulation. b) Sympatholytics: are drugs that inhibit the activity of sympathetic nerve or that of sympathomimetics. B. Drugs acting on the parasympathetic nervous system a) Parasympathomimetics or cholinergic drugs: are drugs which mimic acetylcholine or 1 the effects of parasympathetic nerve stimulation. b) Parasympatholytics: are drugs that inhibit parasympathetic nervous system activity or that of cholinergic drugs. Note: The contents of the teaching plan mainly includes the specific teaching content, time arrangement, the use of teaching aids, important professional vocabulary, complement of teaching content, etc. Summary Assignments The nervous system controls all the major functions of the body. It is divided into central and peripheral nervous systems. The peripheral nervous system includes the somatic and autonomic nervous systems which control voluntary and involuntary functions respectively. The ANS controls the vegetative functions of the body. These include functions like circulation, respiration, digestion and the maintenance of body temperature. The ANS is subdivided into two major sub-divisions; this classification is based on both anatomic and physiologic grounds; the two subdivisions are sympathetic (thoracolumbar) and parasympathetic (craniosacral). Autonomic nerves are actually composed of two neuron systems, termed preganglionic and postganglionic, based on anatomical location relative to the ganglia. A preganglionic neuron has its cell body in the spinal cord or brain. The sympathetic nervous system arises from the thoracic and lumbar areas of the spinal cord and the preganglionic fibers for the parasympatheticnervous system arise from the cranial and sacral nerves. The postganglionic neurons send their axons directly to the effector organs (peripheral involuntary visceral organs). Autonomic innervation, irrespective of whether it belongs to the parasympathetic or the sympathetic nervous system, consists of a myelinated preganglionic fiber which forms a synapse withthe cell body of a non-myelinated second neuron termed post-ganglionic fiber. The synapse is defined as a structure formed by the close apposition of a neuron either with another neuron or with effector cells 1. If both sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve are activated ,what will the effectors do? 2. When are both sympathetic and parasympathetic activated ? Preview Anticholinesterase Drug and Cholinesterase Reactivator 2 Implementation Implementation in good condition, the students would like to understand ANS, and and analysis then have the idea about the drugs effects on ANS. Comments of Department Head of Department: Date: 3