* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download gluconeogenesis
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
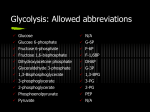
CHO Metabolism In mammals, some tissues depend almost completely on glucose for their metabolic energy The brain alone requires about 120 g of glucose each day—more than half of all the glucose stored as glycogen in muscle and liver. However, the supply of glucose from these stores is not always sufficient; between meals and during longer fasts, or after vigorous exercise, glycogen is depleted. For these times, organisms need a method for synthesizing glucose from noncarbohydrate precursors. This is accomplished by a pathway called….. gluconeogenesis (“formation of new sugar”) The important precursors of glucose in animals are three-carbon compounds such as lactate, pyruvate, and glycerol, as well as certain amino acids In mammals, gluconeogenesis takes place mainly in the liver, and to a lesser extent in renal cortex. Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are not identical pathways running in opposite directions, although they do share several steps In glycolysis, glucose converted into pyruvate; gluconeogenesis, pyruvate converted into glucose is in is seven of the ten enzymatic reactions of gluconeogenesis are the reverse of glycolytic reactions. However, three reactions of glycolysis are essentially irreversible in vivo and cannot be used in gluconeogenesis: • the conversion of glucose to glucose 6-phosphate by hexokinase, •the phosphorylation of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6bisphosphate by phosphofructokinase-1, •the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate by pyruvate kinase. In gluconeogenesis, the three irreversible steps are bypassed by a separate set of enzymes Conversion of Pyruvate to Phosphoenolpyruvate • The carboxylation of pyruvate to form oxaloacetate at the expense of a molecule of ATP. • Then, oxaloacetate is decarboxylated and phosphorylated to yield phosphoenolpyruvate, at the expense of the highphosphoryl-transfer potential of GTP. This reaction cannot occur by reversal of the pyruvate kinase reaction of glycolysis The first reaction is catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase and the second by phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. The sum of these reactions is: Oxaloacetate Is Shuttled into the Cytosol and Converted into Phosphoenolpyruvate Pyruvate carboxylase is a mitochondrial enzyme, whereas the other enzymes of gluconeogenesis are cytoplasmic. Oxaloacetate, the product of the pyruvate carboxylase reaction, is reduced to malate inside the mitochondrion for transport to the cytosol. cont…. The reduction is accomplished by an NADH-linked malate dehydrogenase. When malate has been transported across the mitochondrial membrane, it is reoxidized to oxaloacetate by an NAD+-linked malate dehydrogenase in the cytosol. Finally, oxaloacetate is simultaneously decarboxylated and phosphorylated by phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in the cytosol. The CO2 that was added to pyruvate by pyruvate carboxylase comes off in this step. The Conversion of Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate into Fructose 6-phosphate The Generation of Free Glucose Is an Important Control Point The fructose 6-phosphate generated by fructose 1,6 bisphosphatase is readily converted into glucose 6-phosphate. In most tissues, gluconeogenesis ends here. Free glucose is not generated; rather, the glucose 6-phosphate is processed (notably to form glycogen). Generation of glucose does not take place in the cytosol, rather, glucose 6-phosphate is transported into the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum, where it is hydrolyzed to glucose by glucose 6phosphatase.