* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology - The Roblesite
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
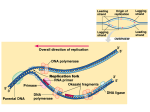
Biology Señor Robles More Than You Ever Wanted to Know About Protein Synthesis Study Guide 1. The “point” of protein synthesis, as stated in the ___________ _____________is that information flows in a single direction from DNA to RNA to proteins. 2. This statement was articulated by a Nobel Prize-winning scientist named __________ __________. 3. You know him because he and _____________ ________________elucidated the double helix structure of the DNA molecule back in 1953 (even before Señor Robles was born.) 4. What famous celebrity did he meet in the late ‘80s (before YOU were born?) __________________ 5. Transcription looks like DNA replication because it involves unwinding the DNA double helix and creating what looks like a replication bubble. What enzyme catalyzes this action and the formation of the RNA? ___________ ________________________________. 6. One strand of the DNA will now act as a _____________________________. 7. RNA polymerase will now begin to attach ______ _______________onto this open strand. 8. Each nucleotide is composed of a ______________, a _________________, and a _____________base. 9. Don’t forget: the RNA uses the nitrogen base ___________instead of thymine. 10. The assembled nucleotides make a new molecule called ____________, or messenger ribonucleic acid for long. 11. mRNA, like DNA, is a type of macromolecule called a ___________________ ___________. 12. The RNA polymerase “knew” where to start because of the presence of a molecule called the ________________, which lets the enzyme recognize the start of a gene. 13. When mRNA is being assembled, it grows in the ________to __________direction. 14. These numbers are based on the position of ____________atoms in the ________________molecules, which, along with phosphate groups, comprise the backbone of the mRNA molecule. 15. This whole process is called _________________________and takes place in the nucleus. 16. Remember, transcription doesn’t occur along the entire 3 billion bp stretch of the DNA molecule, but only along specific _________________. 17. It’s about to be sent out of the nucleus and into the _________________ for the next step, but first must go through some processing to remove unnecessary sections of DNA. 18. Portions of the mRNA, called ___________________, are removed, (and remain IN the nucleus.) 19. The other portions, called ________________, are spliced together and EXit the nucleus. 20. Additionally a _____ _______ and a tail are added to opposite ends of the mRNA piece. (Know what these two end sections do.) 21. Now the mRNA fragment leaves the nucleus via a nuclear ____________. 22. It enters an organelle called the __________________, particularly in the ____________subunit. 23. The mRNA is made of triplets called ________________. 24. These code for particular amino acids. For example, AAA codes for _______________, an amino acid mentioned in the movie __________________ ____________. 25. One important codon is the “start” codon. Its three letters are _______________ (think of the sound Charlie Brown makes when he’s upset.) 26. As the mRNA enters the ribosome, 5’ end first, it attracts the attention of another molecule: ________. 27. The tRNA carries its own triplet, the ___________________. At its other end is attached an _____________ __________. 28. As the tRNA enters the large subunit of the ribosome, its _____________connect to the ___________ of the mRNA already in the small subunit. 29. Step by step tRNA molecules come and go, each time bringing another amino acid. The tRNA molecules leave one step at a time, but the amino acids remain, connected to each other by a _______________ bond. In fact, they eventually make a _______________________. 30. This process, in which the genetic information held by the mRNA is TRANSLATED into the molecular language of protein, is called: ___________________________.