* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name Date Ch 7 – Cellular Respiration and Fermentation (Biology
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
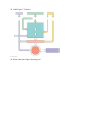
Name _______________________________ Date __________________ Ch 7 – Cellular Respiration and Fermentation (Biology in Focus) – to be used in conjunction with Mr. Anderson video on Cellular Respiration Concept 7.1 Catabolic Pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels 1. Define the following terms: a. fermentation b. aerobic respiration 2. What types of organic compounds can be consumed as fuel for cell respiration? 3. Explain what happens in a redox reaction. 4. Define: a. reducing agent b. oxidizing agent 5. One of the most potent oxidizing agents is __________________. 6. Look at the equation for cellular respiration on p. 137. Which substance is being oxidized? Which substance is being reduced? 7. What is the purpose of NAD+? (remember this – important) 8. What is the purpose of an electron transport chain? How does it work? 9. What is oxidative phosphorylation? How is it used in cellular respiration? Concept 7.2 Glycolysis harvests chemical energy by oxidizing glucose to pyruvate 10. Label the summary of glycolysis below. (p. 141) – You should memorize the products and reactants in this. Figure 7.8 **Also note in Figure 7.9 how each step requires a different enzyme Concept 7.3 After pyruvate is oxidized, the citric acid cycle completes the energy-yielding oxidation of organic molecules. 11. Summarize the reactants and the products of the Citric Acid Cycle. 12. What does Acetyl-CoA combine with to start the cycle? 13. Why is the citric acid cycle considered a cycle? Concept 7.4 During oxidative phosphorylation, chemiosmosis couples electron transport to ATP synthesis 14. How many ATP does glycolysis and the citric acid cycle produce? 15. Explain how the electron transport chain works. 16. Define chemiosmosis. 17. Explain how ATP is synthesized using the following diagram. (p. 145) 18. How many ATP can one NADH create? 19. How many ATP can one FADH2 create? Why does it create less than NADH? 20. How much of the original potential energy of glucose has actually been transferred to ATP? 21. What happens to the rest of the potential energy that has not been transferred to ATP? 22. How have some animals adapted to the reduction in efficiency of cellular respiration? Concept 7.5 Fermentation and anaerobic respiration enable cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen. 23. What conditions force the cell to go into the fermentation process? At what point in the three processes of cellular respiration does this happen? 24. What molecule accepts the electrons from NADH in anaerobic fermentation? 25. Create a chart showing the difference between alcoholic and lactic acid fermentation in terms of the pathways, products and what types of cells these occur in. 26. What is the evolutionary significance of glycolysis? Concept 7.6 Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle connect to many other metabolic pathways 27. What is beta-oxidation? What is its function? 28. Label Figure 7.18 below. 29. What is the above figure showing you?