* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cells_can_you
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
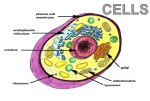
Can you… Describe and draw the structure of an epithelial cell from the small intestine, and a palisade mesophyll cell from a plant, as seen with a light microscope. Recall that eukaryotic cells have organelles, including the cell wall, the cell membrane, the nucleus, the mitochondrion, the chloroplast, rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum, the golgi body and ribsosomes. Describe the structure of each of these organelles and relate this to their function in the cell. Recognise the organelles in electron micrographs. List the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Describe the ultrastructure of a typical bacterial cell, showing its cell wall, cell membrane, genetic material, ribosomes, plasmic and capsule. Describe the use of electron microscopy and differential centrifugation techniques as a means of investigating the structure and function of cells. Explain that the cells of multicellular organisms can differentiate and become adapted for specific functions. Recall that tissues are aggregations of similar cells, and organs are structures that perform specific physiological functions. Describe and explain the adaptations of epithelial cells from the small intestine and palisade mesophyll cells, and use examples from the human digestive system to illustrate the features of tissues and organs.