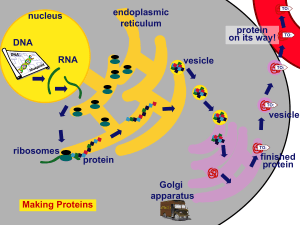
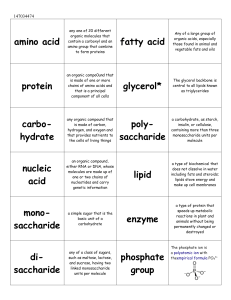
Gene Control of Cellular Activities
... The cut up pieces are then separated in a gel using the negative charge of the DNA to move it across an agrose gel. The smaller pieces will move faster then the larger pieces. ...
... The cut up pieces are then separated in a gel using the negative charge of the DNA to move it across an agrose gel. The smaller pieces will move faster then the larger pieces. ...
DNA/RNA Worksheet TACGGCACCGTTAGGATT
... Please answer the following questions in the space provided. ...
... Please answer the following questions in the space provided. ...
Protein Synthesis
... Other proteins transcribe a strand of DNA and make a messenger RNA (mRNA) The mRNA is single stranded. The mRNA uses U instead of T. (A,U,G,C) The DNA zips back together. ...
... Other proteins transcribe a strand of DNA and make a messenger RNA (mRNA) The mRNA is single stranded. The mRNA uses U instead of T. (A,U,G,C) The DNA zips back together. ...
DNA to Proteins
... located. • This mirror copy of DNA is called messenger RNA or mRNA • This is called transcription ...
... located. • This mirror copy of DNA is called messenger RNA or mRNA • This is called transcription ...
Protein Synthesis
... amino acid proline. A long string of amino acids forms a protein. Each gene is usually a set of instructions for making a protein. Proteins are responsible for most of the differences in organisms that we see. EX: height, curly or straight hair, etc. ...
... amino acid proline. A long string of amino acids forms a protein. Each gene is usually a set of instructions for making a protein. Proteins are responsible for most of the differences in organisms that we see. EX: height, curly or straight hair, etc. ...
END OF SEMESTER EXAM PREPARATION AND REVISION
... • Lagging strand: Okazaki fragments to form daughter strand (discontinuous) • RNA replication requires primers ...
... • Lagging strand: Okazaki fragments to form daughter strand (discontinuous) • RNA replication requires primers ...
Chapter 14 – RNA molecules and RNA processing
... – Any exons not included will yield a different polypeptide ...
... – Any exons not included will yield a different polypeptide ...
outline File - selu moodle
... Wobble effect at third position Near universal 15.3 Prokaryotic Transcription Begins at a promoter transcribes the transcription unit ends at the terminator Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that are complementary to the template strand Most com ...
... Wobble effect at third position Near universal 15.3 Prokaryotic Transcription Begins at a promoter transcribes the transcription unit ends at the terminator Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that are complementary to the template strand Most com ...
Ecology
... a part, substance, or element that lies beneath and supports another part, substance or element; the reactant in reactions catalyzed by enzymes ...
... a part, substance, or element that lies beneath and supports another part, substance or element; the reactant in reactions catalyzed by enzymes ...
Transcribe and Translate a Gene
... BI4. a. Students know the general pathway by which ribosomes synthesize proteins, using tRNAs to translate genetic information in mRNA. BI5. a. Students know the general structures and functions of DNA, RNA, and protein. .Objectives: SWBAT… Explain the genetic factors that influence the way we l ...
... BI4. a. Students know the general pathway by which ribosomes synthesize proteins, using tRNAs to translate genetic information in mRNA. BI5. a. Students know the general structures and functions of DNA, RNA, and protein. .Objectives: SWBAT… Explain the genetic factors that influence the way we l ...
Section 1.3 Name:
... second difference is that RNA has the nitrogen base _______________ (U) instead of _______________ (T). Uracil always pairs with _______________ (A), while cytosine (C) will still always pair with ______________ (g). • There are three types of RNA that work together to produce proteins: o RNA that i ...
... second difference is that RNA has the nitrogen base _______________ (U) instead of _______________ (T). Uracil always pairs with _______________ (A), while cytosine (C) will still always pair with ______________ (g). • There are three types of RNA that work together to produce proteins: o RNA that i ...
RNA
... RNA stands for ____________________________________ RNA takes the DNA’s instructions out of the __________________ and into the _______________________ of the cell where there is room for ____________________________________(protein synthesis) ...
... RNA stands for ____________________________________ RNA takes the DNA’s instructions out of the __________________ and into the _______________________ of the cell where there is room for ____________________________________(protein synthesis) ...
Chapter 11 Vocabulary and Objectives
... explain that organisms have systems to fight diseases Lesson 1: How are Molecules of Life Involved in Heredity? I. Objectives: Describe the structure of nucleotides; Explain the structure of a DNA molecule; Explain complementary pairing. II. Vocabulary: sugarphosphate backbone cytosine ( ...
... explain that organisms have systems to fight diseases Lesson 1: How are Molecules of Life Involved in Heredity? I. Objectives: Describe the structure of nucleotides; Explain the structure of a DNA molecule; Explain complementary pairing. II. Vocabulary: sugarphosphate backbone cytosine ( ...
Study Guide
... How are the functions of mRNA and tRNA different? Describe the process of transcription and translation. What is a codon? What is an anticodon? How are they related? Why is RNA necessary for expressing the code in DNA? How does an organism’s DNA code for its traits? Summarize the process ...
... How are the functions of mRNA and tRNA different? Describe the process of transcription and translation. What is a codon? What is an anticodon? How are they related? Why is RNA necessary for expressing the code in DNA? How does an organism’s DNA code for its traits? Summarize the process ...
RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS (ch. 17) TERMS TO KNOW: RNA polymerase - the enzyme responsible for RNA transcription. Moves along gene and bonds appropriate RNA nucleotide to complimentary DNA nucleotide. Promoter - binding site on gene that RNA polymerase attaches to at the start of transcription. Codon ...
... RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS (ch. 17) TERMS TO KNOW: RNA polymerase - the enzyme responsible for RNA transcription. Moves along gene and bonds appropriate RNA nucleotide to complimentary DNA nucleotide. Promoter - binding site on gene that RNA polymerase attaches to at the start of transcription. Codon ...
Eukaryotic Gene Expression ppt
... -May be turned on in related species but not in us Exon- genes that are expressed and code for polypeptides ...
... -May be turned on in related species but not in us Exon- genes that are expressed and code for polypeptides ...
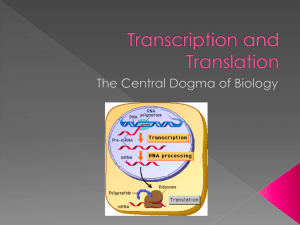
Transcription and Translation
... Usually double stranded Stores the code (like the master blueprint) ...
... Usually double stranded Stores the code (like the master blueprint) ...
Previously in Bio308
... How does RNA polymerase work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? How does a ribosome work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? If the DNA in every cell in your body is the ...
... How does RNA polymerase work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? How does a ribosome work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? If the DNA in every cell in your body is the ...
Study Guide Foldable .Answer Key
... information for the inheritance of traits. A gene has the information for making a specific protein. 5. Chromosomes where genes are located ...
... information for the inheritance of traits. A gene has the information for making a specific protein. 5. Chromosomes where genes are located ...
Protein Synthesis
... sure it matches the RNA pattern on the ribosome. 3. If it matches correctly then Transfer RNA goes and picks up its amino acid in the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA occurs in groups of threes because three bases code one amino acid. 4. Transfer RNA takes the amino acid to the ribosome and Transfer RNA lock ...
... sure it matches the RNA pattern on the ribosome. 3. If it matches correctly then Transfer RNA goes and picks up its amino acid in the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA occurs in groups of threes because three bases code one amino acid. 4. Transfer RNA takes the amino acid to the ribosome and Transfer RNA lock ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.