Slide 1
... • Extract selection information from conservation of secondary structure of alignments of homologous RNA sequences from different species, for different RNA families. ...
... • Extract selection information from conservation of secondary structure of alignments of homologous RNA sequences from different species, for different RNA families. ...
Science 103: Outline 17
... Gene (DNA) (b) Functions (i) (ii) (c) Location (d) Process A single-stranded RNA copy of the DNA is made by RNA polymerase: (i) RNA pol binds to and moves down the DNA, separating the strands. (ii) As it goes, it pairs complementary nucleotides with ONE strand, the template strand (*NOT coding str ...
... Gene (DNA) (b) Functions (i) (ii) (c) Location (d) Process A single-stranded RNA copy of the DNA is made by RNA polymerase: (i) RNA pol binds to and moves down the DNA, separating the strands. (ii) As it goes, it pairs complementary nucleotides with ONE strand, the template strand (*NOT coding str ...
BIO_Protein_Synthesis_Outline - Cole Camp R-1
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
Protein Synthesis - Manhasset Public Schools
... Protein Synthesis Involves two processes: 1. Transcription: the copying of the genetic message (DNA) into a molecule of mRNA 2. Translation: mRNA is used to assemble an amino acid sequence into a polypeptide ...
... Protein Synthesis Involves two processes: 1. Transcription: the copying of the genetic message (DNA) into a molecule of mRNA 2. Translation: mRNA is used to assemble an amino acid sequence into a polypeptide ...
Protein Synthesis - Doral Academy High School
... RNA contains the base uracil (U) DNA has thymine (T) ...
... RNA contains the base uracil (U) DNA has thymine (T) ...
Topic 3 The Chemistry of Life - wfs
... 4. The genetic code is actually composed of triplets of bases called codons. The codons are present on the RNA formed during translation. Therefore, codons do not contain thymine. 5. The RNA formed during transcription is called messenger or mRNA. This mRNA carries the genetic code out of the nucleu ...
... 4. The genetic code is actually composed of triplets of bases called codons. The codons are present on the RNA formed during translation. Therefore, codons do not contain thymine. 5. The RNA formed during transcription is called messenger or mRNA. This mRNA carries the genetic code out of the nucleu ...
Document
... The storage of genetic information in DNA, the use of an RNA intermediate that is read in three letter words, and the mechanism of protein synthesis are essentially the same in all ...
... The storage of genetic information in DNA, the use of an RNA intermediate that is read in three letter words, and the mechanism of protein synthesis are essentially the same in all ...
Transcription
... RNA that is wrapped with proteins to form ribosomes. Purpose Synthesis of primary protein structure ...
... RNA that is wrapped with proteins to form ribosomes. Purpose Synthesis of primary protein structure ...
File
... Because only certain sections of DNA code for a protein and what were those sections called? ...
... Because only certain sections of DNA code for a protein and what were those sections called? ...
replication (nucleus) transcription (nucleus) translation (cytoplasm
... A large transcription complex, including RNA polymerase and other proteins, assembles at the start of a gene and begins to unwind the DNA. Using one strand of the DNA as a template, RNA polymerase strings together a complementary strand of RNA. The RNA strand detaches from the DNA as it is transcri ...
... A large transcription complex, including RNA polymerase and other proteins, assembles at the start of a gene and begins to unwind the DNA. Using one strand of the DNA as a template, RNA polymerase strings together a complementary strand of RNA. The RNA strand detaches from the DNA as it is transcri ...
Chapter 8.4, 8.5, 8.6, 8.7 Study Guide Key terms: Ribonucleic acid
... 1. Why do cells regulate gene expression? 2. What happens to the information on a DNA molecule during transcription? 3. What are repressor proteins and where do they bind? 4. mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm (with or without) a complete set of both introns and exons. (please circle t ...
... 1. Why do cells regulate gene expression? 2. What happens to the information on a DNA molecule during transcription? 3. What are repressor proteins and where do they bind? 4. mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm (with or without) a complete set of both introns and exons. (please circle t ...
Protein Synthesis - Helena High School
... 7. If a section of DNA has the following order of bases, what would the complementary mRNA be? DNA segment: ...
... 7. If a section of DNA has the following order of bases, what would the complementary mRNA be? DNA segment: ...
Improving site-directed RNA editing by screening RNA editing
... naturally recognizes with high affinity a BoxB RNA hairpin in bacteriophages. In order to direct this recombinant editase to a target adenosine, we fused the BoxB RNA hairpin to an antisense guide RNA oligo that is complementary to the target. This complex will allow site-specific mRNA editing. The ...
... naturally recognizes with high affinity a BoxB RNA hairpin in bacteriophages. In order to direct this recombinant editase to a target adenosine, we fused the BoxB RNA hairpin to an antisense guide RNA oligo that is complementary to the target. This complex will allow site-specific mRNA editing. The ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... C. Proteins are made outside the nucleus. Why? That is where they are needed the most! III. Types of RNA 1. mRNA (Messenger RNA) a. A copy of the information found in DNA. b. Carries instructions to the ribosomes on how to make a ...
... C. Proteins are made outside the nucleus. Why? That is where they are needed the most! III. Types of RNA 1. mRNA (Messenger RNA) a. A copy of the information found in DNA. b. Carries instructions to the ribosomes on how to make a ...
DNA
... • Why: DNA can’t leave the nucleus but the message must get to the ribosome • You are now using U’s no T’s. • RNA polymerase – Enzyme that brings in RNA nucleotides to match up with DNA ...
... • Why: DNA can’t leave the nucleus but the message must get to the ribosome • You are now using U’s no T’s. • RNA polymerase – Enzyme that brings in RNA nucleotides to match up with DNA ...
Asymptotics of RNA Shapes: secondary structure
... models and novel algorithms to solve fundamental problems of molecular biology in the post-genome era. A central problem of structural biology concerns the algorithmic prediction of the structure of RNA and protein from only the nucleotide resp. amino acid sequence. In the context of RNA, nucleotide ...
... models and novel algorithms to solve fundamental problems of molecular biology in the post-genome era. A central problem of structural biology concerns the algorithmic prediction of the structure of RNA and protein from only the nucleotide resp. amino acid sequence. In the context of RNA, nucleotide ...
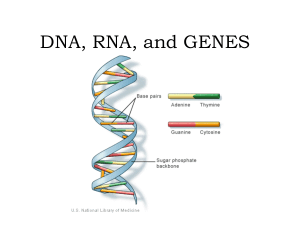
DNA, RNA, and GENES
... made up of nitrogen bases. The bonding of these bases is • Adenine bonds with Thymine • Cytosine bonds with Guanine • A to T and C to G ...
... made up of nitrogen bases. The bonding of these bases is • Adenine bonds with Thymine • Cytosine bonds with Guanine • A to T and C to G ...
Distinguish between these 3 root types: - mvhs
... Secretory Protein— A protein that will be _________ from the cell. The mRNA for this protein contains a signal recognition sequence that is recognized by a signal recognition particle (SRP). The SRP brings the growing polypeptide to the receptor protein in the ___________________. ...
... Secretory Protein— A protein that will be _________ from the cell. The mRNA for this protein contains a signal recognition sequence that is recognized by a signal recognition particle (SRP). The SRP brings the growing polypeptide to the receptor protein in the ___________________. ...
second of Chapter 10: RNA processing
... molecules were larger than predicted, based on protein structure. • In 1977, internal, non-coding sequences were discovered. • These internal, non-coding sequences are called introns. ...
... molecules were larger than predicted, based on protein structure. • In 1977, internal, non-coding sequences were discovered. • These internal, non-coding sequences are called introns. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene
... SO, how does this occur? • Transcription and translation are linguistic terms, so….. • nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and polypeptides (chain of amino acids linked by peptide bond) Have their own language! What is their language? • A, T, G, C in DNA and A, U, G, C in RNA ...
... SO, how does this occur? • Transcription and translation are linguistic terms, so….. • nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and polypeptides (chain of amino acids linked by peptide bond) Have their own language! What is their language? • A, T, G, C in DNA and A, U, G, C in RNA ...
Section 1.5 Name:
... Remember, proteins are a molecule of life that are made from different kinds of monomers known as ___________________________. Proteins can have many different shapes and functions. ...
... Remember, proteins are a molecule of life that are made from different kinds of monomers known as ___________________________. Proteins can have many different shapes and functions. ...
Lecture 18
... iv. All of DNA is double stranded v. RNA can be double or single stranded vi. Evidence for model that RNA precedes DNA 1. RNA involved in synthesis of both itself and DNA 2. DNA cannot synthesize itself, it only provides the encoding 3. Diagram of templates 4. RNA ubiquitous in all DNA functions 5. ...
... iv. All of DNA is double stranded v. RNA can be double or single stranded vi. Evidence for model that RNA precedes DNA 1. RNA involved in synthesis of both itself and DNA 2. DNA cannot synthesize itself, it only provides the encoding 3. Diagram of templates 4. RNA ubiquitous in all DNA functions 5. ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Deoxyribose sugar Double-stranded Thymine pairs with adenine ...
... Deoxyribose sugar Double-stranded Thymine pairs with adenine ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.