PG1005 Lecture 17 Gene Transcription
... -Linear polymer composed of 4 nucleotide subunits --Nucleotides are ribonucleotides (ribose sugar) -AGCU (adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil) -Intramolecular complimentary sequences found in RNA Can form intramolecular bonds permitting folding and generation of precise 3D structures ...
... -Linear polymer composed of 4 nucleotide subunits --Nucleotides are ribonucleotides (ribose sugar) -AGCU (adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil) -Intramolecular complimentary sequences found in RNA Can form intramolecular bonds permitting folding and generation of precise 3D structures ...
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA - Tenafly Public Schools
... up all proteins The genetic code = the language of instructions in DNA and RNA Nucleotides in mRNA are read in groups of three ...
... up all proteins The genetic code = the language of instructions in DNA and RNA Nucleotides in mRNA are read in groups of three ...
slides
... – ~20,000 protein-‐coding genes were studies, which covers 2.94% of the genome – Non-‐protein coding regions of the genome? • >80% of the genome is funcFonal as regulatory sequences, based on the analysis ...
... – ~20,000 protein-‐coding genes were studies, which covers 2.94% of the genome – Non-‐protein coding regions of the genome? • >80% of the genome is funcFonal as regulatory sequences, based on the analysis ...
2012 Boc314 TT02m(1) - Learning
... It when the genes on a Chromosome of a sequenced genome Occur in the same order to those On the chromosome of a related plant ...
... It when the genes on a Chromosome of a sequenced genome Occur in the same order to those On the chromosome of a related plant ...
Transcription: Synthesizing RNA from DNA
... tRNA: transfer appropriate amino acid to the ribosome to build proteins. Short ~70-90 nucleotides. rRNA: structural component of ribosome, along with a protein it forms the ribosome which provides the construction site for polypeptide assembly snRNA: small nuclear RNA involved in modification of mRN ...
... tRNA: transfer appropriate amino acid to the ribosome to build proteins. Short ~70-90 nucleotides. rRNA: structural component of ribosome, along with a protein it forms the ribosome which provides the construction site for polypeptide assembly snRNA: small nuclear RNA involved in modification of mRN ...
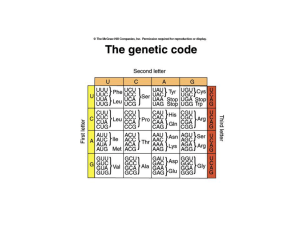
Features of the genetic code
... • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (mutation that generates any of the three stop codons leading a a premature truncation of the polypeptide. ...
... • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (mutation that generates any of the three stop codons leading a a premature truncation of the polypeptide. ...
Protein Synthesis Continued
... After a strand of RNA is constructed by transcription, it must be altered before it moves to the cytoplasm Introns are sections of the RNA that do not code for a protein and are “cut out” of the RNA strand (they stay IN the nucleus) Exons are then spliced back together because they code for the prot ...
... After a strand of RNA is constructed by transcription, it must be altered before it moves to the cytoplasm Introns are sections of the RNA that do not code for a protein and are “cut out” of the RNA strand (they stay IN the nucleus) Exons are then spliced back together because they code for the prot ...
Albert Libchaber Detlev W. Bronk Professor The Rockefeller
... In the fascinating puzzle of the origin of life, two main phenomena distinguish biology from non-equilibrium thermodynamic processes: the presence of a code and the ability of machines to self-reproduce. - In the RNA world of the early soup we are studying how a genetic code could originate, buildin ...
... In the fascinating puzzle of the origin of life, two main phenomena distinguish biology from non-equilibrium thermodynamic processes: the presence of a code and the ability of machines to self-reproduce. - In the RNA world of the early soup we are studying how a genetic code could originate, buildin ...
1: How is ribonucleic acid like DNA
... Name ____________________________________Date ____________________ ...
... Name ____________________________________Date ____________________ ...
Reverse Transcription - St. Michael`s Hospital
... activities: as a RNA‐dependent DNA polymerase, a DNA‐dependent DNA polymerase and ribonuclease H. Many commercially available kits, such as Super Script® III (Invitrogen/Life Technologies) have specifically engineered enzymes that possess reduced RNase H activity and provide increased thermal sta ...
... activities: as a RNA‐dependent DNA polymerase, a DNA‐dependent DNA polymerase and ribonuclease H. Many commercially available kits, such as Super Script® III (Invitrogen/Life Technologies) have specifically engineered enzymes that possess reduced RNase H activity and provide increased thermal sta ...
Unit 5 practice FRQ #3 for final - KEY 3. 2009 AP Bio FRQ # 4 The
... Codes for amino acids/signals RNA → _protein or site of protein synthesis Ribosomes tRNA Transports amino acids (b) Cells regulate both protein synthesis and protein activity. Discuss TWO specific mechanisms of protein regulation in eukaryotic cells. (4 points maximum) Idea of the mechanism Discussi ...
... Codes for amino acids/signals RNA → _protein or site of protein synthesis Ribosomes tRNA Transports amino acids (b) Cells regulate both protein synthesis and protein activity. Discuss TWO specific mechanisms of protein regulation in eukaryotic cells. (4 points maximum) Idea of the mechanism Discussi ...
RNA and Central Dogma
... acts as the template for RNA synthesis (Making RNA) • Translation: RNA directs the assembly of a protein (Using RNA) ...
... acts as the template for RNA synthesis (Making RNA) • Translation: RNA directs the assembly of a protein (Using RNA) ...
Wed 12-2 Computers Lab (40 points if all correct or 0 if not) Open up
... but differs in a few important structural details: in the cell, RNA is usually single-stranded, while DNA is usually double-stranded; RNA nucleotides contain ribose while DNA contains deoxyribose (a type of ribose that lacks one oxygen atom); and RNA has the base uracil rather than thymine that is p ...
... but differs in a few important structural details: in the cell, RNA is usually single-stranded, while DNA is usually double-stranded; RNA nucleotides contain ribose while DNA contains deoxyribose (a type of ribose that lacks one oxygen atom); and RNA has the base uracil rather than thymine that is p ...
the primary transcript
... interrupted by noncoding segments (introns). Both exons and introns are transcribed in the nucleus. Introns are removed during processing of the RNA molecule in the nucleus. In eukaryotes, all mRNA is monocistronic. The mature mRNA is translated in the cytoplasm. The structure and transcription of a ...
... interrupted by noncoding segments (introns). Both exons and introns are transcribed in the nucleus. Introns are removed during processing of the RNA molecule in the nucleus. In eukaryotes, all mRNA is monocistronic. The mature mRNA is translated in the cytoplasm. The structure and transcription of a ...
RNA interference 1. The central dogma 3. The RNAi mechanism
... translation of mRNA to protein. C. In the research laboratory, dsRNA molecules are tailor-made to activate the RISC complex to degrade mRNA for a specific gene. ...
... translation of mRNA to protein. C. In the research laboratory, dsRNA molecules are tailor-made to activate the RISC complex to degrade mRNA for a specific gene. ...
dna ppt ques – ANSWERS2
... the nucleus will _____HOOK UP________________ with the now one sided DNA. ...
... the nucleus will _____HOOK UP________________ with the now one sided DNA. ...
1 Biology 20 Protein Synthesis DNA: How is this linear information
... Sugar: Nitrogenous bases: Strands: Genetic code: (p. 194; Fig. 10.8A) ...
... Sugar: Nitrogenous bases: Strands: Genetic code: (p. 194; Fig. 10.8A) ...
HB B EXAM ReviewJeopardy
... chromosomal material, but he found some skin cells with double the chromosomal material. What might be the explanation for these findings? ...
... chromosomal material, but he found some skin cells with double the chromosomal material. What might be the explanation for these findings? ...
pptx - WVU School of Medicine
... • different σ factors recognize different promoters (σ70 = most genes; σ32 = heat shock proteins; σ28 = flagella & chemotaxis genes). • 2 DNA sequences (-35 & -10) found in most prokaryotic promoters – “upstream” of transcription start site (+1). ...
... • different σ factors recognize different promoters (σ70 = most genes; σ32 = heat shock proteins; σ28 = flagella & chemotaxis genes). • 2 DNA sequences (-35 & -10) found in most prokaryotic promoters – “upstream” of transcription start site (+1). ...
File
... RNA splicing – removal of introns so that only exons remain (exons = mRNA that exits nucleus (includes leader and trailer )) Roberts and Sharp 1977 RNA polymerase II transcribes whole transcription unit (DNA that is transcribed), but many nucleotides need to be spliced to form true mRNA from primary ...
... RNA splicing – removal of introns so that only exons remain (exons = mRNA that exits nucleus (includes leader and trailer )) Roberts and Sharp 1977 RNA polymerase II transcribes whole transcription unit (DNA that is transcribed), but many nucleotides need to be spliced to form true mRNA from primary ...
View file - University of California San Diego
... "By putting these functional groups on RNA, the molecules are ready to carry out all the chemistry that's done by proteins now," said Miller. "That's what we think." As proof, the chemists reacted HMU with several simple molecules thought to be present in the prebiotic soup of early Earth such as hy ...
... "By putting these functional groups on RNA, the molecules are ready to carry out all the chemistry that's done by proteins now," said Miller. "That's what we think." As proof, the chemists reacted HMU with several simple molecules thought to be present in the prebiotic soup of early Earth such as hy ...
Nucleic Acids Powerpoint
... • Nucleic acids are large biomolecules (polymers) – essential for all known forms of life • Include DNA and RNA • Made from long strands of nucleotides (monomers) – A nucleotide contains a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base – The nitrogeneous bases are connected by the sugar ...
... • Nucleic acids are large biomolecules (polymers) – essential for all known forms of life • Include DNA and RNA • Made from long strands of nucleotides (monomers) – A nucleotide contains a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base – The nitrogeneous bases are connected by the sugar ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.