Raven (7th) Guided Notes Chapter 15
... 1. Briefly describe the function of each type of RNA. a. rRNA __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ b. mRNA _________________________________________________________________ ______________________ ...
... 1. Briefly describe the function of each type of RNA. a. rRNA __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ b. mRNA _________________________________________________________________ ______________________ ...
Transcription Biology Review
... Gene structure Chromatin structure & modifications Transcription apparatus Transcription factors and cofactors Elongation and termination RNA capping, splicing, and adenylation RNA processing and miRNA’s ...
... Gene structure Chromatin structure & modifications Transcription apparatus Transcription factors and cofactors Elongation and termination RNA capping, splicing, and adenylation RNA processing and miRNA’s ...
Advance Animal Science Lesson Title: Protein Synthesis Unit: 4
... DNA is the master plan of the cell, RNA is the blue print of the master cell. ...
... DNA is the master plan of the cell, RNA is the blue print of the master cell. ...
RNA AND TYPES
... RIBOSOMAL RNA rRNA, or Ribosomal RNA, contributes significantly to the structure of the ribosomes in a cell. mRNA, and tRNA work together the the ribosomes to synthesize proteins. In eukaryotes, rRNA is transcribed exclusively within the nucleolus while other types of RNA are synthesized through ...
... RIBOSOMAL RNA rRNA, or Ribosomal RNA, contributes significantly to the structure of the ribosomes in a cell. mRNA, and tRNA work together the the ribosomes to synthesize proteins. In eukaryotes, rRNA is transcribed exclusively within the nucleolus while other types of RNA are synthesized through ...
Transcription and Translation
... • RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence and separates the DNA strands • Complementary ribonucleotides align opposite complementary base pairs • RNA polymerase joins the ribonucleotides together with covalent bonds • The transcription process stops when a termination sequence is reached ...
... • RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence and separates the DNA strands • Complementary ribonucleotides align opposite complementary base pairs • RNA polymerase joins the ribonucleotides together with covalent bonds • The transcription process stops when a termination sequence is reached ...
Genes and How they work!
... • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – made of several RNA molecules and over 50 proteins • Messenger RNA (mRNA) • Transfer RNA (tRNA) ...
... • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – made of several RNA molecules and over 50 proteins • Messenger RNA (mRNA) • Transfer RNA (tRNA) ...
Topic 3 The Chemistry of Life - wfs
... 3. The exposed bases of each strand are then paired with an available nucleotide by complementary base pairing. The result is two strands where only one was first present. 4. DNA polymerase is an enzyme that allows the connection between nucleotides lined up by basepairing. 5. This replication is ca ...
... 3. The exposed bases of each strand are then paired with an available nucleotide by complementary base pairing. The result is two strands where only one was first present. 4. DNA polymerase is an enzyme that allows the connection between nucleotides lined up by basepairing. 5. This replication is ca ...
RNA
... Single strand of nucleotides (unlike DNA) Contains 5-C sugar ribose Uracil replaces Thymine 3 types of RNA produced 1. Messenger RNA (m-RNA) - code for order of amino acids 2. Transfer RNA (t-RNA) - carry amino acids and fit them in proper place 3. Ribosomal RNA (r-RNA) - major component of ribosome ...
... Single strand of nucleotides (unlike DNA) Contains 5-C sugar ribose Uracil replaces Thymine 3 types of RNA produced 1. Messenger RNA (m-RNA) - code for order of amino acids 2. Transfer RNA (t-RNA) - carry amino acids and fit them in proper place 3. Ribosomal RNA (r-RNA) - major component of ribosome ...
Building Proteins - Marblehead High School
... Transfer RNA (tRNA)-carries the correct amino acid to the ribosome to build proteins ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA)-carries the correct amino acid to the ribosome to build proteins ...
Chapter 17: Transcription, RNA Processing, and Translation
... with? Think back to RNAs with tertiary structure. 4.) What catalyzes the addition of amino acids to the tRNA? How is the molecule able to do this? (What within its structure allows it and what is it recognizing). 5.) What is the term used to describe a tRNA molecule covalently linked to an AA? 6.) W ...
... with? Think back to RNAs with tertiary structure. 4.) What catalyzes the addition of amino acids to the tRNA? How is the molecule able to do this? (What within its structure allows it and what is it recognizing). 5.) What is the term used to describe a tRNA molecule covalently linked to an AA? 6.) W ...
Protocol S1.
... denatured in RNA dilution buffer [1 × SSC (0.15 M NaCl plus 0.015 M sodium citrate), 50% formamide and 6.7% formaldehyde] at 68°C for 15 min and put on ice. RNA was applied to nylon membranes (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) using a Bio-Dot microfiltration apparatus (BioRad, Hercules, CA). Following tran ...
... denatured in RNA dilution buffer [1 × SSC (0.15 M NaCl plus 0.015 M sodium citrate), 50% formamide and 6.7% formaldehyde] at 68°C for 15 min and put on ice. RNA was applied to nylon membranes (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) using a Bio-Dot microfiltration apparatus (BioRad, Hercules, CA). Following tran ...
Name:
... Go to Mr. Mason’s site, and then to the link for “Genetics – DNA Replication/Protein Synthesis” 1. The first step in DNA replication is this: 2. What is it specifically that causes the DNA to “unzip”? 3. Try to match the bases (the letters) together to replicate the DNA strands. What do you notice a ...
... Go to Mr. Mason’s site, and then to the link for “Genetics – DNA Replication/Protein Synthesis” 1. The first step in DNA replication is this: 2. What is it specifically that causes the DNA to “unzip”? 3. Try to match the bases (the letters) together to replicate the DNA strands. What do you notice a ...
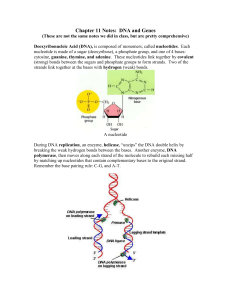
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
gene expression - Aurora City Schools
... • RNA’s “language” is translated into amino acids (which will become a protein) • RNA’s language is set of three nucleotides called a codon…3 nitrogen bases in a row • Codons match with specific amino acids to make polypeptide chain (which will be modified to make a protein) • 20 amino acids all tog ...
... • RNA’s “language” is translated into amino acids (which will become a protein) • RNA’s language is set of three nucleotides called a codon…3 nitrogen bases in a row • Codons match with specific amino acids to make polypeptide chain (which will be modified to make a protein) • 20 amino acids all tog ...
Sept24_26_07 - Salamander Genome Project
... faster replication time after a few serial transfers ...
... faster replication time after a few serial transfers ...
Chapter 17: Transcription, RNA Processing, and Translation
... with? Think back to RNAs with tertiary structure. 4.) What catalyzes the addition of amino acids to the tRNA? How is the molecule able to do this? (What within its structure allows it and what is it recognizing). 5.) What is the term used to describe a tRNA molecule covalently linked to an AA? 6.) W ...
... with? Think back to RNAs with tertiary structure. 4.) What catalyzes the addition of amino acids to the tRNA? How is the molecule able to do this? (What within its structure allows it and what is it recognizing). 5.) What is the term used to describe a tRNA molecule covalently linked to an AA? 6.) W ...
Objectives 2
... functions: mRNA carries messages transcribed from DNA to be translated into protein, hnRNA is immature form of mRNA, tRNA carries activated amino acids, and rRNA is a structural component of ribosomes. 2) List the principal chemical building blocks that comprise nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed ...
... functions: mRNA carries messages transcribed from DNA to be translated into protein, hnRNA is immature form of mRNA, tRNA carries activated amino acids, and rRNA is a structural component of ribosomes. 2) List the principal chemical building blocks that comprise nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.