glossary of technical terms
... chromosomes of almost all organisms, made up of four different kinds of bases, which are abbreviated A, C, T and G. A DNA fragment that is ten bases long might have a base sequence of, for example, ATCGTTCCTG. The particular sequence of bases encodes important information in an individual’s genetic ...
... chromosomes of almost all organisms, made up of four different kinds of bases, which are abbreviated A, C, T and G. A DNA fragment that is ten bases long might have a base sequence of, for example, ATCGTTCCTG. The particular sequence of bases encodes important information in an individual’s genetic ...
DNA Transcription & Translation
... genetic information code is copied into a single strand of mRNA. mRNA is known as “messenger” RNA because it carries the DNA code or message out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm. • DNA cannot travel out of the nucleus but RNA can. • RNA contains the base Uracil instead of Thymine. ...
... genetic information code is copied into a single strand of mRNA. mRNA is known as “messenger” RNA because it carries the DNA code or message out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm. • DNA cannot travel out of the nucleus but RNA can. • RNA contains the base Uracil instead of Thymine. ...
DNA, RNA, and Proteins part 2 - Tri-City
... Differs from DNA in three ways • Single strand of nucleotides • Contain the five-carbon sugar ribose • In addition to A,G, and C nitrogen bases, also includes U (uracil) • NO thymine! • Uracil is complementary to adenine ...
... Differs from DNA in three ways • Single strand of nucleotides • Contain the five-carbon sugar ribose • In addition to A,G, and C nitrogen bases, also includes U (uracil) • NO thymine! • Uracil is complementary to adenine ...
RNA Structure and Function
... bases) in the proper order to spell out the recipe for the protein to be made. The N bases are the letters in the genetic code and the sugar/phosphate backbone is the “paper” on which the code is “written”. E. Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) a. Encodes a protein b. refers to the “recipe copies” ...
... bases) in the proper order to spell out the recipe for the protein to be made. The N bases are the letters in the genetic code and the sugar/phosphate backbone is the “paper” on which the code is “written”. E. Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) a. Encodes a protein b. refers to the “recipe copies” ...
From DNA to Protein
... Tay Sachs – One wrong letter - from PBS Cracking the Code of Life – 9:38 and 57:00 ...
... Tay Sachs – One wrong letter - from PBS Cracking the Code of Life – 9:38 and 57:00 ...
lecture1
... transfer RNA (tRNA). RNA molecules that carry amino acids to the growing polypeptide. ...
... transfer RNA (tRNA). RNA molecules that carry amino acids to the growing polypeptide. ...
Nucleic Acids (DNA and RNA) are not boring long polymers
... nucleic acids, DNA and RNAs. They are particularly abundant in noncoding RNAs, such as transfer RNAs and ribosomal RNAs of metazoan. By increasing the structural diversity of nucleic acids, naturally occurring modified nucleosides play important roles in gene ex ...
... nucleic acids, DNA and RNAs. They are particularly abundant in noncoding RNAs, such as transfer RNAs and ribosomal RNAs of metazoan. By increasing the structural diversity of nucleic acids, naturally occurring modified nucleosides play important roles in gene ex ...
BCH-201:Nucleotides and Nucleic acids
... transfer RNA (tRNA). RNA molecules that carry amino acids to the growing polypeptide. ...
... transfer RNA (tRNA). RNA molecules that carry amino acids to the growing polypeptide. ...
RNA
... First genes were RNA molecules that polymerized abiotically and replicated themselves autocatalytically ...
... First genes were RNA molecules that polymerized abiotically and replicated themselves autocatalytically ...
B8. Nucleic Acids (HL)
... and are bonded together by covalent phosphodiester bonds • The sugar and nitrogenous bases are also bonded together by covalent bonds ...
... and are bonded together by covalent phosphodiester bonds • The sugar and nitrogenous bases are also bonded together by covalent bonds ...
Bacterial Nucleic Acids
... • Their information is used to make protein with the help of RNA through Transcription...Translation. • The DNA double helix is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the bases attached to the two strands. • One major difference between DNA and RNA is the sugar, with the 2deoxyribose in DNA being repl ...
... • Their information is used to make protein with the help of RNA through Transcription...Translation. • The DNA double helix is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the bases attached to the two strands. • One major difference between DNA and RNA is the sugar, with the 2deoxyribose in DNA being repl ...
Protein Synthesis
... – copies DNA in the nucleus and carries the info to the ribosomes (in cytoplasm) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): – makes up a large part of the ribosome; reads and decodes mRNA Transfer RNA (tRNA): – carries amino acids to the ribosome where they are joined to form proteins ...
... – copies DNA in the nucleus and carries the info to the ribosomes (in cytoplasm) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): – makes up a large part of the ribosome; reads and decodes mRNA Transfer RNA (tRNA): – carries amino acids to the ribosome where they are joined to form proteins ...
Model Description Sheet
... pathway, small RNAs derived from viruses are used by Ago-2 to slice virus mRNA, protecting the cells from infection. In the miRNA pathway, Ago-2 utilizes naturally occurring miRNA to slice cellular mRNAs to control protein production. Ago-2 works by binding small (~22 nucleotide) regulatory RNAs (si ...
... pathway, small RNAs derived from viruses are used by Ago-2 to slice virus mRNA, protecting the cells from infection. In the miRNA pathway, Ago-2 utilizes naturally occurring miRNA to slice cellular mRNAs to control protein production. Ago-2 works by binding small (~22 nucleotide) regulatory RNAs (si ...
From Gene to Protein Part 2
... FROM GENE TO PROTEIN PART 2 Goal 1- Understand the process of transcription • How is RNA made? •How ...
... FROM GENE TO PROTEIN PART 2 Goal 1- Understand the process of transcription • How is RNA made? •How ...
Key
... D. modified to make a Shine-Dalgarno sequence. E. not modified. 3. The mRNA cap is an unusual structure because it A. contains a deoxyribose sugar, that is usually only found in DNA. B. has two purines base-paired together. C. consistes of several hundred A nucleotides that are not found in the gene ...
... D. modified to make a Shine-Dalgarno sequence. E. not modified. 3. The mRNA cap is an unusual structure because it A. contains a deoxyribose sugar, that is usually only found in DNA. B. has two purines base-paired together. C. consistes of several hundred A nucleotides that are not found in the gene ...
BioIIch17notesRNAfilled.p pt
... -A site: holds tRNA carrying the next amino acid -E site: discharges tRNAs after they deliver the amino acid -act like a vise and holds the tRNA and mRNA close together and positions the new amino acid for addition to the growing protein ...
... -A site: holds tRNA carrying the next amino acid -E site: discharges tRNAs after they deliver the amino acid -act like a vise and holds the tRNA and mRNA close together and positions the new amino acid for addition to the growing protein ...
Honors Biology
... 2. Relate the structure of the DNA molecule to the structure of chromatin and chromosomes. 3. Know the types and roles of RNAs. 4. Compare and contrast RNA with DNA (consider both the structure of each and the purpose of each in the cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcrip ...
... 2. Relate the structure of the DNA molecule to the structure of chromatin and chromosomes. 3. Know the types and roles of RNAs. 4. Compare and contrast RNA with DNA (consider both the structure of each and the purpose of each in the cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcrip ...
Protein Synthesis
... beads and pipe cleaners. When you have your protein completed, have your teacher check it. If there are any errors, please go back and find your mistakes. 8. Did you have any “mutations” during the process? ____________ ...
... beads and pipe cleaners. When you have your protein completed, have your teacher check it. If there are any errors, please go back and find your mistakes. 8. Did you have any “mutations” during the process? ____________ ...
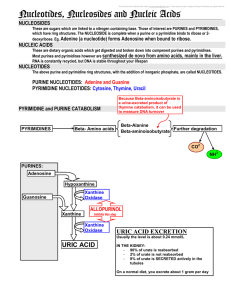
3 Nucleosides nucleotides and nucleic acids
... Extremely long nucleotide chains containing - ADENINE - GUANINE - THYMINE - CYTOSINE The double helix is held together by hudrogen bonds between the bases : - ADENINE BONDS TO THYMINE - GUANINE BONDS TO CYTOSINE A diploid human cell contains 46 chromosomes. Useful factoid to know. - EXONS are portio ...
... Extremely long nucleotide chains containing - ADENINE - GUANINE - THYMINE - CYTOSINE The double helix is held together by hudrogen bonds between the bases : - ADENINE BONDS TO THYMINE - GUANINE BONDS TO CYTOSINE A diploid human cell contains 46 chromosomes. Useful factoid to know. - EXONS are portio ...
From Genes to Proteins
... Keratin is one of the proteins in hair. The gene for keratin is transcribed and translated by certain skin cells. The series of letters on the next slide represents the sequence of nucleotides in a portion of an mRNA molecule transcribed from the gene for keratin. This mRNA strand and the genetic co ...
... Keratin is one of the proteins in hair. The gene for keratin is transcribed and translated by certain skin cells. The series of letters on the next slide represents the sequence of nucleotides in a portion of an mRNA molecule transcribed from the gene for keratin. This mRNA strand and the genetic co ...
Chapter 13 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Chapter 13 RNA and Protein Synthesis ____________ RNA carries amino acids to the ribosome to match them to the coded mRNA message. RNA Synthesis _______________ is the process where DNA will serve as the template to make a strand of RNA. The RNA will be made in the nucleus and then go to ____ ...
... Chapter 13 RNA and Protein Synthesis ____________ RNA carries amino acids to the ribosome to match them to the coded mRNA message. RNA Synthesis _______________ is the process where DNA will serve as the template to make a strand of RNA. The RNA will be made in the nucleus and then go to ____ ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.