Section 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... 17. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about translation. a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the gro ...
... 17. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about translation. a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the gro ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... mutation in your gene. Call this Protein Y. • 5. Did this single deletion cause much change in your protein? ...
... mutation in your gene. Call this Protein Y. • 5. Did this single deletion cause much change in your protein? ...
Metabolism—chapter 4
... -each ATP is made of 3 parts: an adenine, a ribose, and 3 phosphates in a chain -almost half the energy released during cell respiration is used to generate ATP from ADP (this has only 2 phosphate molecules) -this is known as phosphorylation Nucleic Acid synthesis -DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) and RN ...
... -each ATP is made of 3 parts: an adenine, a ribose, and 3 phosphates in a chain -almost half the energy released during cell respiration is used to generate ATP from ADP (this has only 2 phosphate molecules) -this is known as phosphorylation Nucleic Acid synthesis -DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) and RN ...
Chapter 22
... Retroposons of the viral superfamily are transposons that mobilize via an RNA that does not form an infectious particle. Some retroposons directly resemble retroviruses in their use of LTRs, whereas others do not have LTRs. Other elements can be found that were generated by an RNA-mediated transposi ...
... Retroposons of the viral superfamily are transposons that mobilize via an RNA that does not form an infectious particle. Some retroposons directly resemble retroviruses in their use of LTRs, whereas others do not have LTRs. Other elements can be found that were generated by an RNA-mediated transposi ...
The DNA Connection
... proteins Genes and DNA: Chromosomes are made of DNA. Genes are sections of a DNA molecule that codes for one specific protein. May contain several hundred to a million or more base pairs (Ex. ...
... proteins Genes and DNA: Chromosomes are made of DNA. Genes are sections of a DNA molecule that codes for one specific protein. May contain several hundred to a million or more base pairs (Ex. ...
GENE to PROTEIN
... nucleus. • The introns are removed and the “abridged” version of mRNA moves to the cytoplasm as the primary ...
... nucleus. • The introns are removed and the “abridged” version of mRNA moves to the cytoplasm as the primary ...
GENE to PROTEIN
... nucleus. • The introns are removed and the “abridged” version of mRNA moves to the cytoplasm as the primary ...
... nucleus. • The introns are removed and the “abridged” version of mRNA moves to the cytoplasm as the primary ...
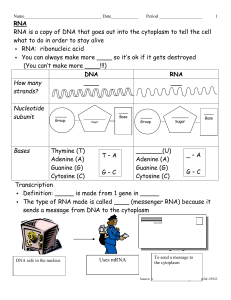
DNA - Gulf Coast State College
... Definition: _____ is made from 1 gene in _____ The type of RNA made is called ____ (messenger RNA) because it sends a message from DNA to the cytoplasm ...
... Definition: _____ is made from 1 gene in _____ The type of RNA made is called ____ (messenger RNA) because it sends a message from DNA to the cytoplasm ...
Basics of Biology (part 3): transcripCon, translaCon ADN, ARNs
... RNA (ribonucleid acid) is a single-stranded polymer, up to few 1000 nucleotides long.! Its bases differ slightly from DNA: U replaces T! ...
... RNA (ribonucleid acid) is a single-stranded polymer, up to few 1000 nucleotides long.! Its bases differ slightly from DNA: U replaces T! ...
DNA Replication, RNA Molecules and Transcription
... A transcription reaction requires a DNA molecule to serve as template for transcription with a promoter (and, in vivo, transcription factors) to indicate where to begin transcribing and which strand to transcribe. Transcription reactions also require an RNA polymerase that recognizes the promoter on ...
... A transcription reaction requires a DNA molecule to serve as template for transcription with a promoter (and, in vivo, transcription factors) to indicate where to begin transcribing and which strand to transcribe. Transcription reactions also require an RNA polymerase that recognizes the promoter on ...
Brooker Chapter 11
... • cis-acting elements • DNA sequences that exert their effect only on nearby genes • Example: TATA box, enhancers and silencers ...
... • cis-acting elements • DNA sequences that exert their effect only on nearby genes • Example: TATA box, enhancers and silencers ...
Chapter_17_answers
... o ex: I (inosine) in 3rd position of anticodon can pair with U, C, or A o aha! This is why 1 amino acid may correspond with multiple codons, only differing in the last letter aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase joins amino acids to their respective tRNA’s (20 types) ribosomes consist of 2 subunits (large ...
... o ex: I (inosine) in 3rd position of anticodon can pair with U, C, or A o aha! This is why 1 amino acid may correspond with multiple codons, only differing in the last letter aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase joins amino acids to their respective tRNA’s (20 types) ribosomes consist of 2 subunits (large ...
Chapter 11: DNA and Genes
... In the nucleus, enzymes make an RNA copy of a portion of a DNA strand by this process. Forms a single-stranded RNA molecule rather than a double-stranded DNA molecule. Page 296, Figure 11.6 has a diagram and step-bystep information for this process. http://www.dnalc.org/view/15510-TranscriptionDNA-c ...
... In the nucleus, enzymes make an RNA copy of a portion of a DNA strand by this process. Forms a single-stranded RNA molecule rather than a double-stranded DNA molecule. Page 296, Figure 11.6 has a diagram and step-bystep information for this process. http://www.dnalc.org/view/15510-TranscriptionDNA-c ...
From Gene to Protein
... strand. • C with G and this time, A with U (uracil) • DNA acts as a template • DNA is only opened at a small region (gene or genes of interest) • DNA helix reseals as RNA polymerase passes by…. Completely intact and undiluted. ...
... strand. • C with G and this time, A with U (uracil) • DNA acts as a template • DNA is only opened at a small region (gene or genes of interest) • DNA helix reseals as RNA polymerase passes by…. Completely intact and undiluted. ...
RNA & Transcription
... What are the types of RNA & their functions? 1) Messenger RNA (mRNA) – brings DNA code for proteins, from the nucleus to cytoplasm ribosomes, and directs amino acid sequence. It is a single strand without loops. It contains nucleotide sequences called codons. ...
... What are the types of RNA & their functions? 1) Messenger RNA (mRNA) – brings DNA code for proteins, from the nucleus to cytoplasm ribosomes, and directs amino acid sequence. It is a single strand without loops. It contains nucleotide sequences called codons. ...
Chapter 21 (part 1) - Nevada Agricultural Experiment
... • RNA polymerase core enzyme is a multimeric protein a2,b, b’, w • The b’ subunit is involved in DNA binding • The b subunit contains the polymerase active site • The a subunit acts as scaffold on which the other subunits assemble. • Also requires s-factor for initiation –forms holo enzyme complex ...
... • RNA polymerase core enzyme is a multimeric protein a2,b, b’, w • The b’ subunit is involved in DNA binding • The b subunit contains the polymerase active site • The a subunit acts as scaffold on which the other subunits assemble. • Also requires s-factor for initiation –forms holo enzyme complex ...
Protein Synthesis Quick Questions
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
Bio-261-chapter-7
... the non-coding regions are called introns. • The introns are removed by an enzymeRNA complex known as the spliceosome. • A tail of adenine bases is added to the 3 prime end and a modified guanine nucleotide is added to the 5 prime end. ...
... the non-coding regions are called introns. • The introns are removed by an enzymeRNA complex known as the spliceosome. • A tail of adenine bases is added to the 3 prime end and a modified guanine nucleotide is added to the 5 prime end. ...
Replication/ Transcription/Translation Review
... code is used to make a protein. 3. Explain the difference between replication & transcription. Replication is making a DNA copy of the DNA. Both sides of the DNA are replicated using DNA nucleotides. Transcription is making an mRNA copy of a DNA sequence. One side of the DNA is used to make RNA usin ...
... code is used to make a protein. 3. Explain the difference between replication & transcription. Replication is making a DNA copy of the DNA. Both sides of the DNA are replicated using DNA nucleotides. Transcription is making an mRNA copy of a DNA sequence. One side of the DNA is used to make RNA usin ...
worksheet 12-3
... 17. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about translation. a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the gro ...
... 17. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about translation. a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the gro ...
C - TeacherWeb
... the non-coding regions are called introns. • The introns are removed by an enzymeRNA complex known as the spliceosome. • A tail of adenine bases is added to the 3 prime end and a modified guanine nucleotide is added to the 5 prime end. ...
... the non-coding regions are called introns. • The introns are removed by an enzymeRNA complex known as the spliceosome. • A tail of adenine bases is added to the 3 prime end and a modified guanine nucleotide is added to the 5 prime end. ...
(Francis Crick, 1958) (Transcription) (Translation)
... Cells have adapter molecules called tRNA with a three nucleotide sequence on one end (anticodon) that is complementary to a codon of the genetic code. • There are different transfer RNAs (tRNAs) with anticodons that are complementary to the codons for each of the twenty amino acids. • Each tRNA int ...
... Cells have adapter molecules called tRNA with a three nucleotide sequence on one end (anticodon) that is complementary to a codon of the genetic code. • There are different transfer RNAs (tRNAs) with anticodons that are complementary to the codons for each of the twenty amino acids. • Each tRNA int ...
BIOL 222 - philipdarrenjones.com
... 11) From the following list, which is the first event in translation in eukaryotes? A) elongation of the polypeptide B) base pairing of methionine-tRNA to AUG (start codon) of the messenger RNA C) the larger ribosomal subunit binds to smaller ribosomal subunits D) covalent bonding between the first ...
... 11) From the following list, which is the first event in translation in eukaryotes? A) elongation of the polypeptide B) base pairing of methionine-tRNA to AUG (start codon) of the messenger RNA C) the larger ribosomal subunit binds to smaller ribosomal subunits D) covalent bonding between the first ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.