The Story of DNA vs. RNA
... order of the nitrogen bases along a strand of DNA determine the type of protein that will be produced ...
... order of the nitrogen bases along a strand of DNA determine the type of protein that will be produced ...
powerpoint
... SEQUENCES OF MONOMERS- NUCLEOTIDES AND AMINO ACIDS, RESPECTIVELY. • TRANSCRIPTION IS THE NUCLEOTIDE-TONUCLEOTIDE TRANSFER OF INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA, WHILE TRANSLATION IS THE INFORMATIONAL TRANSFER FROM NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE IN RNA TO AMINO ACID SEQUENCE IN A POLYPEPTIDE. ...
... SEQUENCES OF MONOMERS- NUCLEOTIDES AND AMINO ACIDS, RESPECTIVELY. • TRANSCRIPTION IS THE NUCLEOTIDE-TONUCLEOTIDE TRANSFER OF INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA, WHILE TRANSLATION IS THE INFORMATIONAL TRANSFER FROM NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE IN RNA TO AMINO ACID SEQUENCE IN A POLYPEPTIDE. ...
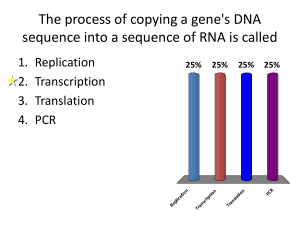
The process of copying a gene`s DNA sequence into a sequence of
... true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
... true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
DNA/RNA
... of cells 9 Holds genetic material that determines the shape, size and growth of an organism 9 Double stranded helix made up of nucleotides – four bases; Adenine, Thymine, Guanine and Cytosine 9 For encoding genetic information, the central feature of DNA structure is the A-T and G-C base pairing. ht ...
... of cells 9 Holds genetic material that determines the shape, size and growth of an organism 9 Double stranded helix made up of nucleotides – four bases; Adenine, Thymine, Guanine and Cytosine 9 For encoding genetic information, the central feature of DNA structure is the A-T and G-C base pairing. ht ...
RNA and Transcription Worksheet File
... This type of RNA carries the protein building instructions from the nucleus to the ribosomes. This type of RNA reads the message, gathers the amino acids, and transports them to the ribosome. This type of RNA is found in the ribosomes. ...
... This type of RNA carries the protein building instructions from the nucleus to the ribosomes. This type of RNA reads the message, gathers the amino acids, and transports them to the ribosome. This type of RNA is found in the ribosomes. ...
Glossary
... RNA-binding proteins :【RNA 結合蛋白質】Proteins that bind to RNA directly through regions that can bind to RNA. This protein family is involved in RNA regulation, such as splicing. Drosha, DGCR8, Dicer, TRBP and TDP-43 are all RNA-binding proteins. ncRNAs (non-coding RNAs) :【非コード RNA】RNAs that do not enco ...
... RNA-binding proteins :【RNA 結合蛋白質】Proteins that bind to RNA directly through regions that can bind to RNA. This protein family is involved in RNA regulation, such as splicing. Drosha, DGCR8, Dicer, TRBP and TDP-43 are all RNA-binding proteins. ncRNAs (non-coding RNAs) :【非コード RNA】RNAs that do not enco ...
Chapter 17 Powerpoint
... • RNA splicing – Initial RNA sequence is approximately 8,000 nucleotides – Generally, only approx. 1,200 are needed, though. – Noncoding areas are found in between coding areas ...
... • RNA splicing – Initial RNA sequence is approximately 8,000 nucleotides – Generally, only approx. 1,200 are needed, though. – Noncoding areas are found in between coding areas ...
max 6
... 6. RNA polymerase joins (RNA) nucleotides together; 7. Pre-mRNA spliced to remove introns. 6 max ...
... 6. RNA polymerase joins (RNA) nucleotides together; 7. Pre-mRNA spliced to remove introns. 6 max ...
The DNA connection - Somerset Academy North Las Vegas
... produce a specific protein. Protein synthesis takes place on the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. The chromosomes are found in the nucleus. How does the information needed to produce proteins get to the ribosomes? ...
... produce a specific protein. Protein synthesis takes place on the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. The chromosomes are found in the nucleus. How does the information needed to produce proteins get to the ribosomes? ...
Biology Ch 10 How Proteins are Made
... From Genes to Proteins • The genes don’t directly make proteins – A combined effort between 3 types of RNA ...
... From Genes to Proteins • The genes don’t directly make proteins – A combined effort between 3 types of RNA ...
Silencing Genes for Life - royalsocietyhighlands.org.au
... Genomics is a branch of biotechnology concerned with the study and manipulation of the genome (the complete set of DNA within a single cell of an organism). One branch of Genomics is called RNA interference (RNAi). [RNA stands for Ribonucleic Acid]. Its inventors Andrew Fire and Craig Mello (Stanfor ...
... Genomics is a branch of biotechnology concerned with the study and manipulation of the genome (the complete set of DNA within a single cell of an organism). One branch of Genomics is called RNA interference (RNAi). [RNA stands for Ribonucleic Acid]. Its inventors Andrew Fire and Craig Mello (Stanfor ...
Protein Synthesis Review Sheet
... 1. What does ‘RNA’ stand for? 2. What are the 4 bases of RNA and how do they pair up? a. b. c. d. 3. Name the two types of RNA and the basic function of each. II. Protein Synthesis List the 5 steps of protein synthesis here (use separate notes handout): ...
... 1. What does ‘RNA’ stand for? 2. What are the 4 bases of RNA and how do they pair up? a. b. c. d. 3. Name the two types of RNA and the basic function of each. II. Protein Synthesis List the 5 steps of protein synthesis here (use separate notes handout): ...
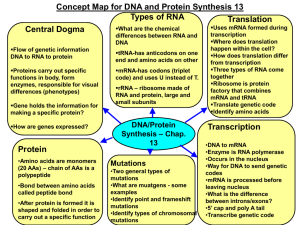
Central Dogma.pptx
... DNA’s message (gene) is expressed (turned on) by first being transcribed into RNA (mRNA, tRNA or rRNA) mRNA=messenger RNA, carries DNA’s message to be later translated into proteins with the help of tRNA and the ribosome. ...
... DNA’s message (gene) is expressed (turned on) by first being transcribed into RNA (mRNA, tRNA or rRNA) mRNA=messenger RNA, carries DNA’s message to be later translated into proteins with the help of tRNA and the ribosome. ...
Daily Trivia - James B. Conant High School
... take it out in the cytoplasm 2. rRNA – Ribosomal RNA-works on matching mRNA - to create the amino acids in the correct order 3. tRNA – Transfer RNA- gives amino acids to rRNA to produce the protein. ...
... take it out in the cytoplasm 2. rRNA – Ribosomal RNA-works on matching mRNA - to create the amino acids in the correct order 3. tRNA – Transfer RNA- gives amino acids to rRNA to produce the protein. ...
The Central Dogma of Biology Classroom Copy
... functional product. It was first proposed in 1958 by Francis Crick, one of the discoverers of the structure of DNA. The central dogma of molecular biology explains the flow of genetic information, from DNA to RNA, to make a functional protein also known as a polypeptide. DNA contains the information ...
... functional product. It was first proposed in 1958 by Francis Crick, one of the discoverers of the structure of DNA. The central dogma of molecular biology explains the flow of genetic information, from DNA to RNA, to make a functional protein also known as a polypeptide. DNA contains the information ...
Chapter 10 Structure and Function of DNA
... What is the backbone Where are the 5’ and 3’ sugars on ribose? DNA replication DNA polymerase Primers 5’ to 3’ direction Helicase Ligase Semiconservative Templates Leading strand ...
... What is the backbone Where are the 5’ and 3’ sugars on ribose? DNA replication DNA polymerase Primers 5’ to 3’ direction Helicase Ligase Semiconservative Templates Leading strand ...
Study_Guide
... State that deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a polynucleotide, usually double-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containi ...
... State that deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a polynucleotide, usually double-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containi ...
nucleic acids - onlinebiosurgery
... Carries the genetic message from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesised (made) accordingly. ...
... Carries the genetic message from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesised (made) accordingly. ...
Slide 1
... functions in body, form enzymes, responsible for visual differences (phenotypes) Gene holds the information for making a specific protein? How are genes expressed? ...
... functions in body, form enzymes, responsible for visual differences (phenotypes) Gene holds the information for making a specific protein? How are genes expressed? ...
Major Functions
... The mRNA and the DNA are base-pairing. One strand is involved in transcription. ...
... The mRNA and the DNA are base-pairing. One strand is involved in transcription. ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.