Powerpoint
... contains the information to code for one complete protein PROTEINS are made up of a chain of amino acids Proteins determine many of the traits in an organism ...
... contains the information to code for one complete protein PROTEINS are made up of a chain of amino acids Proteins determine many of the traits in an organism ...
January 7, 2014 Notes Transcription: process of copying DNA into
... January 7, 2014 Notes Transcription: process of copying DNA into an RNA template. (Occurs in nucleus) ...
... January 7, 2014 Notes Transcription: process of copying DNA into an RNA template. (Occurs in nucleus) ...
HANDOUT: CH 17 pt 1 Study
... CHAPTER 17 STUDY QUESTIONS, part 1: From Gene to Protein (p. 325-344) 1) Summarize the one gene – one polypeptide hypothesis. ...
... CHAPTER 17 STUDY QUESTIONS, part 1: From Gene to Protein (p. 325-344) 1) Summarize the one gene – one polypeptide hypothesis. ...
BIO 103 - Genes
... template strand: used to make RNA coding strand: complementary to the template strand RNA polymerase: puts nucleotides together to make RNA strand ...
... template strand: used to make RNA coding strand: complementary to the template strand RNA polymerase: puts nucleotides together to make RNA strand ...
Transcription
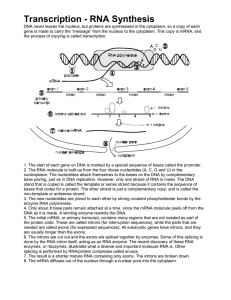
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
Book 11.5 HB Questions
... 4. The triplet of bases on the end of a tRNA molecule is called a(an) _________________________. 5. The process of joining exons together to form an mRNA molecule is called _________________________. 6. During transcription, the _________________________ between base pairs are broken. 7. A mutation ...
... 4. The triplet of bases on the end of a tRNA molecule is called a(an) _________________________. 5. The process of joining exons together to form an mRNA molecule is called _________________________. 6. During transcription, the _________________________ between base pairs are broken. 7. A mutation ...
DNA Connection
... code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. • Proteins are long chains of individual amino acids. • A group 3 DNA bases codes for one specific amino acid. ...
... code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. • Proteins are long chains of individual amino acids. • A group 3 DNA bases codes for one specific amino acid. ...
Protein Synthesis SG
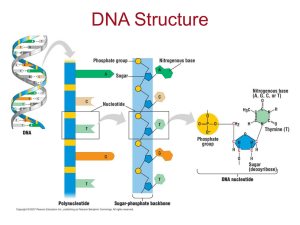
... 1. DNA is also known as the _________________________________. 2. A protein is made up of ____________________________. 3. A protein’s function is determined by its ___________ and ______________________________________. 4. Draw and label the 3 major parts of a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide. ...
... 1. DNA is also known as the _________________________________. 2. A protein is made up of ____________________________. 3. A protein’s function is determined by its ___________ and ______________________________________. 4. Draw and label the 3 major parts of a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide. ...
Word of the Day
... RNA polymerase unzips DNA and copies it into RNA. A’s connect with U’s and G’s connect with C’s. The starting point of transcription is known as the Promoter, the end is known as the terminal signal. After transcription the mRNA moves into the cytosol for protein synthesis. ...
... RNA polymerase unzips DNA and copies it into RNA. A’s connect with U’s and G’s connect with C’s. The starting point of transcription is known as the Promoter, the end is known as the terminal signal. After transcription the mRNA moves into the cytosol for protein synthesis. ...
Bio 1 Unit Objectives Protein Synthesis Readings
... A gene provides the information for making a specific protein Explain the “one-gene-one-polypeptide” hypothesis Trace the information flow from DNA to protein Describe how amino acids are coded ...
... A gene provides the information for making a specific protein Explain the “one-gene-one-polypeptide” hypothesis Trace the information flow from DNA to protein Describe how amino acids are coded ...
RNA
... • Phenotype = physical and chemical state • The phenotype is determined by the proteins synthesised when the genes are expressed ...
... • Phenotype = physical and chemical state • The phenotype is determined by the proteins synthesised when the genes are expressed ...
013368718X_CH13_193
... 1. DNA contains the sugar ribose. 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme ...
... 1. DNA contains the sugar ribose. 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme ...
Review for Molecular Genetics Quest
... 5. Where does this happen? Make sure to label location and type of cell. There are two answers for this!! ...
... 5. Where does this happen? Make sure to label location and type of cell. There are two answers for this!! ...
Document
... SHORT ANSWER Answer the questions in the space provided. 1. Describe three ways that RNA differs from DNA. ...
... SHORT ANSWER Answer the questions in the space provided. 1. Describe three ways that RNA differs from DNA. ...
Part 4 Transcription
... 9. Understand transcription and the role that RNA polymerase plays in it. ...
... 9. Understand transcription and the role that RNA polymerase plays in it. ...
Name
... Fill in the blank to complete each statement. 1. The process of making proteins is called protein ...
... Fill in the blank to complete each statement. 1. The process of making proteins is called protein ...
Biology: Protein Synthesis, Extra Credit Name: Place these
... Two mRNA codons are exposed to the larger ribosomal sub-unit Hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs of DNA break The tRNA molecule carrying the first amino acid binds by its complimentary anticodon to the first codon RNA Nucleotides are attached to the DNA strand according to the rules of b ...
... Two mRNA codons are exposed to the larger ribosomal sub-unit Hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs of DNA break The tRNA molecule carrying the first amino acid binds by its complimentary anticodon to the first codon RNA Nucleotides are attached to the DNA strand according to the rules of b ...
Nucleic Acids - faculty at Chemeketa
... What will be the composition of the DNA strand complementary to –AGCCA– ? a. b. c. d. ...
... What will be the composition of the DNA strand complementary to –AGCCA– ? a. b. c. d. ...
Mentor: James A. MacKay Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka
... Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive go ...
... Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive go ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.