Slide 1
... • Can be used directly by the cell for energy, stored as glycogen in the muscle and liver or converted to fat • The function of the liver is to convert glycogen into glucose when it is needed for energy production ...
... • Can be used directly by the cell for energy, stored as glycogen in the muscle and liver or converted to fat • The function of the liver is to convert glycogen into glucose when it is needed for energy production ...
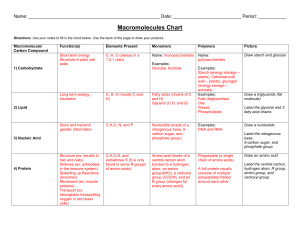
Nucleic acids
... Nucleic acids carry and transmit genetic information. The two most common forms of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. Nucleic acids are made up of smaller monomers of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and hydrogen called nucleotides. The chemical groups that make up nucleotides are phosphates, nitro ...
... Nucleic acids carry and transmit genetic information. The two most common forms of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. Nucleic acids are made up of smaller monomers of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and hydrogen called nucleotides. The chemical groups that make up nucleotides are phosphates, nitro ...
43) What are the membrane structures that function in active
... C) It is a passive processin which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region concentration. D) It is an active processin which molecules move from a region of lower concentration to one of higher concentration. E) It requires integral Proteins in the cell membrane. 46) Which o ...
... C) It is a passive processin which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region concentration. D) It is an active processin which molecules move from a region of lower concentration to one of higher concentration. E) It requires integral Proteins in the cell membrane. 46) Which o ...
Name - MsOttoliniBiology
... in the immune system) Speeding up Reactions (enzymes) Movement (ex: muscle proteins) Transport (ex: hemoglobin transporting oxygen in red blood cells) ...
... in the immune system) Speeding up Reactions (enzymes) Movement (ex: muscle proteins) Transport (ex: hemoglobin transporting oxygen in red blood cells) ...
Lecture-Intro to metabolism - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... Corresponding catabolic and anabolic pathways have one or more distinct enzymes that can be separately controlled ...
... Corresponding catabolic and anabolic pathways have one or more distinct enzymes that can be separately controlled ...
Pertubation of metabolism in IDD Q3-5 Joe - PBL-J-2015
... 3. Indicate the mechanisms by which beta ketoacid production is increased in response to oversupply of fatty acid to the liver, including the steps of the pathways of fatty acid metabolism that are up regulated The oversupply of fatty acids in the liver cells (in the absence of insulin) leads to the ...
... 3. Indicate the mechanisms by which beta ketoacid production is increased in response to oversupply of fatty acid to the liver, including the steps of the pathways of fatty acid metabolism that are up regulated The oversupply of fatty acids in the liver cells (in the absence of insulin) leads to the ...
Carbon Compounds
... • Plants and Animals also use certain carbohydrates as structural building materials ...
... • Plants and Animals also use certain carbohydrates as structural building materials ...
Cellular Metabolism and Nutrition notes
... To release the stored energy, the last phosphate is removed and ADP (adenosine diphosphate) + a phosphate group is formed. ...
... To release the stored energy, the last phosphate is removed and ADP (adenosine diphosphate) + a phosphate group is formed. ...
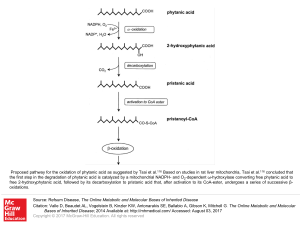
Slide 1 - Ommbid.com
... Proposed pathway for the oxidation of phytanic acid as suggested by Tsai et al.116 Based on studies in rat liver mitochondria, Tsai et al.116 concluded that the first step in the degradation of phytanic acid is catalyzed by a mitochondrial NADPH- and O2-dependent ω-hydroxylase converting free phytan ...
... Proposed pathway for the oxidation of phytanic acid as suggested by Tsai et al.116 Based on studies in rat liver mitochondria, Tsai et al.116 concluded that the first step in the degradation of phytanic acid is catalyzed by a mitochondrial NADPH- and O2-dependent ω-hydroxylase converting free phytan ...
Biological (organic) Molecules
... Transport molecules between cells Relay messages – hormones Speed up reactions – enzymes Test for proteins: use biuret’s reagent, turns from blue to violet in the presence of proteins ...
... Transport molecules between cells Relay messages – hormones Speed up reactions – enzymes Test for proteins: use biuret’s reagent, turns from blue to violet in the presence of proteins ...
Test Review Answers - Northwest ISD Moodle
... -nucleic acids: Nucleotides (Phosphate group, nitrogen base, 5 carbon pentose sugar) 5. Name the Bio-Molecule associated with each item below: -hydrophobic (repels water): Lipids -made entirely of sugar molecules: carbohydrates -contains a phosphate group: nucleic acids -polypeptides: amino acids 6. ...
... -nucleic acids: Nucleotides (Phosphate group, nitrogen base, 5 carbon pentose sugar) 5. Name the Bio-Molecule associated with each item below: -hydrophobic (repels water): Lipids -made entirely of sugar molecules: carbohydrates -contains a phosphate group: nucleic acids -polypeptides: amino acids 6. ...
Lecture 6 POWERPOINT here
... The biosynthetic pathway for the two amino acids E and H is shown schematically below. You are able to show that E inhibits enzyme V, and H inhibits enzyme X. Enzyme T is most likely to be subject to feedback inhibition by __________________ alone. ...
... The biosynthetic pathway for the two amino acids E and H is shown schematically below. You are able to show that E inhibits enzyme V, and H inhibits enzyme X. Enzyme T is most likely to be subject to feedback inhibition by __________________ alone. ...
Ch. 7 Study Guide
... □ I can summarize and explain the role of ATP in cellular metabolism Vocabulary ATP Synthase Complex Chemiosmosis NADH NAD+ FADH FAD+ Active transport Aerobic Anaerobic Glycolysis Mitochondrion Mitochondrial matrix Intermembrane space Krebs cycle Alcohol fermentation Lactic acid fermentation ...
... □ I can summarize and explain the role of ATP in cellular metabolism Vocabulary ATP Synthase Complex Chemiosmosis NADH NAD+ FADH FAD+ Active transport Aerobic Anaerobic Glycolysis Mitochondrion Mitochondrial matrix Intermembrane space Krebs cycle Alcohol fermentation Lactic acid fermentation ...
Unit 2 Test Review
... Molecules that are ‘used’ in a chemical reaction; on the left side of the equation Fats and oils; used for long term energy storage Organic compound that is the building block of organisms; made of amino acids Number (from 0-14) measuring the amount of hydrogen ions in a solution Molecules made duri ...
... Molecules that are ‘used’ in a chemical reaction; on the left side of the equation Fats and oils; used for long term energy storage Organic compound that is the building block of organisms; made of amino acids Number (from 0-14) measuring the amount of hydrogen ions in a solution Molecules made duri ...
Remember: Condensation makes bonds: Hydrolysis breaks bonds.
... There are many organic molecules in living things. The same (or very similar) molecules are used in many different living things for the same purpose. 3. Saccharides are sugars and carbohydrates. Sugars (monosaccharides and disaccharides) are used to build up carbohydrates (polysaccharides). a. Stat ...
... There are many organic molecules in living things. The same (or very similar) molecules are used in many different living things for the same purpose. 3. Saccharides are sugars and carbohydrates. Sugars (monosaccharides and disaccharides) are used to build up carbohydrates (polysaccharides). a. Stat ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... (a) Opponents argued that the weight loss was almost entirely due to water loss and would be regained very soonafter a normal diet was resumed. What is the biochemical basis for this argument? (b) A number of people on this diet died. What are some of the dangers inherent in the diet and how can the ...
... (a) Opponents argued that the weight loss was almost entirely due to water loss and would be regained very soonafter a normal diet was resumed. What is the biochemical basis for this argument? (b) A number of people on this diet died. What are some of the dangers inherent in the diet and how can the ...
Key Terms and Ideas: Fill in the blanks or provide a definition in your
... releases the most random form of energy d. As a surroundings disorder decreases, the system’s disorder increases; as someone holds a ball over a ledge, it drops. e. A, C, and D 2. Spontaneous reactions a. Have a negative ΔG b. Have less useable free energy at the end c. Have more structured substrat ...
... releases the most random form of energy d. As a surroundings disorder decreases, the system’s disorder increases; as someone holds a ball over a ledge, it drops. e. A, C, and D 2. Spontaneous reactions a. Have a negative ΔG b. Have less useable free energy at the end c. Have more structured substrat ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.