Chemistry notes 2013
... move molecules from one place to another around the body. Examples include hemoglobin and cytochromes. Hemoglobin transports oxygen through the blood. Cytochromes operate in the electron transport chain as electron carrier proteins ...
... move molecules from one place to another around the body. Examples include hemoglobin and cytochromes. Hemoglobin transports oxygen through the blood. Cytochromes operate in the electron transport chain as electron carrier proteins ...
4. Sports nutrition, pyramid of health, healthy eating, Mediterranean
... neither too much nor too little of any food or nutrient. Too much food can result in excess weight and even too much of certain nutrients, while eating too little can lead to numerous nutrient deficiencies and low body mass. ...
... neither too much nor too little of any food or nutrient. Too much food can result in excess weight and even too much of certain nutrients, while eating too little can lead to numerous nutrient deficiencies and low body mass. ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... in the membrane and eventually produce ATP. ATP is adenosine triphosphate and is the molecule of chemical energy in all cell processes. ...
... in the membrane and eventually produce ATP. ATP is adenosine triphosphate and is the molecule of chemical energy in all cell processes. ...
(light) reactions
... chemical reactions • making or breaking of bonds between atoms – result in change in chemical energy – potential kinetic energy ...
... chemical reactions • making or breaking of bonds between atoms – result in change in chemical energy – potential kinetic energy ...
Chapter 16.3: Anaerobic Respiration
... – Reoxygenation of hemoglobin in the blood – High metabolic rate (as many organs are operating at above resting levels) ...
... – Reoxygenation of hemoglobin in the blood – High metabolic rate (as many organs are operating at above resting levels) ...
T-17 Chapter 2B notes Section 2.3 Carbon Based Molecules To this
... Notice that the enzyme for one reaction would not work for the enzyme of another reaction because the shapes would not match up. ...
... Notice that the enzyme for one reaction would not work for the enzyme of another reaction because the shapes would not match up. ...
07-Quiz 3 Key
... a. They cause obesity and should be totally eliminated from a healthful diet. b. They are metabolized in the body, producing energy. c. They can be produced in plants by photosynthesis in an endothermic reaction. d. Simple carbohydrates, such as monosaccharides, are made up of C, H, and 0 in a 1: ...
... a. They cause obesity and should be totally eliminated from a healthful diet. b. They are metabolized in the body, producing energy. c. They can be produced in plants by photosynthesis in an endothermic reaction. d. Simple carbohydrates, such as monosaccharides, are made up of C, H, and 0 in a 1: ...
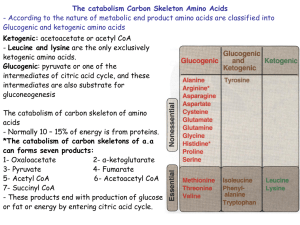
The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
1 - contentextra
... 10 The SA (sinoatrial) node is known as the pacemaker of the heart and gives the heart myogenic properties. However, the function of the node is affected by neuro-endocrine factors. During exercise, blood flow to the skeletal muscle, skin and heart is increased while flood flow to the abdominal orga ...
... 10 The SA (sinoatrial) node is known as the pacemaker of the heart and gives the heart myogenic properties. However, the function of the node is affected by neuro-endocrine factors. During exercise, blood flow to the skeletal muscle, skin and heart is increased while flood flow to the abdominal orga ...
Metabolism
... Concept Definition The processes of biochemical reactions occurring in the body’s cells that are necessary to produce energy, repair, and facilitate the growth of cells, and maintain life. Exemplars None Objectives 1. Explain the concept of metabolism (including definition, antecedents, and attribut ...
... Concept Definition The processes of biochemical reactions occurring in the body’s cells that are necessary to produce energy, repair, and facilitate the growth of cells, and maintain life. Exemplars None Objectives 1. Explain the concept of metabolism (including definition, antecedents, and attribut ...
Biology Unit 2 Organic Notes The Chemistry of Carbon Organic
... Nucleic acids are polymers assembled from individual monomers known as nucleotides. ...
... Nucleic acids are polymers assembled from individual monomers known as nucleotides. ...
CHAPTER 10 REVIEW SHEET Briefly describe metabolism. What
... 28. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the hydrolysis of ATP under standard conditions and in the cellular situation in #27. ...
... 28. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the hydrolysis of ATP under standard conditions and in the cellular situation in #27. ...
Exam II Name
... 23. What can happen if a child with severe protein deficiency is fed very aggressively (a lot of food quickly)? a. the child can die b. the child can become obese c. the child will get better faster 24. A person who has experienced total starvation likely has: a. marasmus b. kwashiorkor 25. A protei ...
... 23. What can happen if a child with severe protein deficiency is fed very aggressively (a lot of food quickly)? a. the child can die b. the child can become obese c. the child will get better faster 24. A person who has experienced total starvation likely has: a. marasmus b. kwashiorkor 25. A protei ...
Prezentacja programu PowerPoint
... Therefore, it should be spread over a few days. It is virtually impossible for one day all kg, and only a few in a few days. First of all, when it is a restrictive diet a person loses water and not fat, ...
... Therefore, it should be spread over a few days. It is virtually impossible for one day all kg, and only a few in a few days. First of all, when it is a restrictive diet a person loses water and not fat, ...
Metabolism
... Liberated from lipid storage in adipose cells by an enzyme (hormonesensitive lipase) Are taken up from the bloodstream by cells Are converted to acetyl CoA which enter the Citric Acid Cycle (CAC) Ketogenesis and ketone bodies Ketogenesis is the process by which ketone bodies are produced a ...
... Liberated from lipid storage in adipose cells by an enzyme (hormonesensitive lipase) Are taken up from the bloodstream by cells Are converted to acetyl CoA which enter the Citric Acid Cycle (CAC) Ketogenesis and ketone bodies Ketogenesis is the process by which ketone bodies are produced a ...
Thermal Homeostasis
... and proteins) is essentially many carbon atoms bound together. Metabolism of food means: • exergonic release of energy between carbon atoms and • release of CO2 as matter. Released energy is either: • coupled to endergonic reactions, or • released as heat ...
... and proteins) is essentially many carbon atoms bound together. Metabolism of food means: • exergonic release of energy between carbon atoms and • release of CO2 as matter. Released energy is either: • coupled to endergonic reactions, or • released as heat ...
Biological Molecules
... Starch (plants) and glycogen (animals) are formed so as not to interfere with cell chemistry and osmosis. They can be quickly broken down to glucose and used as energy. (hydrolysis) ...
... Starch (plants) and glycogen (animals) are formed so as not to interfere with cell chemistry and osmosis. They can be quickly broken down to glucose and used as energy. (hydrolysis) ...
Aesthetic Solutions NY Aleksandr Benji FNP 98
... Inositol (I)- a nutrient belonging to the B vitamin complex, is closely associated with choline. It aids in the metabolism of fats and helps reduce blood cholesterol. Inositol participates in action of serotonin, a neurotransmitter known to control mood and appetite. Choline (C) - supports the healt ...
... Inositol (I)- a nutrient belonging to the B vitamin complex, is closely associated with choline. It aids in the metabolism of fats and helps reduce blood cholesterol. Inositol participates in action of serotonin, a neurotransmitter known to control mood and appetite. Choline (C) - supports the healt ...
Topic 1 PowerPoint
... At rest, a typical systolic blood pressure in a healthy individual ranges from 110140mmHg and 60-90mmHg for diastolic blood pressure. During exercise systolic pressure, the pressure during contraction of the heart (known as systole) can increase to over 200mmHg and levels as high as 250mmHg have bee ...
... At rest, a typical systolic blood pressure in a healthy individual ranges from 110140mmHg and 60-90mmHg for diastolic blood pressure. During exercise systolic pressure, the pressure during contraction of the heart (known as systole) can increase to over 200mmHg and levels as high as 250mmHg have bee ...
Biochemistry Terms
... Lipids include fats and oils, and are important because they store longterm energy in the body. The building blocks of lipids are the fatty acids, which is a chain of carbons with hydrogen attached to each side (see the picture at the right). Saturated fats have two hydrogens attached to each carbon ...
... Lipids include fats and oils, and are important because they store longterm energy in the body. The building blocks of lipids are the fatty acids, which is a chain of carbons with hydrogen attached to each side (see the picture at the right). Saturated fats have two hydrogens attached to each carbon ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.