Document
... Anaerobic metabolic processes have the capacity to provide ATP energy immediately but only for a short duration, while aerobic metabolic processes begin providing ATP energy more slowly but for long durations, provided there is sufficient substrate and oxygen available to the cells. We have large st ...
... Anaerobic metabolic processes have the capacity to provide ATP energy immediately but only for a short duration, while aerobic metabolic processes begin providing ATP energy more slowly but for long durations, provided there is sufficient substrate and oxygen available to the cells. We have large st ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 4 Types of Macromolecules
... Two types of nucleic acids – 1. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – double strand of genetic information 2. RNA (ribonucleic acid) – single strand copy of DNA used to build proteins Examples of nongenetic nucleotides - plays a major role in cell metabolism 1. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) – carries energy ...
... Two types of nucleic acids – 1. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – double strand of genetic information 2. RNA (ribonucleic acid) – single strand copy of DNA used to build proteins Examples of nongenetic nucleotides - plays a major role in cell metabolism 1. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) – carries energy ...
Respiratory Substrates
... • Some can be converted to pyruvate, or acetate and then is carried to Krebs cycle • Some can enter Krebs directly • Number of hydrogen atoms per mole accepted by NAD then used in electron transport chain is slightly more than the number of hydrogen atoms per mole of glucose, so proteins release sli ...
... • Some can be converted to pyruvate, or acetate and then is carried to Krebs cycle • Some can enter Krebs directly • Number of hydrogen atoms per mole accepted by NAD then used in electron transport chain is slightly more than the number of hydrogen atoms per mole of glucose, so proteins release sli ...
control of intermediary metabolism
... SUGAR CAN BE BURNED WITHOUT OXYGEN - ANAEROBICALLY FAR MORE ENERGY RELEASED FROM BURNING SUGAR AEROBICALLY GLYCOLYSIS IS ANAEROBIC-CARRIED OUT IN CYTOSOL GLUCOSE ----> 3 CARBON FRAGMENTS PLUS 2 ATP ...
... SUGAR CAN BE BURNED WITHOUT OXYGEN - ANAEROBICALLY FAR MORE ENERGY RELEASED FROM BURNING SUGAR AEROBICALLY GLYCOLYSIS IS ANAEROBIC-CARRIED OUT IN CYTOSOL GLUCOSE ----> 3 CARBON FRAGMENTS PLUS 2 ATP ...
ChemGym_ForensicsAnswers
... 1. Classify each of the following activities as aerobic or anaerobic. a. walking up a flight of stairs, aerobic b. walking up 50 flights of stairs, aerobic c. studying, aerobic d. weight lifting, anaerobic 2. What are the benefits of increased VO2 max? An increase in VO2 max means that there is more ...
... 1. Classify each of the following activities as aerobic or anaerobic. a. walking up a flight of stairs, aerobic b. walking up 50 flights of stairs, aerobic c. studying, aerobic d. weight lifting, anaerobic 2. What are the benefits of increased VO2 max? An increase in VO2 max means that there is more ...
Compare and contrast organic molecules and inorganic - bl-whs
... inorganic molecules. Organic - All contain Carbon ...
... inorganic molecules. Organic - All contain Carbon ...
Chapter 5 - Missouri State University
... –Through a series of reactions, citric acid is converted to _________________________ to complete the pathway. ...
... –Through a series of reactions, citric acid is converted to _________________________ to complete the pathway. ...
Food - cbbiology
... Sources of proteins: fish, egg, nuts, peas & beans Deamination: If we eat too much protein excess amino acids are brought to the liver and broken down to urea. Following deamination, urea is taken to the kidney where it is used to make urine. ...
... Sources of proteins: fish, egg, nuts, peas & beans Deamination: If we eat too much protein excess amino acids are brought to the liver and broken down to urea. Following deamination, urea is taken to the kidney where it is used to make urine. ...
chapter 4 pptol
... Pyruvic acid is converted to lactic acid Glycolysis is inhibited Q8 IN ANIMALS WHAT IS THE OUTPUT OF FERMENTATION? ...
... Pyruvic acid is converted to lactic acid Glycolysis is inhibited Q8 IN ANIMALS WHAT IS THE OUTPUT OF FERMENTATION? ...
The six elements that make up 99.9% of all living things include
... The properties of water make it very valuable to living systems. Which of the following statements regarding water is not true? 1. it modifies temperature extremes 2. it makes up about 50% of your body 3. it is the greatest solvent in the world 4. it expands slightly when it freezes 5. it covers mo ...
... The properties of water make it very valuable to living systems. Which of the following statements regarding water is not true? 1. it modifies temperature extremes 2. it makes up about 50% of your body 3. it is the greatest solvent in the world 4. it expands slightly when it freezes 5. it covers mo ...
Practice Exam I
... store energy catalyze reactions contain hereditary information make up membranes ...
... store energy catalyze reactions contain hereditary information make up membranes ...
Organic Molecules
... Short to intermediate energy storage Starch in plants, glycogen in animals Cellulose used as structural material Energy is released when cells break down glycogen / starch • Condensation- water taken out (joins) • Hydrolysis- add water (break apart) ...
... Short to intermediate energy storage Starch in plants, glycogen in animals Cellulose used as structural material Energy is released when cells break down glycogen / starch • Condensation- water taken out (joins) • Hydrolysis- add water (break apart) ...
Equine Nutrition
... Cardiovascular system Respiratory system Muscular system Biomechanics and conformation Hematology Nutrition ...
... Cardiovascular system Respiratory system Muscular system Biomechanics and conformation Hematology Nutrition ...
FERMENTATION: an anaerobic biological reaction process in which
... • In bacteria, the trp repressor protein inhibits the transcription of a suite of genes coding for enyzmes required for the synthesis of the amino acid tryptophan • In the absence of tryptophan, the recognition helices are not in the proper orientation to contact the promoter DNA; no repressor binds ...
... • In bacteria, the trp repressor protein inhibits the transcription of a suite of genes coding for enyzmes required for the synthesis of the amino acid tryptophan • In the absence of tryptophan, the recognition helices are not in the proper orientation to contact the promoter DNA; no repressor binds ...
Biochemistry Review
... 2. What type of compound does not contain carbon atoms? Inorganic 3. What are the reasons carbon is unique among elements? Covalent Bonding; Form Wide Variety of Simple and Complex Organic Compounds 4. What type of structures can carbon atoms form? Ring, Straight and Branched Chains, Single, Double, ...
... 2. What type of compound does not contain carbon atoms? Inorganic 3. What are the reasons carbon is unique among elements? Covalent Bonding; Form Wide Variety of Simple and Complex Organic Compounds 4. What type of structures can carbon atoms form? Ring, Straight and Branched Chains, Single, Double, ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... 3. Some bacteria live in hot springs. Their cells contain enzymes that function best at temperatures of 70°C. At a temperature of 95°C, how will the enzymes in these bacterial cells most likely be affected? A. The enzymes will be destroyed by lysosomes. B. The enzymes will lose their shape be unable ...
... 3. Some bacteria live in hot springs. Their cells contain enzymes that function best at temperatures of 70°C. At a temperature of 95°C, how will the enzymes in these bacterial cells most likely be affected? A. The enzymes will be destroyed by lysosomes. B. The enzymes will lose their shape be unable ...
Living things are energy rich complex chemical structures
... DETERMINES IT’S FUNCTION ( WHAT IT DOES) ...
... DETERMINES IT’S FUNCTION ( WHAT IT DOES) ...
BIo Exam Trashketball Review Questions
... A specific reactant acted upon by an enzyme is called the enzyme’s _____________________. ...
... A specific reactant acted upon by an enzyme is called the enzyme’s _____________________. ...
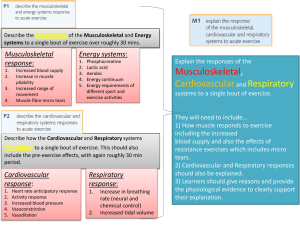
P1, P2, M1 Muscular and energy systems response to acute exercise
... blood supply and also the effects of resistance exercises which includes micro tears. 2) Cardiovascular and Respiratory responses should also be explained. 3) Learners should give reasons and provide the physiological evidence to clearly support ...
... blood supply and also the effects of resistance exercises which includes micro tears. 2) Cardiovascular and Respiratory responses should also be explained. 3) Learners should give reasons and provide the physiological evidence to clearly support ...
Respiration and breathing Task 1 Task 2
... Oxygen is transported in the blood to all parts of the body. Oxygen diffuses into the body cells. Oxygen is used by cells for respiration to release energy from glucose. Carbon dioxide and water are waste products of respiration. Carbon dioxide diffuses from the body cells into the blood. Carbon dio ...
... Oxygen is transported in the blood to all parts of the body. Oxygen diffuses into the body cells. Oxygen is used by cells for respiration to release energy from glucose. Carbon dioxide and water are waste products of respiration. Carbon dioxide diffuses from the body cells into the blood. Carbon dio ...
Energy metabolism
... cholesterol. However, plasma epinephrine and serum free fatty acid concentrations were increased (P < 0[middle dot]05). In the third experiment, BM(7.5 and 15 g/kg) and 1[middle dot]5 % BM lowered triacylglycerol concentration in red gastrocnemius and tibialis anterior (P < 0[middle dot]05) muscle, ...
... cholesterol. However, plasma epinephrine and serum free fatty acid concentrations were increased (P < 0[middle dot]05). In the third experiment, BM(7.5 and 15 g/kg) and 1[middle dot]5 % BM lowered triacylglycerol concentration in red gastrocnemius and tibialis anterior (P < 0[middle dot]05) muscle, ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.