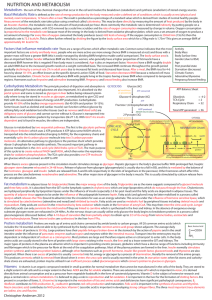
Metabolism08
... compounds (CATABOLIC) or build more complex compounds (ANABOLIC) Metabolic pathways are never completely inactive ...
... compounds (CATABOLIC) or build more complex compounds (ANABOLIC) Metabolic pathways are never completely inactive ...
BioH Ch 19 Origin of Life 2013
... These self-replicating “units” may have been enclosed in a double layer of phospholipids. This would be considered the “first cell”. ...
... These self-replicating “units” may have been enclosed in a double layer of phospholipids. This would be considered the “first cell”. ...
Organic Molecules - Mr. Swords` Classes
... Speeds up reaction, can be used over and over again. The reaction does not change it (like a key!) ...
... Speeds up reaction, can be used over and over again. The reaction does not change it (like a key!) ...
Study Guide and Potential Essay Questions for Chapter 25
... Study Guide and Potential Essay Questions for Chapter 25 – Metabolism NOTE: We may not have time to cover all of these this term. Concentrate on questions involving what we actually covered in lecture. Some terms Know the definition and physiological/anatomical significance of the following: anaboli ...
... Study Guide and Potential Essay Questions for Chapter 25 – Metabolism NOTE: We may not have time to cover all of these this term. Concentrate on questions involving what we actually covered in lecture. Some terms Know the definition and physiological/anatomical significance of the following: anaboli ...
Glycolysis
... Energy for the body • Trapped in chemical bonds of fats, proteins, and carbs (potential) • liberate energy – break bonds – release energy, CO2 and H20 – Energy is transferred to ATP for use in the body ...
... Energy for the body • Trapped in chemical bonds of fats, proteins, and carbs (potential) • liberate energy – break bonds – release energy, CO2 and H20 – Energy is transferred to ATP for use in the body ...
→ Why organisms need food: → Elements in Food: → Carbohydrates:
... Proteins: o Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen o The elements combine to form amino acids- (20 common amino acids are found in proteins) o Amino acids combine to form peptide bonds (less than 20) or polypeptide bonds (more than 20) o Structural role: Keratin is found in skin, hair an ...
... Proteins: o Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen o The elements combine to form amino acids- (20 common amino acids are found in proteins) o Amino acids combine to form peptide bonds (less than 20) or polypeptide bonds (more than 20) o Structural role: Keratin is found in skin, hair an ...
LECTURE #1 STUDY GUIDE
... Energy Release From Protein After nitrogen removal from an amino acid, what happens to the remaining “carbon skeleton” in energy metabolism? ...
... Energy Release From Protein After nitrogen removal from an amino acid, what happens to the remaining “carbon skeleton” in energy metabolism? ...
Major Metabolic Pathway
... produces ethanol when grown under anaerobic conditions. However, the major product is yeast cells when growth conditions are aerobic. More over, even under aerobic conditions at high glucose concentrations, some ethanol production is observed. Which indicates metabolic regulation not only by oxygen ...
... produces ethanol when grown under anaerobic conditions. However, the major product is yeast cells when growth conditions are aerobic. More over, even under aerobic conditions at high glucose concentrations, some ethanol production is observed. Which indicates metabolic regulation not only by oxygen ...
One Diet Does Not Fit All
... The key to losing weight and keeping it off is to incorporate healthy eating habits and regular exercise into one’s life. By making a few adjustments in one’s daily eating and exercise patterns, changes in physical appearance, as well as in overall health, will result without taking drastic measures ...
... The key to losing weight and keeping it off is to incorporate healthy eating habits and regular exercise into one’s life. By making a few adjustments in one’s daily eating and exercise patterns, changes in physical appearance, as well as in overall health, will result without taking drastic measures ...
1.3.7 Metabolic Role of Biomolecules
... primary source of energy • State that proteins act as enzymes and are made of amino acids • State that hormones (protein) act as regulators of metabolic activity • State that vitamin C & D are used for tissue growth, cell production and health ...
... primary source of energy • State that proteins act as enzymes and are made of amino acids • State that hormones (protein) act as regulators of metabolic activity • State that vitamin C & D are used for tissue growth, cell production and health ...
Nutrients
... in cytosol (NAD is hydrogenated and carbon dioxide is released) Acetyl CoA is shuttled into the mitochondria Series of reactions takes place One ATP is created (per Acetyl CoA) 2 carbon dioxides are released 3 NADs are hydrogenated One flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is ...
... in cytosol (NAD is hydrogenated and carbon dioxide is released) Acetyl CoA is shuttled into the mitochondria Series of reactions takes place One ATP is created (per Acetyl CoA) 2 carbon dioxides are released 3 NADs are hydrogenated One flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is ...
research abstract form
... Obesity is a chronic condition that primarily develops from an increase in body fat in the form of white adipose tissue (WAT) mass. The resulting adiposity is a risk factor for many diseases, including type 2 diabetes (T2D), cardiovascular diseases, and some forms of cancer. White adipocytes, the ma ...
... Obesity is a chronic condition that primarily develops from an increase in body fat in the form of white adipose tissue (WAT) mass. The resulting adiposity is a risk factor for many diseases, including type 2 diabetes (T2D), cardiovascular diseases, and some forms of cancer. White adipocytes, the ma ...
Sample
... d. Looking up the energy cost of each activity and taking an average e. A treadmill with variable resistance/speed 15. What is “essential” about an essential nutrient? a. It tastes so good b. It is innately programmed to be preferred c. It cannot be made in the body d. It is essential to fuel mitcho ...
... d. Looking up the energy cost of each activity and taking an average e. A treadmill with variable resistance/speed 15. What is “essential” about an essential nutrient? a. It tastes so good b. It is innately programmed to be preferred c. It cannot be made in the body d. It is essential to fuel mitcho ...
Which of the following describes the sum of all chemical reactions
... 18. Body mass index (BMI) is an index of a person’s weight in relation to height. 19. When an adult gains an extra 10 pounds of body weight, approximately how much of this is fat? 20. Approximately what percentage of weight loss during starvation is lean body mass? 21. In what region of the body is ...
... 18. Body mass index (BMI) is an index of a person’s weight in relation to height. 19. When an adult gains an extra 10 pounds of body weight, approximately how much of this is fat? 20. Approximately what percentage of weight loss during starvation is lean body mass? 21. In what region of the body is ...
Animal form and function
... Basal metabolic rate: at rest Endotherm: 1,600 – 2,000Kcal/day Maximum rate: can not sustain for long Use: ATP that’s already present Then make some anaerobically by glycolysis Start to break down glycogen in liver and muscle cells ...
... Basal metabolic rate: at rest Endotherm: 1,600 – 2,000Kcal/day Maximum rate: can not sustain for long Use: ATP that’s already present Then make some anaerobically by glycolysis Start to break down glycogen in liver and muscle cells ...
15_intro-to
... pathway in a steady state is more or less constant • A steady state far from equilibrium is thermodynamically efficient because only a nonequilibrium process can perform work • The flux of intermediates in a pathway is set by the rate-determining step ...
... pathway in a steady state is more or less constant • A steady state far from equilibrium is thermodynamically efficient because only a nonequilibrium process can perform work • The flux of intermediates in a pathway is set by the rate-determining step ...
Poster
... Plants need Magnesium to make chlorophyll and calcium for the cell walls Animals need iron to make haemoglobin and calcium for healthy bones. ...
... Plants need Magnesium to make chlorophyll and calcium for the cell walls Animals need iron to make haemoglobin and calcium for healthy bones. ...
Nutrition and Metabolism
... Metabolism - the sum of the chemical changes that occur in the cell and involve the breakdown (catabolism) and synthesis (anabolism) of stored energy sources. Basal Metabolic Rate is defined as the rate of energy production by the body measured under a defined set of conditions which is usually at r ...
... Metabolism - the sum of the chemical changes that occur in the cell and involve the breakdown (catabolism) and synthesis (anabolism) of stored energy sources. Basal Metabolic Rate is defined as the rate of energy production by the body measured under a defined set of conditions which is usually at r ...
Unit 2: Metabolic Processes Metabolism and Energy
... energy lost by a person’s body over time (at rest) - Decreases with age - Body becomes more efficient at same tasks - Less physical activity, less muscle ...
... energy lost by a person’s body over time (at rest) - Decreases with age - Body becomes more efficient at same tasks - Less physical activity, less muscle ...
Document
... balance. 30-50% of BW variation genetic, the remainder environmental. (B) Appetite – determined by hypothalamus. Influenced by hormones (leptin, ghrelin), drugs (THC), emotions. (C) Obesity – more than 20% over ideal body weight, approximately 1/3 of American adults. Often determined by measuring BM ...
... balance. 30-50% of BW variation genetic, the remainder environmental. (B) Appetite – determined by hypothalamus. Influenced by hormones (leptin, ghrelin), drugs (THC), emotions. (C) Obesity – more than 20% over ideal body weight, approximately 1/3 of American adults. Often determined by measuring BM ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.