lecture1
... Metabolic pathways can be linear, e.g. glycolysis or can be cyclic, e.g. TCA. In general, the rate of catabolism is controlled not by the conc. of nutrients available in the environment of the cell, but by the cell’s need for energy in the form of ATP. Similarly, the rate of biosynthesis of cell com ...
... Metabolic pathways can be linear, e.g. glycolysis or can be cyclic, e.g. TCA. In general, the rate of catabolism is controlled not by the conc. of nutrients available in the environment of the cell, but by the cell’s need for energy in the form of ATP. Similarly, the rate of biosynthesis of cell com ...
Chapter 1 - Private Label Fitness
... You use the “Thigh-Master” and Suzanne Somers Workout Video You workout the same “spot” everyday Applied toward thighs or abdominal areas None of the above – Spot reducing is a myth ...
... You use the “Thigh-Master” and Suzanne Somers Workout Video You workout the same “spot” everyday Applied toward thighs or abdominal areas None of the above – Spot reducing is a myth ...
Factor4 Weight Control
... Leads to the following toxic effects: • Break down of muscle tissue • Poor muscle tone and body definition • Activation of metabolic pathways to store fat • Food cravings, hunger attacks & famished states which lead to eating binges ...
... Leads to the following toxic effects: • Break down of muscle tissue • Poor muscle tone and body definition • Activation of metabolic pathways to store fat • Food cravings, hunger attacks & famished states which lead to eating binges ...
Chapter 7 Cell Membranes & Transport
... catalyze, the rate of reaction in cells – heat can too, but heat can kill cells • Enzymes help the body break down food and free energy stored in chemical ...
... catalyze, the rate of reaction in cells – heat can too, but heat can kill cells • Enzymes help the body break down food and free energy stored in chemical ...
simple basic metabolism
... absorbed into the cells of our body. As these molecules of glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids are broken down further, energy is released. This energy is used in the cells to synthesize high—energy compounds such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Our cells utilize ATP energy when they do work such ...
... absorbed into the cells of our body. As these molecules of glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids are broken down further, energy is released. This energy is used in the cells to synthesize high—energy compounds such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Our cells utilize ATP energy when they do work such ...
Self Assessment Form This is a pre
... Public Health Nutrition. Applicants should use this form to self declare any relevant prior study which can be used as part of the admissions process and as outlined in the admissions requirement information. It is the applicants responsibility to ensure this form is completed sufficiently and writt ...
... Public Health Nutrition. Applicants should use this form to self declare any relevant prior study which can be used as part of the admissions process and as outlined in the admissions requirement information. It is the applicants responsibility to ensure this form is completed sufficiently and writt ...
Self Assessment Form This is a pre
... Public Health Nutrition. Applicants should use this form to self declare any relevant prior study which can be used as part of the admissions process and as outlined in the admissions requirement information. It is the applicant’s responsibility to ensure this form is completed sufficiently and writ ...
... Public Health Nutrition. Applicants should use this form to self declare any relevant prior study which can be used as part of the admissions process and as outlined in the admissions requirement information. It is the applicant’s responsibility to ensure this form is completed sufficiently and writ ...
Chemistry of Cooking, Chemisty in the Kitchen
... 11. one of 3 main nutrients: contain elements C,H,O (commonly 2 Hydrogen for each Oxygen atom) 12. Fe(II) wheel 13. a 'carboxylic acid' that fuels living cells 16. uncommon in nature - ie: elaidic acid 17. element Fe: blood, Flatirons are red b/c of this 18. one of 3 main nutrients: chain of amino a ...
... 11. one of 3 main nutrients: contain elements C,H,O (commonly 2 Hydrogen for each Oxygen atom) 12. Fe(II) wheel 13. a 'carboxylic acid' that fuels living cells 16. uncommon in nature - ie: elaidic acid 17. element Fe: blood, Flatirons are red b/c of this 18. one of 3 main nutrients: chain of amino a ...
Name: Date: Concept Check Questions Chapter 8 (orange) or 6
... 2. A key process in metabolism is the transfer of H+ ions across a membrane to create a concentration gradient. In some conditions, H+ ions flow back across the membrane and come to equal concentrations on each side. In which conditions can the H+ ions perform work in this system? 8.3 ATP powers cel ...
... 2. A key process in metabolism is the transfer of H+ ions across a membrane to create a concentration gradient. In some conditions, H+ ions flow back across the membrane and come to equal concentrations on each side. In which conditions can the H+ ions perform work in this system? 8.3 ATP powers cel ...
Metabolomic Profiling of Dynamic and Basal Measures of Glucose
... underlying risk factors in minority populations. With an emphasis on metabolic disease, her research concentration is on diabetes, obesity, liver disease, nephropathy, and cardiovascular disease. She was awarded a K99/R00 Pathway to Independence award which advanced her expertise in the areas of hig ...
... underlying risk factors in minority populations. With an emphasis on metabolic disease, her research concentration is on diabetes, obesity, liver disease, nephropathy, and cardiovascular disease. She was awarded a K99/R00 Pathway to Independence award which advanced her expertise in the areas of hig ...
Ch7METABOLISM
... Protein is only used for energy in the absence of carbohydrate or fat Carbon skeletons: are formed by the deamination of amino acids and can enter the metabolic pathways at several points depending on their structure (# carbons) Glucogenic Amino Acids: become pyruvate or a citric acid cycle intermed ...
... Protein is only used for energy in the absence of carbohydrate or fat Carbon skeletons: are formed by the deamination of amino acids and can enter the metabolic pathways at several points depending on their structure (# carbons) Glucogenic Amino Acids: become pyruvate or a citric acid cycle intermed ...
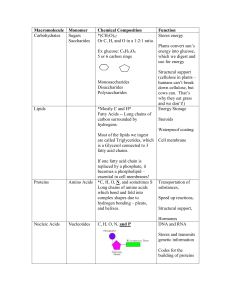
Macronutrients and Their Roles in the Body
... Without enough protein, body will take the protein already stored and use for energy è can’t use to build up body ...
... Without enough protein, body will take the protein already stored and use for energy è can’t use to build up body ...
organic compounds
... 1. Feedback mechanisms are cycles in which the product of one reaction causes another to start or stop. D) While organisms are balanced, they are not unchanging. The term used to describe the balanced state is dynamic equilibrium. 1. Dynamic Equilibrium: A balanced state created by many small, oppos ...
... 1. Feedback mechanisms are cycles in which the product of one reaction causes another to start or stop. D) While organisms are balanced, they are not unchanging. The term used to describe the balanced state is dynamic equilibrium. 1. Dynamic Equilibrium: A balanced state created by many small, oppos ...
2.3 Outline
... • Carbohydrates are a key source of energy, and they are found in most foods--especially fruits, vegetables, and grains. • The building blocks of carbohydrates are single sugars, called _________________________, such as glucose, C6H12O6, and fructose. • Simple sugars such as glucose are a major sou ...
... • Carbohydrates are a key source of energy, and they are found in most foods--especially fruits, vegetables, and grains. • The building blocks of carbohydrates are single sugars, called _________________________, such as glucose, C6H12O6, and fructose. • Simple sugars such as glucose are a major sou ...
Nutrients Info. Sheet
... -helps transport nutrients to body and extract wastes from the body -gives the body shape (cells are filled with water) -helps regulate the body’s temperature -least expensive nutrient -most important nutrient (animals can’t live without it) ...
... -helps transport nutrients to body and extract wastes from the body -gives the body shape (cells are filled with water) -helps regulate the body’s temperature -least expensive nutrient -most important nutrient (animals can’t live without it) ...
Nutrients that have Calories
... • Made from hundreds or thousands of amino acids linked together. • Humans need twenty different amino acids • All proteins are either structural or enzymes • Structural – proteins that form structures (like hair or tendons) • Enzymes – make body process happen and efficient ...
... • Made from hundreds or thousands of amino acids linked together. • Humans need twenty different amino acids • All proteins are either structural or enzymes • Structural – proteins that form structures (like hair or tendons) • Enzymes – make body process happen and efficient ...
Metabolism_PartII Group work
... o Fermentation Part B: Now label on each diagram how the harvested energy is stored during each catabolic process. ATP • Substrate-level phosphorylation and/or • Oxidative phosphorylation Proton motive force • Electron transport chain o Oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions o Active transport ...
... o Fermentation Part B: Now label on each diagram how the harvested energy is stored during each catabolic process. ATP • Substrate-level phosphorylation and/or • Oxidative phosphorylation Proton motive force • Electron transport chain o Oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions o Active transport ...
`Keto-adapt` your clients in 3 months in 8 easy steps
... Founder, executive & scientific director Alliance for Natural Health International www.anhinternational.org ...
... Founder, executive & scientific director Alliance for Natural Health International www.anhinternational.org ...
Macromolecule
... down cellulose, but cows can. That’s why they eat grass and we don’t!) Energy Storage Steroids Waterproof coating ...
... down cellulose, but cows can. That’s why they eat grass and we don’t!) Energy Storage Steroids Waterproof coating ...
Name: Date: Concept Check Questions Chapter 9 Cellular
... molecule acts as the oxidizing agent? The reducing agent? 9.3 The citric acid cycle completes the energy-yielding oxidation of organic molecules ...
... molecule acts as the oxidizing agent? The reducing agent? 9.3 The citric acid cycle completes the energy-yielding oxidation of organic molecules ...
Topic One: Chemistry of Living Things I. All living things must
... Converted into ___________by soil bacteria. Nitrates are ___________by plants and then eaten by animals. Excreted as waste in ammonia or ___________. E) Acids and Bases: Used for different functions in body (such as digestion). Measured by the __________scale Very high and very low pHs are u ...
... Converted into ___________by soil bacteria. Nitrates are ___________by plants and then eaten by animals. Excreted as waste in ammonia or ___________. E) Acids and Bases: Used for different functions in body (such as digestion). Measured by the __________scale Very high and very low pHs are u ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.