PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 6 Cellular Respiration
... glycogen, in our liver & muscle cells. How is glycogen used between meals? Glycogen is hydrolyzed to glucose to serve as fuel between meals. ...
... glycogen, in our liver & muscle cells. How is glycogen used between meals? Glycogen is hydrolyzed to glucose to serve as fuel between meals. ...
NUTRITION & DIGESTION - Fox Valley Lutheran High School
... • Our diets should be limited in fats, especially saturated fats. • Fats and Energy ...
... • Our diets should be limited in fats, especially saturated fats. • Fats and Energy ...
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... Examples of structural support polysaccharides: -cellulose = structural component of plant cell walls that -chitin = forms exoskeletons of arthropods ...
... Examples of structural support polysaccharides: -cellulose = structural component of plant cell walls that -chitin = forms exoskeletons of arthropods ...
Answers for extension worksheet – Option C
... amino acids, which are then deaminated (the NH2 group is removed). The remainder of the molecule enters the respiratory process. Some amino acids are converted to pyruvate, others enter the Krebs cycle. In either case, ATP is synthesised in the usual way. This only occurs during starvation because t ...
... amino acids, which are then deaminated (the NH2 group is removed). The remainder of the molecule enters the respiratory process. Some amino acids are converted to pyruvate, others enter the Krebs cycle. In either case, ATP is synthesised in the usual way. This only occurs during starvation because t ...
Slide 1
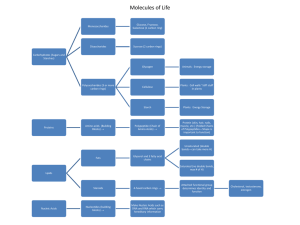
... maintenance of life. In metabolism some substances are broken down to yield energy for vital processes while other substances, necessary for life, are synthesized. B. Polymers – a large molecule that is made up of many small molecules linked (covalent bonds) together. 1. Dehydration synthesis – when ...
... maintenance of life. In metabolism some substances are broken down to yield energy for vital processes while other substances, necessary for life, are synthesized. B. Polymers – a large molecule that is made up of many small molecules linked (covalent bonds) together. 1. Dehydration synthesis – when ...
... carbon to carbon bonds is double or triple. 12. What are proteins? macromolecules containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen; usually made of more than one polypeptide chain. 13. What are amino acids? building blocks (monomers) of proteins; twenty kinds 14. What are Reactants? Substances that ...
File
... Similar in composition to lipids, but structurally composed of interconnected carbon rings Most common steroid is cholesterol Used to create sex hormones, hormones from the adrenal cortex, and vitamin D Found in large amounts in nerve tissue Component of gallstones ...
... Similar in composition to lipids, but structurally composed of interconnected carbon rings Most common steroid is cholesterol Used to create sex hormones, hormones from the adrenal cortex, and vitamin D Found in large amounts in nerve tissue Component of gallstones ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
... The effect of injury severity on nitrogen wasting. (From Long CL, Schaffel N, Geiger J, et al. Metabolic response to injury and illness: estimation of energy and protein needs from indirect calorimetry and nitrogen balance. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1979;3(6):452. Copyright © 1979 by A.S.P.E.N. ...
... The effect of injury severity on nitrogen wasting. (From Long CL, Schaffel N, Geiger J, et al. Metabolic response to injury and illness: estimation of energy and protein needs from indirect calorimetry and nitrogen balance. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1979;3(6):452. Copyright © 1979 by A.S.P.E.N. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 21. What are perturbations? How are they helpful in analyzing flux? 22. Describe Pentose phosphate pathway and its regulation. 23. Give a schematic representation of various types of enzyme inhibition. 24. What are secondary metabolites? Discuss its production in a plant cell. 25. What are the crite ...
... 21. What are perturbations? How are they helpful in analyzing flux? 22. Describe Pentose phosphate pathway and its regulation. 23. Give a schematic representation of various types of enzyme inhibition. 24. What are secondary metabolites? Discuss its production in a plant cell. 25. What are the crite ...
Unit 2 Metabolism and Survival Glossary
... Ligase an enzyme which joins fragments of DNA together Metabolites the intermediates and products of metabolic reactions that take place in organisms Migration a process which avoids metabolic adversity by expending energy to relocate to a more suitable environment Mitochondria a structure in the ce ...
... Ligase an enzyme which joins fragments of DNA together Metabolites the intermediates and products of metabolic reactions that take place in organisms Migration a process which avoids metabolic adversity by expending energy to relocate to a more suitable environment Mitochondria a structure in the ce ...
Blue Flashcards (CR) - mvhs
... Products per molecule glucose: ____________________________ Occurs in two metabolic processes: ____________________ and ____________________ ...
... Products per molecule glucose: ____________________________ Occurs in two metabolic processes: ____________________ and ____________________ ...
Ch 8 Carbon Chem
... 1. Diamond-A crystalline form of carbon where each carbon atom is strongly bonded to four other carbons. 2. Graphite-each carbon is bonded to 3 other carbons in layers. The layers have a weak attraction to each other. B. Shapes made by scientists 1.Fulerene-Carbon atoms arranged in the shape of a ho ...
... 1. Diamond-A crystalline form of carbon where each carbon atom is strongly bonded to four other carbons. 2. Graphite-each carbon is bonded to 3 other carbons in layers. The layers have a weak attraction to each other. B. Shapes made by scientists 1.Fulerene-Carbon atoms arranged in the shape of a ho ...
7. Metabolism
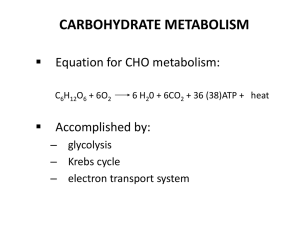
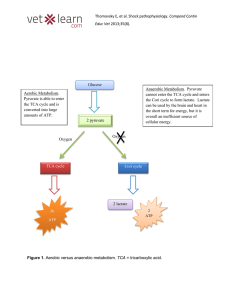
... A. Glucose 1. Glucose-to-pyruvate is called glycolysis or glucose splitting. 2. Pyruvate’s Options a. Anaerobic – lactic acid b. Aerobic – acetyl CoA 3. Pyruvate-to-Lactate a. Oxygen is not available or cells lack sufficient mitochondria b. Lactate is formed when hydrogen is added to pyruvate. c. Li ...
... A. Glucose 1. Glucose-to-pyruvate is called glycolysis or glucose splitting. 2. Pyruvate’s Options a. Anaerobic – lactic acid b. Aerobic – acetyl CoA 3. Pyruvate-to-Lactate a. Oxygen is not available or cells lack sufficient mitochondria b. Lactate is formed when hydrogen is added to pyruvate. c. Li ...
Carbohydrates
... V. Unsaturated Fats • liquid at room temperature • they lack one pair of hydrogen atoms • olive oil, peanut oil, vegetable oil ...
... V. Unsaturated Fats • liquid at room temperature • they lack one pair of hydrogen atoms • olive oil, peanut oil, vegetable oil ...
BIOS 1300 SI WORKSHEET 2 (Chapter 2) SI Leader: Merrin Jeffries
... Dehydration synthesis: The joining of two molecules associated with the removal of a water molecule Hydrolysis: The breakage of a chemical bond through the addition of a water molecule; the reverse of dehydration synthesis Hydrophilic: freely associating with water; readily entering into solution; w ...
... Dehydration synthesis: The joining of two molecules associated with the removal of a water molecule Hydrolysis: The breakage of a chemical bond through the addition of a water molecule; the reverse of dehydration synthesis Hydrophilic: freely associating with water; readily entering into solution; w ...
Outline
... 1. To be used for energy, amino acids are converted into pyruvic acid or keto-acids that can then enter into Krebs A) this process involves the following events: 1) One of any number of amino acids transfers their amine group to -ketoglutaric acid resulting in the formation of a) this process is kn ...
... 1. To be used for energy, amino acids are converted into pyruvic acid or keto-acids that can then enter into Krebs A) this process involves the following events: 1) One of any number of amino acids transfers their amine group to -ketoglutaric acid resulting in the formation of a) this process is kn ...
Text S3: Fatty acid synthesis and catabolism
... Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 is able to synthesize fatty acids de novo from acetyl-CoA and incorporate them into phospholipids. This strain has an absolute requirement for several volatile acids for growth [1], utilizing isobutyrate and valerate for production of phospholipid molecules [2] containin ...
... Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 is able to synthesize fatty acids de novo from acetyl-CoA and incorporate them into phospholipids. This strain has an absolute requirement for several volatile acids for growth [1], utilizing isobutyrate and valerate for production of phospholipid molecules [2] containin ...
ppt Oxygen Debt-Energy Systems - NCEA-Physical
... Absolute oxygen uptake (ml.min.) Relative oxygen uptake (ml.kg.min.) ...
... Absolute oxygen uptake (ml.min.) Relative oxygen uptake (ml.kg.min.) ...
Biomolecules PPT
... primary source of energy • State that proteins act as enzymes and are made of amino acids • State that hormones (protein) act as regulators of metabolic activity • State that vitamin C & D are used for tissue growth, cell production and health ...
... primary source of energy • State that proteins act as enzymes and are made of amino acids • State that hormones (protein) act as regulators of metabolic activity • State that vitamin C & D are used for tissue growth, cell production and health ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.