BIOMOLECULES UNIT 3 Chemistry Review: Atoms
... Chemical reactions- reactions between atoms and/or groups of atoms that rearrange into new substances. Macromolecules: large molecules formed joining small molecules together. Polymers-repeating units of identical, or mostly identical units Monomer- single unit All bonds of macromolecules are covale ...
... Chemical reactions- reactions between atoms and/or groups of atoms that rearrange into new substances. Macromolecules: large molecules formed joining small molecules together. Polymers-repeating units of identical, or mostly identical units Monomer- single unit All bonds of macromolecules are covale ...
biochem2
... Organic molecules are a class of molecules which contain CARBON. Organic molecules are composed of C, H, O, N, P, and S. They are large molecules known as MACROMOLECULES. The macromolecules are composed of submits called MONOMERS. A POLYMER is composed of many monomers. ...
... Organic molecules are a class of molecules which contain CARBON. Organic molecules are composed of C, H, O, N, P, and S. They are large molecules known as MACROMOLECULES. The macromolecules are composed of submits called MONOMERS. A POLYMER is composed of many monomers. ...
Organic Compounds
... Organic molecules are a class of molecules which contain CARBON. Organic molecules are composed of C, H, O, N, P, and S. They are large molecules known as MACROMOLECULES. The macromolecules are composed of submits called MONOMERS. A POLYMER is composed of many monomers. ...
... Organic molecules are a class of molecules which contain CARBON. Organic molecules are composed of C, H, O, N, P, and S. They are large molecules known as MACROMOLECULES. The macromolecules are composed of submits called MONOMERS. A POLYMER is composed of many monomers. ...
Cellular Respiration - Chapter 8 (new book).
... protein organic molecules that act as “shuttle” molecules carrying substances from one enzyme catalyzed reaction to another 1. some carry electrons (FAD, NAD+, FMN, coenzyme Q) 2. ATP carries phosphate groups 3. H carrying coenzymes (NAD+) II. Chemical Reactions of Cellular Respiration A. Overall re ...
... protein organic molecules that act as “shuttle” molecules carrying substances from one enzyme catalyzed reaction to another 1. some carry electrons (FAD, NAD+, FMN, coenzyme Q) 2. ATP carries phosphate groups 3. H carrying coenzymes (NAD+) II. Chemical Reactions of Cellular Respiration A. Overall re ...
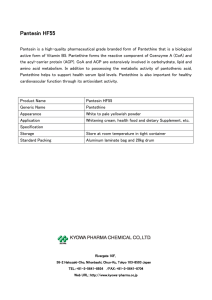
Pantesin HF55
... Pantesin is a high-quality pharmaceutical grade branded form of Pantethine that is a biological active form of Vitamin B5. Pantethine forms the reactive component of Coenzyme A (CoA) and the acyl-carrier protein (ACP). CoA and ACP are extensively involved in carbohydrate, lipid and amino acid metabo ...
... Pantesin is a high-quality pharmaceutical grade branded form of Pantethine that is a biological active form of Vitamin B5. Pantethine forms the reactive component of Coenzyme A (CoA) and the acyl-carrier protein (ACP). CoA and ACP are extensively involved in carbohydrate, lipid and amino acid metabo ...
2 Biochemistry
... Radioisotopes: larger, unstable, atomic decay called radioactivity Radioisotopes used in medicine, PET scans to see physiology ...
... Radioisotopes: larger, unstable, atomic decay called radioactivity Radioisotopes used in medicine, PET scans to see physiology ...
Chapter 5 notes cont.
... At any moment in the cell's life, the specific enzymes that are present and active determine which reactions occur. ...
... At any moment in the cell's life, the specific enzymes that are present and active determine which reactions occur. ...
Introduction to Metabolism
... Enzymes are the basic units of metabolism. The substrates of these enzymes are called metabolites. A metabolic pathway is a series of connected enzymatic reactions that produce a specific product. ...
... Enzymes are the basic units of metabolism. The substrates of these enzymes are called metabolites. A metabolic pathway is a series of connected enzymatic reactions that produce a specific product. ...
Nutrition You Are What You Eat?
... Sources include - citrus fruits, green peppers, leafy vegetables ...
... Sources include - citrus fruits, green peppers, leafy vegetables ...
Notes
... electron transport chain to produce additional ATP. The electron transport chain is a series of electron transport molecules attached to the inner mitochondrial membrane. This electron-transport chain of molecules consists of a flavo protein (derived from the vitamin riboflavin), coenzyme Q (from Vi ...
... electron transport chain to produce additional ATP. The electron transport chain is a series of electron transport molecules attached to the inner mitochondrial membrane. This electron-transport chain of molecules consists of a flavo protein (derived from the vitamin riboflavin), coenzyme Q (from Vi ...
Recitation 3 - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
... products (metabolites) is determined by many regulatory mechanisms. ...
... products (metabolites) is determined by many regulatory mechanisms. ...
Slide 1
... True/False: Energy exists in many forms—including light, heat, chemical energy, mechanical energy, and electrical energy- and cannot be converted from one for to another. ...
... True/False: Energy exists in many forms—including light, heat, chemical energy, mechanical energy, and electrical energy- and cannot be converted from one for to another. ...
Document
... acid to produce citric acid • citric acid is changed into oxaloacetic acid through a series of reactions • cycle repeats as long as pyruvic acid and oxygen are available • for each citric acid molecule: • one ATP is produced • eight hydrogen atoms are transferred to NAD+ and FAD • two CO2 produced ...
... acid to produce citric acid • citric acid is changed into oxaloacetic acid through a series of reactions • cycle repeats as long as pyruvic acid and oxygen are available • for each citric acid molecule: • one ATP is produced • eight hydrogen atoms are transferred to NAD+ and FAD • two CO2 produced ...
Alcoholic fermentation
... a) what is caused by a build-up of lactate in muscle cells? Muscle pain; fatigue b) what happens to the accumulated lactate? Carried to the liver where it is converted to pyruvate 11) Describe 3 lines of evidence that glycolysis is one of the “oldest” metabolic pathways. 1) oldest known fossils are ...
... a) what is caused by a build-up of lactate in muscle cells? Muscle pain; fatigue b) what happens to the accumulated lactate? Carried to the liver where it is converted to pyruvate 11) Describe 3 lines of evidence that glycolysis is one of the “oldest” metabolic pathways. 1) oldest known fossils are ...
Energy Production
... 1) Aerobic metabolism: dependent on oxygen. 2) Anaerobic metabolism: independent of oxygen. The use of which systems depend on: 1) Duration. 2) Intensity. 3) Type of physical activity. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP): It is an energy-rich compound that continuously supply fuel for the body used by ener ...
... 1) Aerobic metabolism: dependent on oxygen. 2) Anaerobic metabolism: independent of oxygen. The use of which systems depend on: 1) Duration. 2) Intensity. 3) Type of physical activity. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP): It is an energy-rich compound that continuously supply fuel for the body used by ener ...
BIO C211 - BITS Pilani
... In addition to Part One (General Handout for all courses appended to the time table) this part gives further specific details regarding the course. Course No. ...
... In addition to Part One (General Handout for all courses appended to the time table) this part gives further specific details regarding the course. Course No. ...
Lesson One: The Four Basic Food Molecules
... It has unique properties due to the highly effective formation of hydrogen bonds. It is ubiquitous. It is polar and an excellent solvent for salts. It is a "V" shaped molecule. It exists in all three states: solid, liquid, gas at ordinary Earth temperatures. Its solid form floats on its liquid form. ...
... It has unique properties due to the highly effective formation of hydrogen bonds. It is ubiquitous. It is polar and an excellent solvent for salts. It is a "V" shaped molecule. It exists in all three states: solid, liquid, gas at ordinary Earth temperatures. Its solid form floats on its liquid form. ...
Chapter 10 Lesson 2 Nutrients
... moving food through the digestive system. digesting carbohydrates and protein, and aiding other chemical reactions in the body. transporting nutrients and removing wastes. storing and releasing heat. cooling the body through perspiration. cushioning the eyes, brain, and spinal cord. lubricating the ...
... moving food through the digestive system. digesting carbohydrates and protein, and aiding other chemical reactions in the body. transporting nutrients and removing wastes. storing and releasing heat. cooling the body through perspiration. cushioning the eyes, brain, and spinal cord. lubricating the ...
Molecules of Life Worksheet
... 13. The main difference among amino acids is their ____ group. What is the R-group on glycine? on alanine? 14. Differences in R-groups give different proteins different ______________. 15. How does a dipeptide form? 16. What do you call the covalent bonds that hold amino acids together? 17. Long cha ...
... 13. The main difference among amino acids is their ____ group. What is the R-group on glycine? on alanine? 14. Differences in R-groups give different proteins different ______________. 15. How does a dipeptide form? 16. What do you call the covalent bonds that hold amino acids together? 17. Long cha ...
Chapter 34 HEIN
... • This polymer breaks down to glucose, which is oxidized to replenish the ATP supply. • Because glucose oxidation is a complex process, muscle contraction must proceed at a slower rate. • This energy supply is only useful for about 2 minutes of work; muscles rapidly deplete their glycogen stores and ...
... • This polymer breaks down to glucose, which is oxidized to replenish the ATP supply. • Because glucose oxidation is a complex process, muscle contraction must proceed at a slower rate. • This energy supply is only useful for about 2 minutes of work; muscles rapidly deplete their glycogen stores and ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.