* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Recitation 3 - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
Survey
Document related concepts
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
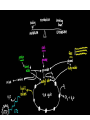
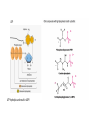
Intermediary Metabolism and Enzymes Metabolism: comprises the entire set of chemical reactions that occur in a living organism that allow it to reproduce, develop, maintain its structure and respond to the environment. These chemical reactions form an intricate network of pathways and cycles in which the flow of reaction products (metabolites) is determined by many regulatory mechanisms. Catabolism, the breaking down of complex molecules and degredation Metabolism Anabolism, processes related to the synthesis of complex organic substances like protein synthesis, DNA synthesis Energy and Energy Conversion Two laws of thermodynamics: • energy is neither created or destroyed, when energy is converted form one form to another form the total energy before and after the conversion is the same. • When energy is transformed, some forms are unavailable to work with, lost as heat We eat carbohydrates: In glycolysis, a series of enzymatic reactions will convert sugars (typically glucose) pyruvate. During this process, small amounts of ATP are generated and electron carriers are loaded with electrons (NAD+ is reduced to NADH + H+) Consequently, pyruvate is translocated to the mitochondria, decarboxylated and converted into acetyl-CoA Acetyl-CoA then enters the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also called Krebs cycle, by condensing with oxaloacetate to form citrate. As the acetyl-CoA goes through this cycle, things are bounced off and things that are bounced off are these high energy carriers. High energy carriers bounce down a staircase A series of oxidation reactions then ensue with the result that two carbons are expelled as CO2, (G/A)TP is produced and the electron carriers (NAD+ and FAD+) are reduced. ATP ATP hydrolysis and result in ADP! Enzymes: • Enzymes speed up reactions without being changed themselves. Most of the enzymes are proteins Activating Energy • Enzymes work with lowering the activation energy. Regulation of enzymes: • Irreversible inhibition: Diisopropyl fluorophosphate • Reversible inhibition: (C ) Allosteric inhibition