* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carbon (Organic) Chemistry
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
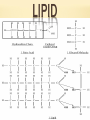
CARBON (ORGANIC) CHEMISTRY INTRODUCTION TO MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules are large molecules, also known as polymers. Polymers are built by smaller units called monomers. The process of joining together monomers is called polymerization. TYPES OF MACROMOLECULES 1. 2. 3. 4. Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids Proteins CARBOHYDRATE CHARACTERISTICS Made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1 They are the main source of energy for living things. They have structural purposes in plants and animals Monomers are monosaccharides, Polymers are polysaccharides Important carbohydrates are: Glucose: The energy for all cell activities Starches: Complex carbohydrates that living things use to store sugar Glycogen: A sugar storage molecule LIPID CHARACTERISTICS Made from carbon and hydrogen atoms Common types are fats, oils and waxes Can be used to store energy Formed when a glycerol combines with a fatty acid Fatty acids that are connected by single bonded carbons are called saturated fatty acids Fatty acids that are connected by double bonded carbons are called unsaturated fatty acids LIPID NUCLEIC ACID A macromolecule containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus Monomers are a nucleotides: These consist of a 5carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base Nucleic acids are the polymers Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary (genetic information) The two types are ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) NUCLEIC ACIDS PROTEINS Contain carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen Monomers are amino acids, which contain an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (COOH) WHAT DO PROTEINS DO? Control the rate of chemical reactions Aid in the replication of DNA Help your body respond to stimuli Transport molecules around your body PROTEIN STRUCTURES ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS How do we obtain macromolecules? What do we do with the macromolecules that we break down in our body?