Biochemistry Chapter 6
... • What are carbs broken down into? • What does this provide? • If this compound isn’t used, what is it stored as? • Where is it stored? • What are the purpose of lipids? • Difference between Unsaturated and Saturated fats? • What are HDL and LDL? ...
... • What are carbs broken down into? • What does this provide? • If this compound isn’t used, what is it stored as? • Where is it stored? • What are the purpose of lipids? • Difference between Unsaturated and Saturated fats? • What are HDL and LDL? ...
Week 4:
... We balanced the equation for cellular respiration: 6 O2 + C6H12O6 6 CO2 + 6 H2O (plus energy) and pointed out that cellular respiration allows for inputs other than glucose, including fats, proteins, and other sugars. Introduction of Photosynthesis: Reverse equation of Respiration, and can be divi ...
... We balanced the equation for cellular respiration: 6 O2 + C6H12O6 6 CO2 + 6 H2O (plus energy) and pointed out that cellular respiration allows for inputs other than glucose, including fats, proteins, and other sugars. Introduction of Photosynthesis: Reverse equation of Respiration, and can be divi ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation
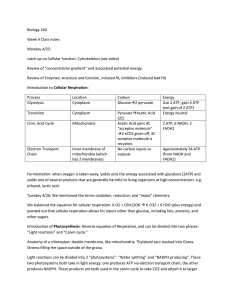
... Metabolism is the sum of all chemical changes occurring in a cell , tissue or the body It is composed of pathways Pathway is a multistep sequence of reactions in which the product of one reaction serves as the substrate of the subsequent reaction Each reaction is catalyzed by a specific enzyme (may ...
... Metabolism is the sum of all chemical changes occurring in a cell , tissue or the body It is composed of pathways Pathway is a multistep sequence of reactions in which the product of one reaction serves as the substrate of the subsequent reaction Each reaction is catalyzed by a specific enzyme (may ...
Chapter 18 - King William County Public Schools
... Chemical reactions and substances that provide energy for cell growth 2 types: 1. catabolic reaction – complex molecules are broken down and release energy 2. anabolic reaction – use energy to build large molecules from smaller molecules ...
... Chemical reactions and substances that provide energy for cell growth 2 types: 1. catabolic reaction – complex molecules are broken down and release energy 2. anabolic reaction – use energy to build large molecules from smaller molecules ...
BC 367 Biochemistry of the Cell I
... South Dakota and a 56-year-old patient is brought in by his wife because of a newlyonset rapidly progressive dementia. He also has been suffering recently from diarrhea and dry skin on his face, neck, and back of his hands. For the patient to develop this disease, his diet must be deficient in which ...
... South Dakota and a 56-year-old patient is brought in by his wife because of a newlyonset rapidly progressive dementia. He also has been suffering recently from diarrhea and dry skin on his face, neck, and back of his hands. For the patient to develop this disease, his diet must be deficient in which ...
Limits of Human Performance
... – Metabolic rate: can be measured as heat production – O2 consumption provides for almost all of our metabolic needs, so Vo2 provides a very good index of metabolic rate – High Vo2 means high metabolic capacity ...
... – Metabolic rate: can be measured as heat production – O2 consumption provides for almost all of our metabolic needs, so Vo2 provides a very good index of metabolic rate – High Vo2 means high metabolic capacity ...
Biology Section 2 Molecules of Life Carbohydrates Carbohydrates
... o Polypeptides- long string of amino acids o Protein shape influenced by bonding, solvent, temperature Enzymes o Enzymes- RNA or protein catalysts o Physical fit between enzyme and substrate (substance being catalyzed) o Active site- folds o Slight change in shape weakens chemical bonds o Enzymes ...
... o Polypeptides- long string of amino acids o Protein shape influenced by bonding, solvent, temperature Enzymes o Enzymes- RNA or protein catalysts o Physical fit between enzyme and substrate (substance being catalyzed) o Active site- folds o Slight change in shape weakens chemical bonds o Enzymes ...
Food & Energy
... Waxy, fatlike substance found only in animal products. Important part of the body’s cells. Liver can make the cholesterol your body needs, making it an unnecessary part of the diet. ...
... Waxy, fatlike substance found only in animal products. Important part of the body’s cells. Liver can make the cholesterol your body needs, making it an unnecessary part of the diet. ...
Building Blocks of Bodybuilding
... Nutritional aspects of Bodybuilding. Metabolic utilisation of nutritional building blocks as an energy source & for muscle cell growth and repair. ...
... Nutritional aspects of Bodybuilding. Metabolic utilisation of nutritional building blocks as an energy source & for muscle cell growth and repair. ...
Biochemistry File - Northwest ISD Moodle
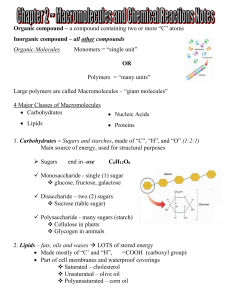
... 4. Proteins – polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds Used to build cells, transport molecules, and control the rate of reactions Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, and “N” 20 different amino acids ...
... 4. Proteins – polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds Used to build cells, transport molecules, and control the rate of reactions Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, and “N” 20 different amino acids ...
ORIGIN OF CELLS
... Tiny compartments in mineral structures can shelter simple molecules, while mineral surfaces can provide the scaffolding on which those molecules assemble and grow. Beyond these sheltering and supportive functions, crystal faces of certain minerals can actively select particular molecules resembling ...
... Tiny compartments in mineral structures can shelter simple molecules, while mineral surfaces can provide the scaffolding on which those molecules assemble and grow. Beyond these sheltering and supportive functions, crystal faces of certain minerals can actively select particular molecules resembling ...
Ch.23Pt.1_001
... • Free energy differences between reactants & products is low • Concentration differences keep enzyme-run reactions going in one direction • How? • Products are constantly removed so no build up at the end. Concentration stays low for products ...
... • Free energy differences between reactants & products is low • Concentration differences keep enzyme-run reactions going in one direction • How? • Products are constantly removed so no build up at the end. Concentration stays low for products ...
Respiration Eq. for reaction: C6H12O6 + 6O2 ------
... - occurs in the cytoplasm and then the cristae and matrix of the mitochondria - reaction is an oxidation reaction (uses oxygen): aerobic respiration - energy is in the form of ATP (adenosine tri-phosphate) - some is lost as heat (responsible for organism’s body temperature) - produces 38 ATP (2 from ...
... - occurs in the cytoplasm and then the cristae and matrix of the mitochondria - reaction is an oxidation reaction (uses oxygen): aerobic respiration - energy is in the form of ATP (adenosine tri-phosphate) - some is lost as heat (responsible for organism’s body temperature) - produces 38 ATP (2 from ...
Biology Passage 2 - HCC Learning Web
... 2. First Law of Thermodynamics? Energy conserved 3. Second Law of Thermodynamics? Entropy increases 4. Gibbs Free Energy Change mathematically defines thermodynamics G = H – TS (kcal/mol) ...
... 2. First Law of Thermodynamics? Energy conserved 3. Second Law of Thermodynamics? Entropy increases 4. Gibbs Free Energy Change mathematically defines thermodynamics G = H – TS (kcal/mol) ...
Exercise PDF PPT
... Positive carry-‐over of increased basal metabolic rate after cardiovascular exercise ...
... Positive carry-‐over of increased basal metabolic rate after cardiovascular exercise ...
Glossary Protein
... fluid balance maintenance of the proper types and amounts of fluid in each compartment of the body fluids. gene expression the process by which a cell converts the genetic code into RNA and protein. hemoglobin the globular protein of the red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the cell ...
... fluid balance maintenance of the proper types and amounts of fluid in each compartment of the body fluids. gene expression the process by which a cell converts the genetic code into RNA and protein. hemoglobin the globular protein of the red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the cell ...
Metabolic Pathways - University of California, Santa Barbara
... molecule of NADH produces ___________ molecules of ATP and 1 molecule of FADH2 produces ____________ molecules of ATP. Therefore for each molecule of acetyl CoA that enters the citric acid cycle ____________ molecules of ATP are produced. For every 1 molecule of glucose that is catabolized _________ ...
... molecule of NADH produces ___________ molecules of ATP and 1 molecule of FADH2 produces ____________ molecules of ATP. Therefore for each molecule of acetyl CoA that enters the citric acid cycle ____________ molecules of ATP are produced. For every 1 molecule of glucose that is catabolized _________ ...
Metabolism
... occurs in the cytoplasm of all cells. This process does not require oxygen. It is therefore referred to as an anaerobic process. ...
... occurs in the cytoplasm of all cells. This process does not require oxygen. It is therefore referred to as an anaerobic process. ...
(i)
... (d) Lactate is water soluble/ dissolve in blood or tissue fluid causing outward movement of water from the tissue cells by osmosis. (e) Amino acid acts as buffer. Some ions such as HPO4=/ PO43- is a buffer. Haemoglobin of red blood cells is also a buffer. (any TWO) (f) Amino acids can be converted i ...
... (d) Lactate is water soluble/ dissolve in blood or tissue fluid causing outward movement of water from the tissue cells by osmosis. (e) Amino acid acts as buffer. Some ions such as HPO4=/ PO43- is a buffer. Haemoglobin of red blood cells is also a buffer. (any TWO) (f) Amino acids can be converted i ...
Notes_Biochemistry_Short_Course
... INORGANIC COMPOUNDS: Define: do ______ contain Carbon with Hydrogen together (may have either one but NOT at the same time) - ___________________ compounds I. (pgs 36-37) Water - ___________________ % of body Match each property of water with its description/importance _____attracts molecules & form ...
... INORGANIC COMPOUNDS: Define: do ______ contain Carbon with Hydrogen together (may have either one but NOT at the same time) - ___________________ compounds I. (pgs 36-37) Water - ___________________ % of body Match each property of water with its description/importance _____attracts molecules & form ...
Nutrient PPT
... Vitamins, minerals and water do not directly give us energy. They do not have calories. ...
... Vitamins, minerals and water do not directly give us energy. They do not have calories. ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.