Chapter 1 Review Understanding Concepts
... 17. RNA nucleotides contain the five-carbon sugar ribose and contain the nitrogenous base uracil, whereas DNA contains the five-carbon sugar deoxyribose and the nitrogenous base thymine instead of uracil. 18. DNA possesses hydrogen bonds as two DNA strands run antiparallel to each other, allowing hy ...
... 17. RNA nucleotides contain the five-carbon sugar ribose and contain the nitrogenous base uracil, whereas DNA contains the five-carbon sugar deoxyribose and the nitrogenous base thymine instead of uracil. 18. DNA possesses hydrogen bonds as two DNA strands run antiparallel to each other, allowing hy ...
GLYCOLYSIS and respiration review worksheet
... WORKSHEET REVIEW: Anaerobic and Aerobic Glycolysis Answer in complete sentences. Glycolysis, the breakdown of carbon-containing molecules, is common to all organisms and occurs in the cytoplasm of all cells. It may occur in the presence or absence of oxygen and yields a small amount of energy in the ...
... WORKSHEET REVIEW: Anaerobic and Aerobic Glycolysis Answer in complete sentences. Glycolysis, the breakdown of carbon-containing molecules, is common to all organisms and occurs in the cytoplasm of all cells. It may occur in the presence or absence of oxygen and yields a small amount of energy in the ...
hapch2updated2013final
... – Most enzymes are produced in inactive form and must be activated/some inactivated immediately after they catalyze reaction—example in blood clotting process ...
... – Most enzymes are produced in inactive form and must be activated/some inactivated immediately after they catalyze reaction—example in blood clotting process ...
Lactanase - Vita Flex
... dominate after galloping only one-quarter of a mile, and for many horses it kicks in sooner. Lactanase addresses some of the fundamental nutritional needs of anaerobic metabolism to provide targeted support for high-intensity equine athletes. The Bridge to ATP D-Glycogen is the main energy source fo ...
... dominate after galloping only one-quarter of a mile, and for many horses it kicks in sooner. Lactanase addresses some of the fundamental nutritional needs of anaerobic metabolism to provide targeted support for high-intensity equine athletes. The Bridge to ATP D-Glycogen is the main energy source fo ...
Solutions to Questions in the Cellular Respiration booklet
... requires energy while exergonic is any process that gives off energy. #2. glucose #3. Movement; production of proteins; active transport: cellular division #4. Aerobic respiration is when oxygen is used within the mitochondrion to produce 36 ATP molecules and the waste products of water and carbon d ...
... requires energy while exergonic is any process that gives off energy. #2. glucose #3. Movement; production of proteins; active transport: cellular division #4. Aerobic respiration is when oxygen is used within the mitochondrion to produce 36 ATP molecules and the waste products of water and carbon d ...
No Slide Title
... When a process is conditioned as to its rapidity by a number of separate factors the rate of the process is limited by the pace of the slowest factor. This statement is wrong if taken literally. In a linear metabolic pathway all reactions operate at the same rate in the steady state. What was really ...
... When a process is conditioned as to its rapidity by a number of separate factors the rate of the process is limited by the pace of the slowest factor. This statement is wrong if taken literally. In a linear metabolic pathway all reactions operate at the same rate in the steady state. What was really ...
StudyGuide_Biochemistry
... 36. How many calories per gram do proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates contain? 37. What is the body’s primary source of energy? If that is not available, what will the body use? If both of those are not available, what will the body turn to for energy? 38. What is the purpose of a chemical reaction? ...
... 36. How many calories per gram do proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates contain? 37. What is the body’s primary source of energy? If that is not available, what will the body use? If both of those are not available, what will the body turn to for energy? 38. What is the purpose of a chemical reaction? ...
WP2: Diets with varying amount and amino acid composition
... implications for the treatment of obesity and metabolic diseases [14]. Compared to white fat, BAT is more metabolically active and burns off energy to heat and it has been suggested that dietary increased brown fat metabolism may induce weight loss – where high leucine may be one dietary factor acti ...
... implications for the treatment of obesity and metabolic diseases [14]. Compared to white fat, BAT is more metabolically active and burns off energy to heat and it has been suggested that dietary increased brown fat metabolism may induce weight loss – where high leucine may be one dietary factor acti ...
L10v01a_intro_to_metabolism.stamped_doc
... [00:00:01.06] SPEAKER 1: Hi. With this video we begin the second portion of the course, where we'll look at things at a more integrated systems level, rather than the molecular level which we concentrated on in the first portion. In this lecture, specifically, we'll speak about metabolism and how th ...
... [00:00:01.06] SPEAKER 1: Hi. With this video we begin the second portion of the course, where we'll look at things at a more integrated systems level, rather than the molecular level which we concentrated on in the first portion. In this lecture, specifically, we'll speak about metabolism and how th ...
Key Terms:
... H+ gradient drives ATP synthesis Glycolysis is universal, anaerobic and cytosolic 2 ATP in; 4 ATP out & 2 reduced coenzymes glucose (six carbons, C6) 2 moleucles of pyruvate (three carbons, C3) Citric Acid Cycle, in the mitochondria Pyruvate crosses into mitochondrial matrix and is converted to ac ...
... H+ gradient drives ATP synthesis Glycolysis is universal, anaerobic and cytosolic 2 ATP in; 4 ATP out & 2 reduced coenzymes glucose (six carbons, C6) 2 moleucles of pyruvate (three carbons, C3) Citric Acid Cycle, in the mitochondria Pyruvate crosses into mitochondrial matrix and is converted to ac ...
Lecture 7
... – Carbon and nitrogen atoms from certain amino acids form the backbones of the purines and pyrimidines ...
... – Carbon and nitrogen atoms from certain amino acids form the backbones of the purines and pyrimidines ...
Organic Molecule Notes
... -ex: Maltose (Sugar used in alcohol) =1 glucose+1 glucose --used for… -ex: Lactose (Milk sugar) =1 glucose+1galactose -produced by animals Long term Energy Storage Molecules Starch=primary storage form of energy in plants --polysaccharide = --shape is a long highly branched chain. --ex: Amylopectin= ...
... -ex: Maltose (Sugar used in alcohol) =1 glucose+1 glucose --used for… -ex: Lactose (Milk sugar) =1 glucose+1galactose -produced by animals Long term Energy Storage Molecules Starch=primary storage form of energy in plants --polysaccharide = --shape is a long highly branched chain. --ex: Amylopectin= ...
chapter review questions
... deposit it in cells To convert fat to protein To maintain blood glucose at around 70–110 mg/100 ml of blood To elevate blood glucose to the highest possible level to ensure adequate delivery to the brain ...
... deposit it in cells To convert fat to protein To maintain blood glucose at around 70–110 mg/100 ml of blood To elevate blood glucose to the highest possible level to ensure adequate delivery to the brain ...
ppt - University of Illinois Urbana
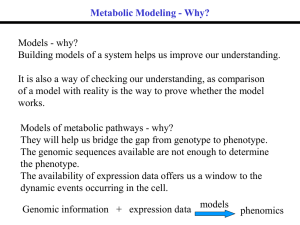
... – Metabolic network: a system of interacting proteins and small molecules converting raw materials to energy and other useful substances in a living organism – Metabolites: materials consumed or produced in a metabolic network – Enzymes: proteins that catalyze reactions – The sets of metabolites and ...
... – Metabolic network: a system of interacting proteins and small molecules converting raw materials to energy and other useful substances in a living organism – Metabolites: materials consumed or produced in a metabolic network – Enzymes: proteins that catalyze reactions – The sets of metabolites and ...
8/27 Organic Chemistry
... – amphipathic - has polar and non-polar regions – can hydrogen bond with water due to phosphate’s polarity • Found in cell membranes ...
... – amphipathic - has polar and non-polar regions – can hydrogen bond with water due to phosphate’s polarity • Found in cell membranes ...
Organic Chemistry and Macromolecules
... made of many bonded glucose units; typically found in cell walls of plants and provides nutritional roughage. • Hemoglobin—a type of protein that is in red blood cells; contains iron and carries oxygen from lungs to body cells. • Biurets Solution—a blue reagent that turns purple in the presence of p ...
... made of many bonded glucose units; typically found in cell walls of plants and provides nutritional roughage. • Hemoglobin—a type of protein that is in red blood cells; contains iron and carries oxygen from lungs to body cells. • Biurets Solution—a blue reagent that turns purple in the presence of p ...
Macromolecules of Life
... Description Used for support such as connective tissue and keratin that forms hairs and fingernails Transport proteins move many substances through the body Ex. Hemoglobin which transports oxygen through the blood Hormone proteins. Ex, insulin which regulates the amount of sugar in the blood Help co ...
... Description Used for support such as connective tissue and keratin that forms hairs and fingernails Transport proteins move many substances through the body Ex. Hemoglobin which transports oxygen through the blood Hormone proteins. Ex, insulin which regulates the amount of sugar in the blood Help co ...
SYLLABUS COURSE TITLE Biochemistry Faculty/Institute Faculty of
... -contents of lectures 1 Basic metabolic processes occurring in the cell. The biochemical composition of human organism. 2 Biological basis for the integrity of the human body. 3 Structure and function of macromolecules present in the human body: -amino acids and proteins; the amino acid metabolism - ...
... -contents of lectures 1 Basic metabolic processes occurring in the cell. The biochemical composition of human organism. 2 Biological basis for the integrity of the human body. 3 Structure and function of macromolecules present in the human body: -amino acids and proteins; the amino acid metabolism - ...
Hardening of the arteries
... A protein in blood cells that has this quaternary structure. C 300 ...
... A protein in blood cells that has this quaternary structure. C 300 ...
Biological (organic) Molecules
... Provide energy to cells Consist of atoms of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen Usually twice as many hydrogen as oxygen atoms ...
... Provide energy to cells Consist of atoms of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen Usually twice as many hydrogen as oxygen atoms ...
Slide 1
... Some of the glucose molecules are linked together to build large carbohydrates called starch. Plants can store starch and later break it down into glucose or other sugars when they need energy. ...
... Some of the glucose molecules are linked together to build large carbohydrates called starch. Plants can store starch and later break it down into glucose or other sugars when they need energy. ...
Anaerobic metabolism is the production of ATP with oxygen
... 2. True or False: An enzyme is not changed by the reaction it causes. 3. True or False: An enzyme does not need to fit precisely with the reactant to catalyze the reaction. 4. True or False: The electron transport system is where most of the ATP is produced during aerobic metabolism. 5. True or Fals ...
... 2. True or False: An enzyme is not changed by the reaction it causes. 3. True or False: An enzyme does not need to fit precisely with the reactant to catalyze the reaction. 4. True or False: The electron transport system is where most of the ATP is produced during aerobic metabolism. 5. True or Fals ...
File
... 1. The four major groups are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. B. Macromolecules are typically polymers 1. Polymers are chains of repeating units (poly means “many”) 2. The units they’re made up of are called monomers (mono means “one”) 3. Take a brick wall, for example: each indivi ...
... 1. The four major groups are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. B. Macromolecules are typically polymers 1. Polymers are chains of repeating units (poly means “many”) 2. The units they’re made up of are called monomers (mono means “one”) 3. Take a brick wall, for example: each indivi ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.