* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GLYCOLYSIS and respiration review worksheet
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
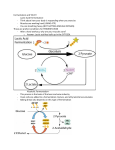
Name Date Period_____ WORKSHEET REVIEW: Anaerobic and Aerobic Glycolysis Answer in complete sentences. Glycolysis, the breakdown of carbon-containing molecules, is common to all organisms and occurs in the cytoplasm of all cells. It may occur in the presence or absence of oxygen and yields a small amount of energy in the form of ATP. 1. What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis pathways for making ATP? 2. What is the equation for the overall process of aerobic respiration? 3. What happens to the glucose in glycolysis? 4. If four ATP are produced for each molecule of glucose, why do we say that the yield is only 2? 5. What is the chemical role of the NAD+ (and hence NADH) molecules? 6. What normally happens to the two NADH’s that are produced, in the presence of oxygen? 7. What 3-carbon compound is left after glycolysis? 8. How do yeast cells get rid of waste (pyruvic acid) and recycle the NADH back to NAD+ when they don’t have enough oxygen to complete the Krebs cycle and electron transport? 9. How do your muscle cells get rid of waste (pyruvic acid) when they don’t have enough oxygen? Name Date_ Period_____ WORKSHEET REVIEW: Aerobic Respiration Answer in complete sentences. Respiration occurs when the end products of glycolysis enter the mitochondria. These products are then broken down into smaller molecules with the help of oxygen. A large amount of energy (ATP) is formed in the process. 1. Where exactly does the Krebs cycle occur in the cell? 2. What is the major waste product of the Krebs cycle (HINT: Very common molecule) 3. What molecule actually enters the Krebs cycle, serving as a common link for the breakdown of not only sugars but also fats and amino acids? (HINT: Next step after pyruvate...) 4. Why is the Krebs cycle so important to the cell, even if it doesn’t make many ATP directly? 5. As electrons are passed “downhill” from NADH to cytochromes and other carriers in the inner membranes of the mitrochrondria, the energy is being used to pump ____ across the membrane 6. At the end of the electron transport chain, two electrons are joined with two _____ ions and half a molecule of _______ to form one molecule of ________. (HINT: Very common substance) 7. Why is this whole process called the “chemiosmotic” mechanism? 8. Both the mitochondria and the chloroplasts contain very convoluted stacks of membranes on the inside. Explain why this is not a coincidence.