* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biochemistry File - Northwest ISD Moodle
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
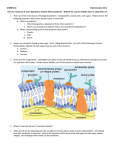
Organic compound – a compound containing two or more “C” atoms Inorganic compound – all other compounds Organic Molecules Monomers = “single unit” OR Polymers = “many units” Large polymers are called Macromolecules – “giant molecules” 4 Major Classes of Macromolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids Proteins 1. Carbohydrates = Sugars and starches, made of “C”, “H”, and “O” (1:2:1) Main source of energy, used for structural purposes Sugars end in -ose C6H12O6 Monosaccharide - single (1) sugar glucose, fructose, galactose Disaccharide – two (2) sugars Sucrose (table sugar) Polysaccharide - many sugars (starch) Cellulose in plants Glycogen in animals 2. Lipids – fats, oils and waxes LOTS of stored energy Made mostly of “C’ and “H”, =COOH (carboxyl group) Part of cell membranes and waterproof coverings Saturated – cholesterol Unsaturated – olive oil Polyunsaturated – corn oil 3. Nucleic Acids – store and transmit hereditary or genetic information Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, “N”, and “P” Assembled from nucleotides 5-Carbon sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base DNA- deoxyribonucleic acid RNA – Ribonucleic acid 4. Proteins – polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds Used to build cells, transport molecules, and control the rate of reactions Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, and “N” 20 different amino acids a process of change in one set of chemicals into another set of chemical (involves breaking bonds in reactants to form new bonds in products) Reactants – what goes in Products – what comes out Catalysts - used to speed up a reaction (not used or changed in reaction) Ex. = Enzymes (proteins) - catalyze important chemical reactions in living organisms Each enzyme contains active sites that will fit only specific items. These items are called substrates. Only those specific substrates fit the active site. Lock Key