* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
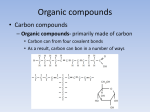
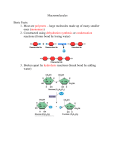
NOTES: 2.3, part 1 - Macromolecules, Carbs & Lipids The Chemistry of Carbon Why is CARBON so important to life? Living things are and other elements (H, O, P, S, and N) Carbon atoms have , allowing them to form strong covalent bonds with many other elements Carbon has the ability to form millions of different ! Polymer Principles POLYMER: large molecule consisting of many MONOMER: molecule of a polymer MACROMOLECULE: large organic polymer *Examples: POLYMERIZATION REACTIONS: chemical reactions that link 2 or more small molecules ( larger molecules ( ) to form ) DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS REACTIONS (or CONDENSATION): reactions during which ; an –H and and –OH are removed, producing for each covalent linkage HYDROLYSIS: process that water molecules by the addition of *Example: CARBOHYDRATES Monosaccharides = *are major nutrients for cells *glucose is most common *examples: Disaccharides = *Also a source of energy *Formed when 2 monosaccharides combine in a dehydration reaction; *Examples: lactose ( ): sucrose ( ): Polysaccharides = *formed by linking monomers in Examples of energy storage polysaccharides: -starch = glucose polymer in plants used for energy storage ( , etc.) -glycogen = glucose polymer in animals stored in vertebrates of humans & other Examples of structural support polysaccharides: -cellulose = structural component of plant cell walls that -chitin = forms exoskeletons of arthropods LIPIDS insoluble in water (because they are , or ) include: 1) Fats; 2) Phospholipids; 3) Steroids 1. FATS Composed of: -A large proportion of C-H bonds and less oxygen than carbohydrates (the nonpolar C-H bonds make the chain hydrophobic and insoluble in water) - Example: during formation of a fat, link fatty acids to glycerol Fatty acids may vary in # of carbon atoms (usually even #) Saturated Fats no C-C double bonds in fatty acid tail Unsaturated Fats one or more C-C double bonds in fatty acid tail __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ e.g.:_______________________________________ e.g.:______________________________________ Functions of Fats (1 g of fat stores 2x as much energy as 1 g of carbohydrate) cushions vital organs in mammals (e.g. ) (e.g. whales, seals) 2. PHOSPHOLIPIDS Important component of 3. STEROIDS Important component of some hormones Cholesterol … is used to make many other steroids (including sex hormones in vertebrates) common component of cell membranes (if have too much)