Nucleic acids
... Nucleic acids carry and transmit genetic information. The two most common forms of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. Nucleic acids are made up of smaller monomers of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and hydrogen called nucleotides. The chemical groups that make up nucleotides are phosphates, nitro ...
... Nucleic acids carry and transmit genetic information. The two most common forms of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. Nucleic acids are made up of smaller monomers of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and hydrogen called nucleotides. The chemical groups that make up nucleotides are phosphates, nitro ...
Test Review Unit 1
... 13) What is similar to a cell but is not considered a living thing because it can’t reproduce without a host? 14) What are the levels of organization in a living thing? (list smallest to largest? 15) What is a tissue? ...
... 13) What is similar to a cell but is not considered a living thing because it can’t reproduce without a host? 14) What are the levels of organization in a living thing? (list smallest to largest? 15) What is a tissue? ...
Chapter 4 - Cellular Metabolism
... Cofactors and coenzymes are special molecules or ions that must attach to certain enzymes before the enzyme becomes active 4.4 Energy for Metabolic Reactions A. Energy is the capacity to do work. B. Common forms of energy include heat, light, and sound, and electrical, mechanical, and chemical energ ...
... Cofactors and coenzymes are special molecules or ions that must attach to certain enzymes before the enzyme becomes active 4.4 Energy for Metabolic Reactions A. Energy is the capacity to do work. B. Common forms of energy include heat, light, and sound, and electrical, mechanical, and chemical energ ...
ETC Details
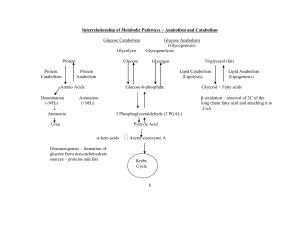
... • Splits into either glycerol or fatty acids (hydrocarbon tails) • Glycerol splits into G3P and enters glycolysis • Fatty acids undergo oxidation splits hydrocarbon tails and enter Krebs as acetyl CoA ...
... • Splits into either glycerol or fatty acids (hydrocarbon tails) • Glycerol splits into G3P and enters glycolysis • Fatty acids undergo oxidation splits hydrocarbon tails and enter Krebs as acetyl CoA ...
Chapter 4: Cellular metabolism
... • Physiological processes that break larger molecules into smaller ones • Hydrolysis is an example • Decomposes carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins & splits a water molecule in the process ...
... • Physiological processes that break larger molecules into smaller ones • Hydrolysis is an example • Decomposes carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins & splits a water molecule in the process ...
Bio302 Biochemistry II
... Bio302 Biochemistry II Final Examination, June 7, 2005 Please answer all the questions, each 10 points. Good luck! ...
... Bio302 Biochemistry II Final Examination, June 7, 2005 Please answer all the questions, each 10 points. Good luck! ...
Nutrition Power Point
... provided by the muscle glycogen stores – which directly depend on the amount of carbohydrates ingested. This is not the only reason why dietary carbohydrates play a crucial role in athletic performance; they have also been found to prevent the onset of early muscle fatigue and hypoglycaemia during e ...
... provided by the muscle glycogen stores – which directly depend on the amount of carbohydrates ingested. This is not the only reason why dietary carbohydrates play a crucial role in athletic performance; they have also been found to prevent the onset of early muscle fatigue and hypoglycaemia during e ...
Biochemistry
... You reach a saturation point where even increasing the amount of what you testing doesn’t matter – the other is a limiting factor! ...
... You reach a saturation point where even increasing the amount of what you testing doesn’t matter – the other is a limiting factor! ...
Organic Molecules
... • Carbohydrates comprise the largest number of organic molecules in organisms. • Carbohydrates are made of C, H & O. • The monomer or building block or base unit of carbohydrates are monosaccharides or sugars. • The simplest sugar is glucose, a molecule used to provide fuel for many types of organis ...
... • Carbohydrates comprise the largest number of organic molecules in organisms. • Carbohydrates are made of C, H & O. • The monomer or building block or base unit of carbohydrates are monosaccharides or sugars. • The simplest sugar is glucose, a molecule used to provide fuel for many types of organis ...
NAME: : :______ Honors Biology Reading Guide – Chapter 6
... 52. Describe how kinases and phosphatases interact with enzymes. ...
... 52. Describe how kinases and phosphatases interact with enzymes. ...
Biology 155 - Quiz 6 1. In theory, how many molecules of ATP can
... 1. In theory, how many molecules of ATP can be produced from one molecule of acetylCoA if its carbons are completely metabolized in respiration? a. 7.5 b. 8 c. 9 d. 9.5 e. 15 f. 10 (none of the choices a to e were correct.) 2. In eukaryotic cells, the Krebs Cycle occurs in a. the mitochondrial matri ...
... 1. In theory, how many molecules of ATP can be produced from one molecule of acetylCoA if its carbons are completely metabolized in respiration? a. 7.5 b. 8 c. 9 d. 9.5 e. 15 f. 10 (none of the choices a to e were correct.) 2. In eukaryotic cells, the Krebs Cycle occurs in a. the mitochondrial matri ...
Energy for Physical Activity
... within the muscle cells. Energy system used is ATP-PC and therefore does NOT need oxygen. ...
... within the muscle cells. Energy system used is ATP-PC and therefore does NOT need oxygen. ...
Respiration
... Breakdown of large molecules into smaller molecules Breakdown of carbohydrates manufactured during photosynthesis to release ATP ...
... Breakdown of large molecules into smaller molecules Breakdown of carbohydrates manufactured during photosynthesis to release ATP ...
PE 690 weight training PPt
... • The stretching you do to touch your toes or twist your torso. • This depends on many factors. • Your age, gender, and posture • How muscular you are • How much body fat you have ...
... • The stretching you do to touch your toes or twist your torso. • This depends on many factors. • Your age, gender, and posture • How muscular you are • How much body fat you have ...
Document
... Can you explain HOW/WHY each of these modulators results in a change in enzyme activity ? ...
... Can you explain HOW/WHY each of these modulators results in a change in enzyme activity ? ...
File - Hope Christian College Parent and Student Portal
... This process occurs in the mitochondria and uses the oxygen we breathe in and is called AEROBIC RESPIRATION This allows energy to be used for movement contraction of muscles, nerve transmission of messages, transport, warmth, growth, cell division and moving molecules against the concentration gradi ...
... This process occurs in the mitochondria and uses the oxygen we breathe in and is called AEROBIC RESPIRATION This allows energy to be used for movement contraction of muscles, nerve transmission of messages, transport, warmth, growth, cell division and moving molecules against the concentration gradi ...
The Four Organic Compounds Notes
... Provide structure for cells, bones, muscles, tissues, organs, hormones, most everything in the body! Special Function: Carries out cell metabolism (via enzymes) ...
... Provide structure for cells, bones, muscles, tissues, organs, hormones, most everything in the body! Special Function: Carries out cell metabolism (via enzymes) ...
The Physiology of Fitness
... adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP makes our muscles contract and allows us to take part in exercise. ATP is made up of protein (adenosine) with three (tri) phosphates attached to it. ...
... adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP makes our muscles contract and allows us to take part in exercise. ATP is made up of protein (adenosine) with three (tri) phosphates attached to it. ...
Chapter 1
... • Cluster of risk factors for CVD, CKD & T2DM • Insulin resistance • Weight loss & insulin insensitivity ...
... • Cluster of risk factors for CVD, CKD & T2DM • Insulin resistance • Weight loss & insulin insensitivity ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.