* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
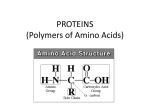
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
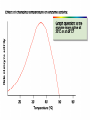
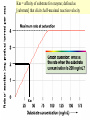
Cell Metabolism Things to look for in the metabolic process: 1. Energy transformations Kinetic energy Examples: work Potential energy 2. Chemical reactions transfer energy What determines how much energy is transferred? Free Energy 3. Chemical reactions proceed based on several factors. 4. Reactions requiring energy are coupled to reactions releasing energy. 5. Many metabolic reactions are reversible; many are irreversible Gibbs Free Energy Changes Rxn# Enzyme DG°'(kJ/mol) DG(kJ/mol) 1 Hexokinase -16.7 -33.5 2 Phosphogluco-isomerase +1.7 -2.5 3 Phosphofructokinase -14.2 -22.2 4 Aldolase +23.9 -1.3 5 Triose phos. Isomerase +7.6 +2.5 6 G-3-PDH +12.6 -3.4 7 Phosphoglycerate kinase -37.6 +2.6 8 Phosphoglycerate mutas +8.8 +1.6 9 Enolase +3.4 -6.6 10 Pyruvate kinase -62.8 -33.4 11 2 3 4 5 6 Identify: potentially coupled reactions 7 8 9 10 ENZYMES What are they? What do they do to help reactions proceed? How do they do this? (induced fit) Important characteristics of enzymes: Specificity May require: activation Cofactors or Coenzymes Enzyme activity may be modulated. Possible modulators include: pH Temperature Other molecules competitive inhibitors noncompetitive inhibitors allosteric modulators covalent modulators Concentration of enzyme/substrate Can you explain HOW/WHY each of these modulators results in a change in enzyme activity ? Km = affinity of substrate for enzyme; defined as [substrate] that elicits half-maximal reaction velocity Km Types of reactions to look for in metabolic pathways: •Oxidation-reduction reactions •Transfer chemical groups phosphate- catalyzed by kinases (+), phosphatases (-) substrate-level phosphorylation oxidative phosphorylation amino acids- catalyzed by aminases (+), deaminases(-) You have just isolated a new enzyme and have determined the speed of the reaction it catalyzes at three increasing substrate concentrations. You find that the slope of the product versus time curve increases as concentration of substrate increases. What can you conclude about the conditions in the reaction mixture? Explain. Activity of phosphofructokinase, which catalyzes step 3 of glycolysis, is affected by several substances that act as allosteric modulators. Effects of some of these modulators are shown in the following graphs. Which of these substances apparently acts to decrease the affinity of the enzyme? Explain your answer in terms of the mechanism of action of the substance you’ve chosen. Reaction rate High [AMP] High [AMP] + citrate No AMP Substrate concentration